

13 Social impacts of tourism + explanations + examples
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Understanding the social impacts of tourism is vital to ensuring the sustainable management of the tourism industry. There are positive social impacts of tourism, demonstrating benefits to both the local community and the tourists. There are also negative social impacts of tourism.
In this article I will explain what the most common social impacts of tourism are and how these are best managed. At the end of the post I have also included a handy reading list for anybody studying travel and tourism or for those who are interested in learning more about travel and tourism management.
The social impacts of tourism
Preserving local culture, strengthening communities, provision of social services, commercialisation of culture and art, revitalisation of culture and art, preservation of heritage, social change, globalisation and the destruction of preservation and heritage, loss of authenticity , standardisation and commercialisation, culture clashes, tourist-host relationships, increase in crime, gambling and moral behaviour, social impacts of tourism: conclusion, social impacts of tourism- further reading.
Firstly, we need to understand what is meant by the term ‘social impacts of tourism’. I have covered this in my YouTube video below!
To put it simply, social impacts of tourism are;
“The effects on host communities of direct and indirect relations with tourists , and of interaction with the tourism industry”
This is also often referred to as socio-cultural impacts.
Tourism is, at its core, an interactive service. This means that host-guest interaction is inevitable. This can have significant social/socio-cultural impacts.
These social impacts can be seen as benefits or costs (good or bad). I will explain these below.

Positive social impacts of tourism
There are many social benefits of tourism, demonstrating positive social impacts. These might include; preserving the local culture and heritage; strengthening communities; provision of social services; commercialisation of culture and art; revitalisation of customs and art forms and the preservation of heritage.

It is the local culture that the tourists are often coming to visit.
Tourists visit Beijing to learn more about the Chinese Dynasties. Tourists visit Thailand to taste authentic Thai food. Tourists travel to Brazil to go to the Rio Carnival, to mention a few…
Many destinations will make a conserved effort to preserve and protect the local culture. This often contributes to the conservation and sustainable management of natural resources, the protection of local heritage, and a renaissance of indigenous cultures, cultural arts and crafts.
In one way, this is great! Cultures are preserved and protected and globalisation is limited. BUT, I can’t help but wonder if this is always natural? We don’t walk around in Victorian corsets or smoke pipes anymore…
Our social settings have changed immensely over the years. And this is a normal part of evolution! So is it right that we should try to preserve the culture of an area for the purposes of tourism? Or should we let them grow and change, just as we do? Something to ponder on I guess…
Tourism can be a catalyst for strengthening a local community.
Events and festivals of which local residents have been the primary participants and spectators are often rejuvenated and developed in response to tourist interest. I certainly felt this was the way when I went to the Running of the Bulls festival in Pamplona, Spain. The community atmosphere and vibe were just fantastic!

The jobs created by tourism can also be a great boost for the local community. Aside from the economic impacts created by enhanced employment prospects, people with jobs are happier and more social than those without a disposable income.
Local people can also increase their influence on tourism development, as well as improve their job and earnings prospects, through tourism-related professional training and development of business and organisational skills.
Read also: Economic leakage in tourism explained

The tourism industry requires many facilities/ infrastructure to meet the needs of the tourist. This often means that many developments in an area as a result of tourism will be available for use by the locals also.
Local people often gained new roads, new sewage systems, new playgrounds, bus services etc as a result of tourism. This can provide a great boost to their quality of life and is a great example of a positive social impact of tourism.
Tourism can see rise to many commercial business, which can be a positive social impact of tourism. This helps to enhance the community spirit as people tend to have more disposable income as a result.
These businesses may also promote the local cultures and arts. Museums, shows and galleries are fantastic way to showcase the local customs and traditions of a destination. This can help to promote/ preserve local traditions.

Some destinations will encourage local cultures and arts to be revitalised. This may be in the form of museum exhibitions, in the way that restaurants and shops are decorated and in the entertainment on offer, for example.
This may help promote traditions that may have become distant.
Many tourists will visit the destination especially to see its local heritage. It is for this reason that many destinations will make every effort to preserve its heritage.
This could include putting restrictions in place or limiting tourist numbers, if necessary. This is often an example of careful tourism planning and sustainable tourism management.
This text by Hyung You Park explains the principles of heritage tourism in more detail.
Negative social impacts of tourism
Unfortunately, there are a large number of socio-cultural costs on the host communities. These negative social impacts include; social change; changing values; increased crime and gambling; changes in moral behaviour; changes in family structure and roles; problems with the tourist-host relationship and the destruction of heritage.

Social change is basically referring to changes in the way that society acts or behaves. Unfortunately, there are many changes that come about as a result of tourism that are not desirable.
There are many examples throughout the world where local populations have changed because of tourism.
Perhaps they have changed the way that they speak or the way that they dress. Perhaps they have been introduced to alcohol through the tourism industry or they have become resentful of rich tourists and turned to crime. These are just a few examples of the negative social impacts of tourism.
Read also: Business tourism explained: What, why and where

Globalisation is the way in which the world is becoming increasingly connected. We are losing our individuality and gaining a sense of ‘global being’, whereby we are more and more alike than ever before.
Globalisation is inevitable in the tourism industry because of the interaction between tourists and hosts, which typically come from different geographic and cultural backgrounds. It is this interaction that encourage us to become more alike.
Here are some examples:
- When I went on the Jungle Book tour on my travels through Goa, the tourists were giving the Goan children who lived in the area sweets. These children would never have eaten such sweets should they not have come into contact with the tourists.
- When I travelled to The Gambia I met a local worker (known as a ‘ bumster ‘) who was wearing a Manchester United football top. When I asked him about it he told me that he was given the top by a tourist who visited last year. If it was not for said tourist, he would not have this top.
- In Thailand , many workers have exchanged their traditional work of plowing the fields to work in the cities, in the tourism industry. They have learnt to speak English and to eat Western food. If it were not for the tourists they would have a different line of work, they would not speak English and they would not choose to eat burger and chips for their dinner!
Many people believe globalisation to be a bad thing. BUT, there are also some positives. Think about this…
Do you want an ‘authentic’ squat toilet in your hotel bathroom or would you rather use a Western toilet? Are you happy to eat rice and curry for breakfast as the locals would do or do you want your cornflakes? Do you want to struggle to get by when you don’t speak the local language or are you pleased to find somebody who speaks English?
When we travel, most tourists do want a sense of ‘familiar’. And globalisation helps us to get that!

You can learn more about globalisation in this post- What is globalisation? A simple explanation .

Along similar lines to globalisation is the loss of authenticity that often results from tourism.
Authenticity is essentially something that is original or unchanged. It is not fake or reproduced in any way.
The Western world believe that a tourist destination is no longer authentic when their cultural values and traditions change. But I would argue is this not natural? Is culture suppose to stay the same or it suppose to evolve throughout each generation?
Take a look at the likes of the long neck tribe in Thailand or the Maasai Tribe in Africa. These are two examples of cultures which have remained ‘unchanged’ for the sole purpose of tourism. They appear not to have changed the way that they dress, they way that they speak or the way that they act in generations, all for the purpose of tourism.
To me, however, this begs the question- is it actually authentic? In fact, is this not the exact example of what is not authentic? The rest of the world have modern electricity and iPhones, they watch TV and buy their clothes in the nearest shopping mall. But because tourists want an ‘authentic’ experience, these people have not moved on with the rest of the world, but instead have remained the same.
I think there is also an ethical discussion to be had here, but I’ll leave that for another day…
You can learn more about what is authenticity in tourism here or see some examples of staged authenticity in this post.
Read also: Environmental impacts of tourism
Similarly, destinations risk standardisation in the process of satisfying tourists’ desires for familiar facilities and experiences.
While landscape, accommodation, food and drinks, etc., must meet the tourists’ desire for the new and unfamiliar, they must at the same time not be too new or strange because few tourists are actually looking for completely new things (think again about the toilet example I have previously).
Tourists often look for recognisable facilities in an unfamiliar environment, like well-known fast-food restaurants and hotel chains. Tourist like some things to be standardised (the toilet, their breakfast, their drinks, the language spoken etc), but others to be different (dinner options, music, weather, tourist attractions etc).
Do we want everything to become ‘standardised’ though? I know I miss seeing the little independent shops that used to fill the high streets in the UK. Now it’s all chains and multinational corporations. Sure, I like Starbucks (my mug collection is coming on quite nicely!), but I also love the way that there are no Starbucks in Italy. There’s something great about trying out a traditional, yet unfamiliar coffee shop, or any independant place for that matter.
I personally think that tourism industry stakeholders should proceed with caution when it comes to ‘standardisation’. Sure, give the tourists that sense of familiar that they are looking for. But don’t dilute the culture and traditions of the destination that they are coming to visit, because if it feels too much like home….. well, maybe they will just stay at home next time? Just a little something to think about…

On a less philosophical note, another of the negative social impacts of tourism is that it can have significant consequences is culture clashes.
Because tourism involves movement of people to different geographical locations cultural clashes can take place as a result of differences in cultures, ethnic and religious groups, values, lifestyles, languages and levels of prosperity.
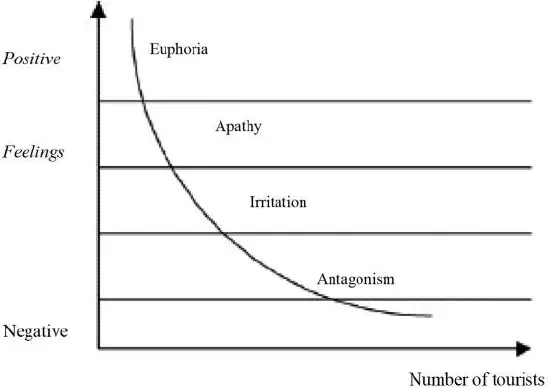
The attitude of local residents towards tourism development may unfold through the stages of euphoria, where visitors are very welcome, through apathy, irritation and potentially antagonism when anti-tourist attitudes begin to grow among local people. This is represented in Doxey’s Irritation Index, as shown below.
Culture clashes can also be exasperated by the fundamental differences in culture between the hosts and the tourists.
There is likely to be economic inequality between locals and tourists who are spending more than they usually do at home. This can cause resentment from the hosts towards the tourists, particularly when they see them wearing expensive jewellery or using plush cameras etc that they know they can’t afford themselves.
Further to this, tourists often, out of ignorance or carelessness, fail to respect local customs and moral values.
Think about it. Is it right to go topless on a beach if within the local culture it is unacceptable to show even your shoulders?
There are many examples of ways that tourists offend the local population , often unintentionally. Did you know that you should never put your back to a Buddha? Or show the sole of your feet to a Thai person? Or show romantic affection in public in the Middle East?
A little education in this respect could go a long way, but unfortunately, many travellers are completely unaware of the negative social impacts that their actions may have.
The last of the social impacts of tourism that I will discuss is crime, gambling and moral behaviour. Crime rates typically increase with the growth and urbanisation of an area and the growth of mass tourism is often accompanied by increased crime.
The presence of a large number of tourists with a lot of money to spend and often carrying valuables such as cameras and jewellery increases the attraction for criminals and brings with it activities like robbery and drug dealing.
Although tourism is not the cause of sexual exploitation, it provides easy access to it e.g. prostitution and sex tourism . Therefore, tourism can contribute to rises in the numbers of sex workers in a given area. I have seen this myself in many places including The Gambia and Thailand .
Lastly, gambling is a common occurrence as a result of tourism. Growth of casinos and other gambling facilities can encourage not only the tourists to part with their cash, but also the local population .
As I have demonstrated in this post, there are many social impacts of tourism. Whilst some impacts are positive, most unfortunately are negative impacts.
Hopefully this post on the social impacts of tourism has helped you to think carefully about the impacts that your actions may have on the local community that you are visiting. I also hope that it has encouraged some deeper thinking with regards to issues such as globalisation, authenticity and standardisation.
If you are interested in learning more about topics such as this subscribe to my newsletter ! I send out travel tips, discount coupons and some material designed to get you thinking about the wider impacts of the tourism industry (like this post)- perfect for any tourism student or keen traveller!
As you can see, the social impacts of tourism are an important consideration for all industry stakeholders. Do you have any comments on the social impacts of tourism? Leave your comments below.
If you enjoyed this article on the social impacts of tourism, I am sure that you will love these too-
- Environmental impacts of tourism
- The 3 types of travel and tourism organisations
- 150 types of tourism! The ultimate tourism glossary
- 50 fascinating facts about the travel and tourism industry
Liked this article? Click to share!
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Socio-economic Impacts of Tourism Development and Their Implications on Local Communities

2016, International Journal of Economics and Business Administration,American Institute of Science (AIS)
Tourism has significant potentials for generating positive social, cultural and economic benefits depending on how tourism activities are managed and developed. However, tourism also has the potential to generate more negative outcomes. Therefore, the objectives of this study are first; to examine the impacts of tourism development on local communities, second; to recognize the attitudes and perception of local communities towards tourism development in their neighbourhoods. The study is based on the data gathered from 108 families in three villages to analysis the attitudes and perceptions of local communities towards tourism development. Additionally, six unstructured interviews were conducted with government officers of these villages to get the precise understanding of the tourism development in local communities and its impacts. The study reveals inadequate government planning, policies and regulations, insufficient knowledge and skills of tour operators, and the broader social...
Related Papers
SARJIT S. Gill / FEM
This article illustrates the role of local communities for tourism development. This study also attempts to highlight the role of tourism local development. This article looks at how local communities can develop tourism in local area. The concepts of community and community development have been important for local tourism development. The implication of this study arises from the fact that there has been little research carried out on interaction between communities and local tourism. Theoretically, the findings of this study enrich the knowledge concerning local tourism industry (Journal of American Science 2010;6(2):155-161). (ISSN: 1545-1003).
TRJ Tourism Research Journal
Filma Festivalia
The research aimed to analyze “The Impact of Tourism on Village Society”. The methodology of the study was quantitative research and descriptive analysis. The research was located in Sumurugul village. Respondents of this research were 92 residents. The data was collected by using convenience sampling. The data was analyzed by using validity and reliability test, frequency, and descriptive (mean) analysis. The study found that there is the positive impact of tourism on village society in Sumurugul in the point of economics, social, and environment aspect. The implication of this study showed that tourism should be one of the alternatives to develop a village.
Journal of Gastronomy, Hospitality and Travel
The perception of the locals respecting the impacts of tourism can be determined by the factors such as how the community, which they are member of is, affected by tourism; how tourism affects social activities and the attitudes of political and administrative authorities towards tourism. The main purpose of this study is to estimate whether locals' negative perceptions (NP) and positive perceptions (PP), locals' support for tourism development (STD) and community participation (CP) differ at rural and urban levels. The sub-aims are to figure out whether there is any mediation effect and correlations among NP, PP, STD and CP. Data were obtained from Muğla (urban) and Fethiye (rural) through face-to-face surveys with a total number of 400 participants. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), validity and reliability analysis and path analysis for Fethiye and Muğla have performed. No statistically significant effect of CP, PP and NP on STD was found in Muğla and Fethiye. In Fethiye locals' PP have a significant and positive effect on STD. Locals' PP and NP have a significant and positive effect on CP. Consequently, a difference has found between Fethiye and Muğla concerning the impact of positive and negative perceptions on the participation in the tourism processes.
Journal of Tourism and Services
GÜRKAN ALAGÖZ
The purpose of this research is to determine the socio-cultural, economic, and environmental effects of tourism perceived by the local community living in Manavgat/Turkey on the satisfaction with the tourism development, to identify the effect of this satisfaction with tourism development, and to ascertain the moderator role of the demographic variables in this relationship. The population of the research is the local community living in Manavgat/Turkey. EFA, CFA, path analyzes, and Slope difference tests have been performed through 384 surveys collected from the local community. As a result, it has been determined that perceived socio-cultural, economic, and environmental positive effects of tourism and negative environmental effects have an impact on satisfaction with tourism development. Meanwhile, it has been determined that the local community's satisfaction with tourism development affects the attitude and gender has a moderator role on this effect. In line with these resu...
African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure,
Lwazi Apleni
The aim of this paper is to assess tourism as a catalyst for rural development and community awareness in a case study of Coffee Bay. Tourism is considered as a viable tool for economic development, specifically in the developing world. It was envisaged and deemed necessary to develop tourism in the local community as it would generate community development, thus supporting its overall development. Apart from this tourist sites enhance community cohesion and promote peace within the host community. The study adopted both qualitative and quantitative methods of data collection. Questionnaires were distributed to community members of Coffee Bay. Furthermore, a random sampling method was used for the purpose of the study. Data obtained was analysed through the use of the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS). The findings of the study revealed a high awareness and a high level of community willingness to participate in tourism ventures. Furthermore, findings of the study revealed that some members of the community have already participated in Small Medium Tourism Enterprises (SMTEs). However, the negative aspects raised by the community in the development processes are the issue of government interference and the lack of sponsors together with the poor infrastructure. Therefore, it is recommended that the government must make a concerted effort in providing a sustainable and conducive environment for tourism to thrive in the Coffee Bay community. Funding was also cited as one of the bottlenecks. As such, funding should be provided either by the government or by the private sector to ensure an on-going process of tourism development.
Dianne Dredge
Development is a challenging concept. Telfer and Sharpley (2008) observe that problems such as poverty, inequality, poor healthcare and a lack of educational opportunities are widely recognized and reflected in the goals of international development programs such as the UN Millennium Project. However, as these authors state, it is unclear as to what extent particular developmental vehicles such as tourism are effective in addressing these issues, especially as many of the problems facing developing countries may be the outcome rather than the cause of underdevelopment (see also Telfer, 2009). The notion of “community” is also problematic, and heterogeneity rather than homogeneity may be far more appropriate to describe communities that are encased with geographic (or virtual) boundaries (see Dicks, 1999). An alternative view of community, characterized by belonging to multiple networks over time and across spatial scales fits our contemporary understanding of a globalized world, but also makes “community” a slippery concept for the purposes of planning and policy. Hence, both the notion of “community” and “development” tend to be contested, adding to the challenge of understanding the meaning and contribution of “community-based tourism.” The recent critique of community participation in tourism by Butcher (2010) in the Research Probe section of Tourism Recreation Research, and responses by Singh (2010) and Weaver (2010), show that the debate around resident responsive tourism and community participation in tourism are far from over. This chapter continues to explore the challenges encapsulated in these debates and attempts to address the overall question: To what extent can tourism contribute to community development? Disadvantaged, low-income and minority populations generally tend to incur a high proportion of negative environmental and sociocultural impacts compared to other social groups, such as tourists, and local elites. How does community-based tourism address inequalities in the distribution of economic, environmental and sociocultural costs? And how do pro-poor and sustainable tourism agendas address pressing issues like climate change in the context of community development? The chapter will take up these questions of tourism’s contribution to community development, first by examining the key issues and challenges that underpin the chapter, followed by an examination of various approaches and forms of tourism. Planning and participatory approaches and mechanisms will then be addressed.
Economic Journal of Nepal
Marianne Heredge
A study of tourism in Upper Mustang was made in 2003 (Heredge, 2003) examining key issues in planning tourism development to maximize benefits to local communities there. In Upper Mustang at the time of writing, there was no evidence that any of the local people benefit ...
Athula Gnanapala
The study is mainly to identify the community perception and their involvement in the tourism development activities. Research was carried out at Passikudha, one of the planned tourism development site in Sri Lanka, adopting the mixed methodology. A survey was conducted using a semi structured questionnaire with 251 respondents from the local community. Additionally, in-depth interviews with six community leaders were conducted. The local community of Passikudha tourism resort area consists of 712 families, which was considered for the survey. The findings indicate that more benefits have been brought to the area due to the ongoing tourism development activities, however the local community is not in a position to get the real benefits of the tourism development due to lack of proper education, knowledge, experience, capacity etc. The community bear mixed perception about the ongoing development in the study area. On the other hand, those who get benefits through tourism hold positive perception and attitudes while those who have not received any tangible benefits hold negative attitudes about the tourism development. The results highlighted that, it is necessary to have a well planned awareness program about the community involvement for the ongoing tourism development activities. Therefore, the authorities should concern more about the community awareness and capacity building programs in order to deliver the benefits of tourism development to the local community also to ensure the long term sustainability of the industry.
Emmanuel Seni
Research Paper
Ala`a Abukhalifeh
This research discusses the role of local stakeholder participation in developing sustainable community-based tourism (CBT). A survey collected in Pulau Redang, Kuala Terengganu from carefully recruited community-based tourism stakeholders is discussed to further solidify the theoretical underpinnings of stakeholder participation and community based tourism nexus. Majority of the research participants indicated that the likelihood of them being included in the decision-making process shows improvement. In connection to this, types of community participation, strengths, motivations, and barriers to participation in community-based tourism development endeavours are highlighted. Research outcomes revealed two major influential factors for the existence of better community participation, namely, the presence of strong (CBT) organizations and committed leadership with growing support. The study concludes by providing with suggestions that further improve community-based tourism stakeholder participation in developing sustainable tourism from the perspective of the remote Island destination.

RELATED PAPERS
Marcos Quispe
Professor Wael Fahmi
Estelle Mare
Fernando Forero Pineda
3rd.International Conference on Architecture, Civil Engineering, Urban Development and Environment
Atiye Jarrahi
Sem Vandekerckhove
Tribology Letters
David Allsopp
Molecular Neurobiology
Anurag Kuhad
Problems and perspectives in management
Caleb M. ADELOWO
MATEC Web of Conferences
Justyna Tomaszewska
arXiv: Accelerator Physics
Kathleen Amm
Wariara Kariuki
Elsa Rute Guerra Caeiro
roshni resmi
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Ontario.ca needs JavaScript to function properly and provide you with a fast, stable experience.
To have a better experience, you need to:
- Go to your browser's settings
- Enable JavaScript

Ministry of Tourism, Culture and Gaming and Ministry of Sport
Supporting and delivering tourism and cultural experiences, and championing participation in sport and recreation activities across Ontario.
- Tourism regions
- Tourism research statistics
- Resource-based tourism
- Tourism Regional Economic Impact Model
- Tourism signs on Ontario’s roadways
- Public libraries
- Resources for artists
- Cultural media industries
- Cultural planning
- Sport and recreation
- Rowan’s Law : Concussion safety
- Provincial sport organizations and multi-sport organizations
- Sport Hosting Program
- Amateur combative sports
- Rules and regulations for professional combative sports
We help Ontario's economy and quality of life through strategic support and investment by:
- working with the tourism industry and regional tourism organizations to support businesses and attract international investment
- investing in festivals and events across the province
- promoting the arts and the creative economy
- funding public libraries and community museums
- supporting community projects and engagement
- promoting a culture that values sport and physical activity
- supporting growth of the sport sector through investments that increase tourism and provide athletes of all abilities and circumstances the opportunity to participate in sport at all levels
- Contact form
- Tel : 416-326-9326
- Toll-free: 1-888-997-9015
- TTY : 416-325-5807
- Toll-free TTY : 1-866-700-0040
Ministry of Tourism, Culture and Gaming and Ministry of Sport 6 th Floor, 438 University Avenue Toronto, Ontario M5G 2K8
- Employee directory
- Regional development advisors
Minister, media and news
- Contact the Minister
- Media contacts
- Ministry news
Agencies, boards and commissions
The ministry operates and manages the following historical attractions:
- Discovery Harbour
- Fort William Historical Park
- Sainte-Marie among the Hurons
The ministry oversees the following provincial agencies and provincially funded organizations:
- Art Gallery of Ontario
- Destination Ontario
- McMichael Canadian Art Collection
- Metro Toronto Convention Centre
- Niagara Parks Commission
- Ontario Arts Council
- Ontario Creates
- Ontario Trillium Foundation
- Ottawa Convention Centre
- Royal Botanical Gardens
- Royal Ontario Museum
- Science North
- St. Lawrence Parks Commission
Legislation
The ministry administers the following legislation:
- Ontario Heritage Act , in respect of clauses 70(1)(a) and (e) as they relate to museums
- Public Libraries Act
- Ontario Trails Act
- Accommodation Sector Registration of Guests Act, 2021 , responsibility for which, when it comes into force, will be shared with the Solicitor General
- Art Gallery of Ontario Act
- Arts Council Act, R.S.O.
- Athletics Control Act
- Combative Sports Act, 2019
- Community Recreation Centres Act
- Foreign Cultural Objects Immunity from Seizure Act, 2019
- George R. Gardiner Museum of Ceramic Art Act
- Historical Parks Act
- Hotel Registration of Guests Act
- Innkeepers Act
- Lawren Harris Day Act
- McMichael Canadian Art Collection Act, R.S.O.
- Metropolitan Toronto Convention Centre Corporation Act
- Ministry of Citizenship and Culture Act , in respect of culture matters
- Ministry of Tourism and Recreation Act
- Niagara Parks Act
- Ontario Wine Week Act
- Ottawa Convention Centre Corporation Act
- Poet Laureate of Ontario Act (In Memory of Gord Downie), 2019
- Rowan's Law (Concussion Safety), 2017
- Royal Botanical Gardens Act, 1989 (private act)
- Royal Ontario Museum Act
- Science North Act
- Special Hockey Day Act, 2018
- St. Lawrence Parks Commission Act
- Status of Ontario’s Artists Act
World Population Prospects 2022
- Download Center
- Data Portal
- Data Sources
- Graphs / Profiles
- Definition of Regions
- Glossary of Demographic Terms
- Methodology
- Definition of Projection Scenarios
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Publications
- World Urbanization Prospects
- Population Division
The 2022 Revision of World Population Prospects is the twenty-seventh edition of official United Nations population estimates and projections that have been prepared by the Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat. It presents population estimates from 1950 to the present for 237 countries or areas, underpinned by analyses of historical demographic trends. This latest assessment considers the results of 1,758 national population censuses conducted between 1950 and 2022, as well as information from vital registration systems and from 2,890 nationally representative sample surveys The 2022 revision also presents population projections to the year 2100 that reflect a range of plausible outcomes at the global, regional and national levels.
The main results are presented in a series of Excel files displaying key demographic indicators for each UN development group, World Bank income group, geographic region, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) region, subregion and country or area for selected periods or dates within 1950-2100. An online database (Data Portal) provides access to a subset of key indicators and interactive data visualization, including an open API for programmatic access. For advanced users who need to use these data in a database form or statistical software, we recommend to use the CSV format for bulk download. Special Aggregates also provide additional groupings of countries. For the first time, the estimates and projections are presented in one-year intervals of age and time instead of the five-year intervals used previously. The various datasets disaggregated by age are available in two forms: by standard 5-year age groups and single ages.
Additional outputs, including results from the probabilistic projections, and more detailed metadata will be posted soon after the initial public release.

Disclaimer: This web site contains data tables, figures, maps, analyses and technical notes from the current revision of the World Population Prospects. These documents do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Secretariat of the United Nations concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The debate on the positive and negative social and cultural impacts of tourism has been a. common reemerging i ssue that surround t ourism development and sustainability. Tourism. development is ...
Abstract: is paper aims to systematically review and analyse the current research on tourism. impacts on destinations for the period 2016-2020. e study evaluated 80 published articles. selected ...
The Social Impacts of Tourism (English version) Description. PDF. This background paper has three objectives. First to identify the most common social impacts arising from tourism development. Second, to suggest reasons why negative impacts occur. Third, to suggest policies and strategies for countries to adopt in the 21ist century to mitigate ...
We would like to show you a description here but the site won't allow us.
It further posits that residents' perceived social impacts of tourism and their interpersonal trust exert a direct influence on residents' place attachment. The proposed model further considers place attachment to exert a direct influence on residents' pro-social and pro-environmental behavioural intentions.
issues that are pertinent to tourism social impacts research, drawing links to the respective chapters in the book. These issues and their respective implica-tions for the tourism industry will set the context for the book. The chapter ends with a brief overview of the organization of the book.
being undertaken into the range of impacts tourism creates and the ways in which these impacts can be managed more carefully. It is usual to classify the positive and negative impacts of tourism under the following headings: • economic impacts • environmental impacts • social impacts • cultural impacts . Economic Impacts . Positive
The socio-cultural impacts of tourism - A review of literature, policy ...
The development of tourism induces changes in the social character of a destination. Tourism is a globalized business activity and thus presents growing challenges in terms of traditional social culture. With the continuous development of the tourism industry, traditional social culture has changed dramatically at many World Heritage sites (WHSs). Additionally, the growing dependence of many ...
The Social Impacts of Tourism (English version) Published: 1997 Pages: 44. eISBN: 978-92-844-1096-5. Abstract: This background paper has three objectives. First to identify the most common social impacts arising from tourism development. Second, to suggest reasons why negative impacts occur. Third, to suggest policies and strategies for ...
The purpose of this work is to review the scientific literature that is focused on the sociology of tourism as a subject to study the economic, social, and environmental impacts of tourism on ...
satisfaction with material well-being, and the relationship between the social impact of tourism and the satisfaction with community well-being may be considered to be the capacity of the destination area to absorb tourists before the host population would feel negative impacts. This is consistent with the theoretical foundation of carrying ...
The social impacts of tourism are difficult to measure, and most published studies are mainly concerned with the social impacts on the host communities rather than the impacts on the tourists themselves. Studies of residents' perceptions of tourism are typically conducted using household surveys.
The positive impacts that they pointed out were predominantly economic, but included a few social factors. The positive impacts were employment opportunities, town's overall tax revenue, income, and standard of living, work attitudes, quality of life, hospitality to strangers, and confidence among people.
The social impact of tourism is the most likely to influence and change a local community. Tourism is an interface for cultural exchange, facilitating the interaction between tourism destination and visitors. It is a positive way for learning each other's culture and manners. ...
tual model developm ent; the advent of case study- based, atheoretical. empirical inquiry; scale de sign, development, and testing; furthe r scale. development/refin ement and theoretical ...
Negative social impacts of tourism. Social Change. Globalisation and the Destruction of Preservation and Heritage. Loss of Authenticity. Standardisation and Commercialisation. Culture clashes. Tourist-host relationships. Increase in crime, gambling and moral behaviour. Social impacts of tourism: Conclusion.
the tourism sector and its impacts on the economy, environment, politics and the socio-cultural being of the host community. The main aim of this research is to highlight the well-organized and managed economic impacts by host communities on the host community. KEYWORDS: Tourism, Economic Impacts, Environmental Impacts, Social and
Pessimistic Impact of Tourism on Community Social Life Furthermore, Murray (2009) has pile up a range of common positive economic impacts relating to the local economy as, direct employment opportunities (including, administration, guiding, tours and transport, construction, hospitality, management, accommodation shopping, food and beverage ...
Tourism is a cultural, social, and economic phenomenon that involves movement of people to places or na tions. away fr om their day- to -day environment. The activities of these people involving ...
working with the tourism industry and regional tourism organizations to support businesses and attract international investment; investing in festivals and events across the province; promoting the arts and the creative economy; funding public libraries and community museums; supporting community projects and engagement
The 2022 Revision of World Population Prospects is the twenty-seventh edition of official United Nations population estimates and projections that have been prepared by the Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat. It presents population estimates from 1950 to the present for 237 countries or areas, underpinned by analyses of ...
652 SOCIAL IMPACTS OF TOURISM and social conditions. It also highlighted major perceptual differences between separate groups of students with and without tourism educa- tion. Brayley and Var (1989) suggested that the strongest held view by students was as a positive economic influence. The positive social and
This paper explored the social impacts of tourism as perceived by the residents, as well as. the factors causing these negative and positive perceptions, in an effort to identify the managerial ...
positive tourism impacts relat ing to the social w e ll-being of. the community as the stimulation of infrastructure. development (road s, communications, healthcare, educat ion, public transport ...
Weather events have the potential to greatly impact business operations and profitability, especially in outdoor-oriented economic sectors such as Tourism, Recreation, and Leisure (TRL).