The state of tourism and hospitality 2024
Tourism and hospitality are on a journey of disruption. Shifting source markets and destinations, growing demand for experiential and luxury travel, and innovative business strategies are all combining to dramatically alter the industry landscape. Given this momentous change, it’s important for stakeholders to consider and strategize on four major themes:
- The bulk of travel is close to home. Although international travel might draw headlines, stakeholders shouldn’t neglect the big opportunities in their backyards. Domestic travel still represents the bulk of travel spending, and intraregional tourism is on the rise.
- Consumers increasingly prioritize travel—when it’s on their own terms. Interest in travel is booming, but travelers are no longer content with a one-size-fits-all experience. Individual personalization might not always be practical, but savvy industry players can use segmentation and hypothesis-driven testing to improve their value propositions. Those that fail to articulate target customer segments and adapt their offerings accordingly risk getting left behind.
- The face of luxury travel is changing. Demand for luxury tourism and hospitality is expected to grow faster than any other travel segment today—particularly in Asia. It’s crucial to understand that luxury travelers don’t make up a monolith. Segmenting by age, nationality, and net worth can reveal varied and evolving preferences and behaviors.
- As tourism grows, destinations will need to prepare to mitigate overcrowding. Destinations need to be ready to handle the large tourist flows of tomorrow. Now is the time for stakeholders to plan, develop, and invest in mitigation strategies. Equipped with accurate assessments of carrying capacities and enhanced abilities to gather and analyze data, destinations can improve their transportation and infrastructure, build tourism-ready workforces, and preserve their natural and cultural heritages.

Now boarding: Faces, places, and trends shaping tourism in 2024
Global travel is back and buzzing. The amount of travel fell by 75 percent in 2020; however, travel is on its way to a full recovery by the end of 2024. More regional trips, an emerging population of new travelers, and a fresh set of destinations are powering steady spending in tourism.
There’s no doubt that people still love to travel and will continue to seek new experiences in new places. But where will travelers come from, and where will they go?
We share a snapshot of current traveler flows, along with estimates for growth through 2030.
The way we travel now
Which trends are shaping traveler sentiment now? What sorts of journeys do today’s travelers dream about? How much are they willing to spend on their trips? And what should industry stakeholders do to adapt to the traveler psychology of the moment?
To gauge what’s on the minds of present-day travelers, we surveyed more than 5,000 of them. The findings reveal disparate desires, generational divides, and a newly emerging set of traveler archetypes.
Updating perceptions about today’s luxury traveler
Demand for luxury tourism and hospitality is expected to grow faster than for any other segment. This growth is being powered in part by a large and expanding base of aspiring luxury travelers with net worths between $100,000 and $1 million, many of whom are younger and increasingly willing to spend larger shares of their wealth on upscale travel options. The increase is also a result of rising wealth levels in Asia.
We dug deeper into this ongoing evolution by surveying luxury travelers around the globe about their preferences, plans, and expectations. Some widely held notions about luxury travelers—such as how much money they have, how old they are, and where they come from—could be due for reexamination.
Destination readiness: Preparing for the tourist flows of tomorrow
As global tourism grows, it will be crucial for destinations to be ready. How can the tourism ecosystem prepare to host unprecedented volumes of visitors while managing the challenges that can accompany this success? A large flow of tourists, if not carefully channeled, can encumber infrastructure, harm natural and cultural attractions, and frustrate locals and visitors alike.
Now is the time for tourism stakeholders to combine their thinking and resources to look for better ways to handle the visitor flows of today while properly preparing themselves for the visitor flows of tomorrow. We offer a diagnostic that destinations can use to spot early-warning signs about tourism concentration, along with suggestions for funding mechanisms and strategies to help maximize the benefits of tourism while minimizing its negative impacts.
Six trends shaping new business models in tourism and hospitality
As destinations and source markets have transformed over the past decade, tourism and hospitality companies have evolved, too. Accommodation, home sharing, cruises, and theme parks are among the sectors in which new approaches could present new opportunities. Stakeholders gearing up for new challenges should look for business model innovations that will help sustain their hard-won growth—and profits.
Unbundling offerings, cross-selling distinctive experiences, and embracing data-powered strategies can all be winning moves. A series of insight-driven charts reveal significant trends and an outlook on the future.
RELATED ARTICLES

The future of tourism: Bridging the labor gap, enhancing customer experience

The promise of travel in the age of AI

From India to the world: Unleashing the potential of India’s tourists
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Competitiveness.
- Market Intelligence
- Policy and Destination Management
Product Development
Share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
As defined by UN Tourism, a Tourism Product is "a combination of tangible and intangible elements, such as natural, cultural and man-made resources, attractions, facilities, services and activities around a specific center of interest which represents the core of the destination marketing mix and creates an overall visitor experience including emotional aspects for the potential customers. A tourism product is priced and sold through distribution channels and it has a life-cycle".
Rural tourism
UN Tourism understands Rural Tourism as "a type of tourism activity in which the visitor’s experience is related to a wide range of products generally linked to nature-based activities, agriculture, rural lifestyle / culture, angling and sightseeing.
Gastronomy and Wine Tourism
As global tourism is on the rise and competition between destinations increases, unique local and regional intangible cultural heritage become increasingly the discerning factor for the attraction of tourists.
Mountain Tourism
Mountain Tourism is a type of "tourism activity which takes place in a defined and limited geographical space such as hills or mountains with distinctive characteristics and attributes that are inherent to a specific landscape, topography, climate, biodiversity (flora and fauna) and local community. It encompasses a broad range of outdoor leisure and sports activities".
Urban Tourism
According to UN Tourism, Urban Tourism is "a type of tourism activity which takes place in an urban space with its inherent attributes characterized by non-agricultural based economy such as administration, manufacturing, trade and services and by being nodal points of transport. Urban/city destinations offer a broad and heterogeneous range of cultural, architectural, technological, social and natural experiences and products for leisure and business".
Sports Tourism
Tourism and sports are interrelated and complementary. Sports – as a professional, amateur or leisure activity – involves a considerable amount of traveling to play and compete in different destinations and countries. Major sporting events, such as the Olympic Games, football and rugby championships have become powerful tourism attractions in themselves – making a very positive contribution to the tourism image of the host destination.
Shopping Tourism
Shopping Tourism is becoming an increasingly relevant component of the tourism value chain. Shopping has converted into a determinant factor affecting destination choice, an important component of the overall travel experience and, in some cases the prime travel motivation.

- Tourism Management Tutorial
- Tourism Management - Home
- Tourism Basics
- Tourism Management - Introduction
- Tourism Management - Types
- Tourism Management - Terminology
- Tourism Management - Factors
- Tourism Management - Demand
- Tourism Mngmt - Motivation Factors
- Maslow's Pyramid of Motivation
- Consumer Behavior in Tourism
- Tourism Management - Plog's Model
- About Tourism Destinations
- Destination Awareness
- Tourism Management - Milieus
- Tourism Management Destination
- Tools for Destination Management
- Managing Tourism
- Tourism Management - Supply
- Tourism Functional Management
- Business Departments
- Market Segmentation
- Tourism Mngmt - Marketing Mix
- Tourism Mngmt - Products & Services
- Developing Product
- Product Development Phases
- Tourism Impacts, Trends, & Future
- Tourism Management - Impacts
- Tourism Mngmt - Trends & Future
- Tourism Management Resources
- Tourism Management - Quick Guide
- Tourism Management - Resources
- Tourism Management - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Products and Services
“Don’t give up and always keep on believing in your product. Because if you don’t, how can you make others believe in it?” − Niels Van Deuren, Founder, housinganywhere.com.
The tourism industry as a whole survives because of various tourism products and services. Tourism industry is flexible. The products of tourism cannot be easily standardized as they are created for the customers of varied interests and demands. As the tourism products are mainly the tourists’ experience, they can be stored only in the tourists’ memories.
Let us understand more about tourism products and services −
Types of Tourism Products
The tourism products are grouped into the following types −
Tourism Oriented Products (TOP)
These are the products and services created primarily for the tourists and also for the locals. These products need a great share of investments in private sector. A few of them are −
- Accommodations; For example, Taj, ITC Hotels.
- Transportation; For example, Owning taxis, luxury buses, and boats.
- Retail Travel Agents
- Tour Operators
- Shopping Centers such as malls
- Cinema Theatres such as PVR
- Restaurants for Food and Beverages
- Tourism Information Centers
- Souvenirs Outlets
- Museums, Temples, Gardens, and Theme parks
Residents Oriented Products (ROP)
Here, the products and services are created mainly for the local residents staying at a particular tourist destination. This category requires investment in public sectors more. Some of them are −
- Public Parks
- Banks and ATMs
- Petrol Pumps
- Postal Service
Intangible Products of Tourism
They include −
Bookings of accommodations, theatres, and at various sites.
Tourists’ experience by visiting a destination, eating at a restaurant, or performing an activity.
Tourists’ memory which is created by storing the details of events and experience on the tour. The high degree of satisfaction or dissatisfaction is often stored as a long term memory.
Transportation of tourists and their luggage from one place to another.
Tour Operator’s Products and Services
To realize the facilities and experience a tourism product offers, service is required by skilled and qualified staff. The tour operator provides the following typical products and services −
Accommodations
The tourist destinations are equipped with different types of accommodations. They cater for tourists’ stay at the destination.
Serviced − This type of accommodation is supported by skilled staff such as housekeepers, drivers, guides, and cooks.
Self-catering − This accommodation offers staying facilities but dining is required to be self-catered. It is equipped with cooking, fuel and facility, some basic supplies such as tea/coffee/sugar sachets, and a drinking water source.
Hotels − Budget rooms to 7* hotels with classy amenities. The hotels contribute a major share of imparting the experience to the tourists by providing best services and amenities.
Guest Houses − Owned by business or government organizations, which can be used by its staff and staff relatives.
Camping Sites − They are open sites often located in areas of lush greenery. They are equipped with clean place to pitch the personal tent, a water supply, and electric supply. Camp sites have common rest rooms.
Reservations
The tour operator is responsible for making reservations for special events or activities the tourists are interested in. At some places, the reservations are required to be done well in advance to avoid last minute hassles. The events or activities such as a music concert or a theatre show, visiting a theme park or a zoo, require people to secure seats or avail entry with prior reservations.
Guided Tours
The tour operators can arrange guided tours. Some qualified staff who can get access to the place, explain the importance of the place, support, and guide the participants through the entire visit. The guide is arranged to accompany the tour participants as a part of tour.
Transport Facilities
These facilities are for travelling from one place to another.
Surface Transport − It includes support of transport by road or water.
Air Transport − This is the support of transport by air, generally given for long distance travel. Many times the tours include a halt of a couple of hours at transit destinations. Today the airports are built and maintained as engaging tourist terminals by providing amenities such as spas, lounges, food joints, bars, and book shops, retail shops for selling authentic local food, clothes, and souvenirs.
Today the Airlines are no more backstage when it comes to caring for their customers. They offer loyalty programs to their customers under Frequent Flyer Program to encourage the customers to travel more and accumulate points and redeem them against travel or rewards.
Dining Facilities
The tour operators can book accommodation that provides dining facilities or it can tie up with the local restaurants which are ready to entertain groups. If the tour package is all inclusive, the tour operator pays for breakfast, lunch, and dinner. If not, the tourists need to pay from their own pocket.

What is Tourism Product? Definition, Types, Characteristics
- Post last modified: 3 October 2021
- Reading time: 14 mins read
- Post category: Uncategorized
What is Tourism Product?
Tourism Products are a combination of goods and services demanded by a tourist during travel to and stay at a destination. These include natural, cultural and manmade attractions and facilities such as hotels, transport and ancillary services.
In this process, tourists derive an experience which varies from individual to individual. From a broader perspective, the sum total of experiences derived by the tourists during the entire trip can be considered as the product.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Tourism Product?
- 2 Definition of Tourism Product
- 3.1 Natural Tourism Product
- 3.2 Man-Made Tourism Product
- 3.3 Symbiotic Tourism Product
- 3.4 Event Based Tourism
- 3.5 Site Based Tourism Product
- 4.1 Intangibility
- 4.2 Inseperatability
- 4.3 Perishability
- 4.4 Heterogeneity
- 4.5 Essentially of Users Presence
- 4.6 Complexity in Marketing
- 4.7 Absence of Ownership
Definition of Tourism Product
Burkat and Medlik say tourism products to an array of integrated products, which consist of objects and attractions, transportation, accommodation and entertainment, where each element of the tourism product is prepared by individual companies and are offered separately to consumers (tourist/tourist).
The tourism “product” is not the destination, but it is about the experiences of that place and what happens there. – Chris Ryan
Economist M. Sinclair and Mike Stabler define the tourism product as a “composite product involving transport, accommodation, catering, natural resources, entertainment and other facilities and services, such as shops and banks, travel agents and tour operators.”
According to Suswantoro (2007:75) on substantially the understanding of tourism products “is obtained and the overall service felt or enjoyed by tourists since he left his residence to the tourist destination of his choice and to return home where she originally departed”.
Types of Tourism Products
Following figure describes the classification of Tourism Product:
Natural Tourism Product
Man-made tourism product, symbiotic tourism product, event based tourism, site based tourism product.
These are the products connected to the natural environment. Natural environment that constitutes natural resources which is related to area, climate and its settings, and the landscapes. These natural resources are the most important elements in a destination’s attraction. Such as countryside, climate, natural beauty, water, flora and fauna, wildlife, beaches, deserts, islands or any scenic attraction.
Some examples of natural tourism products in India are Marina beach- Chennai, Darjeeling hill station-West Bengal, Islands of Andaman & Nicobar- Andaman & Nicobar, Deserts of Thar-Rajasthan, etc
Something which is not natural, found in the destinations to attract the tourists. These are man-made creations. As per the tourism point of view they are made for pleasure, leisure or business.
Man-made tourism products are further divided into three subtypes:
- Sites and areas of archaeological interest
- Historical buildings and monuments
- Places of historical significance l museums and art galleries
- Political and educational institutions
- Religious institutions
- Fairs and festivals
- Arts and handicrafts
- Folklore l native life and customs
- Amusement and recreation parks
- Sporting events
- Zoos and oceanariums
- Cinemas and theatres
- Night life l cuisines
Examples of Man-made tourism products are Ajanta and Ellora cave-Maharashtra (Cultural), Surajkund Craft Mela-Haryana (Traditional), Essel World-Mumbai, etc
This type of tourism product do not fall in any particular category because they are a blend of nature and man but the core attraction is nature. These are the natural resource that has been converted into a tourism product by maintaining and managing them.
In other words man has taken initiative to preserve the natural aspects of earth and also managed in a way to provide best possible services to the tourists who come for the visit, for example, accommodation, parking facilities, etc. Some examples are National Park or Wildlife Sanctuaries, Flower Festival, Marine Park, Aero and Water Sports, Botanical Garden etc.
In India, there are many national parks like Ranthambhore-Rajasthan, where tigers and many animals are preserved and tourists are given facilities like a jungle safari.
Product Here event is the main source of attraction. Tourist comes to observe and participate in the events. Events are temporary in nature and are often mounted in order to increase the number of tourists to a particular destination.
Some events are for a short time scale while other last for longer days. Sometimes events are mounted in those places where the tourist’s eye usually don’t reach such as unusual exhibitions.
Some examples of event-based tourism product include Camel Polo at Jaisalmer- Rajasthan, Kite flying in Ahmedabad-Gujarat, where tourists also participate and observes. In Snake boat race-Kerela, one can enjoy witnessing it. Short time scale event includes Republic day parade-New Delhi and long days event include Khajuraho dance festival-Madhya Pradesh.
It is a particular site or a place, permanent in nature which is the main source of attraction for the tourists. In India examples are like Taj Mahal, Beaches of Goa, Sunset at Kanyakumari, Temples of Khajuraho, etc.
Characteristics of Tourism Product
Following are the main characteristics of tourism products:
Intangibility
Inseperatability, perishability, heterogeneity, essentially of users presence, complexity in marketing, absence of ownership.
As discussed earlier in this chapter, tourism products are actually the services that are being sold to the tourists, and it’s not the goods. Services can’t be seen, smelled, felt or touched, it can only be experienced. What can be seen is their effect.
For example, a guide’s comments can be heard. A travel agents books a ticket from place A to B. The ticket is just a piece of paper, an entry pass for using the service. An airline provides the service of transportation, comfort and leisure. A thorough evaluation of the service before buying it is therefore impossible and leads customers to use other cues to help them assess the service like the interior of the restaurant, the appearance of the hotel entrance or the behaviour of the receptionist.
A service of a tourism product cannot be separated from the provider of the service. For most services, the producer and the seller are the same people. Services are manufactured and consumed at the same time. In the case of products, consumption takes place after production and often far away from the factory.
In the case of tourism products for example a guide has to be present to explain the attraction. A pilot has to be present to fly a plane. Both service providers and the service user have to be physically present for mutually satisfying the exchange of service. The visitor to a national park cannot experience counter service if the receptionist is not present, nor can the receptionist render the service is the visitor is absent.
The tourism product is highly perishable, which means it cannot be stored. For example, a hotel room or an aeroplane seat that is not sold on a particular day, is a lost sale. If the tourists don’t visit a particular place, the opportunity is lost. If the opportunity is lost, the moment is lost. This adversely affects the tourism business.
The demand has to be managed by the marketer in such a way as to ensure that as little capacity as possible is lost. The problem is unique for the tourism industry. Due to these reason sometimes heavy discount is offered by hotels or transport generating organization.
Services offered by most people are never the same. There is some degree of variability present in almost all types of services. This may be due to the extensive involvement of people in the production of service. This issue is not present when a machine dominates. Depending on the mood, behaviour, working style, efficiency and knowledge of the people variability exist.
For example, all air hostesses cannot provide the same quality service like the other. Yet again the same individual air hostess may not perform the same uniform service both in the morning as well as in the evening.
Even the tour package and the aircraft can’t be consistent of equal standards because an aircraft can de-shape the travelling pleasure into a nightmare and a holiday seaside is ruined by the prolonged rainy spell.
Another reason for variability of service is the involvement of customers in the process of product delivery and consumption system. For example, a musician performing at a program may not perform with uniformity. His performance will depend on the response and appreciation of the audience. Hence service varies from person to person, time to time and from situation to situation.
In travel and tourism businesses, service quality depends on uncontrollable factors and there is no sure way of knowing whether the service delivered matched what was planned or promoted, or what was expected by the customer.
Presence of the user is necessary to avail the service. The customer or the guest has to be personally present on the spot. It can’t be brought to the user. As in the case of other tangible goods, the buyer can avail the service from anywhere or from his home. But in the case of tourism products, it is not at all possible. The tourist has to go to the tourist attraction to experience the tour.
However the marketers here need an in-depth study of users behaviour, tastes, preferences, likes and dislikes so that expectations and realities coincide and satisfaction is made possible.
Tourism product involves complexity in marketing. It requires a lot of effort to convince a buyer. As in the case of travel agents. In order to sell their tour package they need to convince the customer by introducing various facilities, discounts and services. Product demonstration is bit difficult in the case of tourism product.
As in the case of tangible goods like television. As soon as we buy it, we become the owner of it. But this is not the case with tourism products. A tourism product when sold to the customer or tourist, he can only avail the service but can’t be its owner.
For example, while buying a hotel room, while buying a seat in an aircraft or a luxurious train, you can only take the facilities of the service for a certain time. You can’t be its owner for lifelong.
Please Share This Share this content
- Opens in a new window X
- Opens in a new window Facebook
- Opens in a new window Pinterest
- Opens in a new window LinkedIn
- Opens in a new window Reddit
- Opens in a new window WhatsApp
You Might Also Like
Order taking procedure in restaurant | sample procedure, methods, tourism destination, transport system: elements, characteristics, types, modes, international union of official travel organisation (iuoto), tourism in tripura, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
No internet connection.
All search filters on the page have been cleared., your search has been saved..
- Sign in to my profile My Profile
Tourism and Hospitality Marketing: A Global Perspective
- By: Simon Hudson
- Publisher: SAGE Publications Ltd
- Publication year: 2008
- Online pub date: December 20, 2013
- Discipline: Business & Management
- Subject: Tourism, Events & Hospitality Marketing , Hospitality, Travel & Tourism Management
- DOI: https:// doi. org/10.4135/9781446280140
- Keywords: customers , markets/marketing , place marketing , prices , tourism , tourism sector , travelers Show all Show less
- Print ISBN: 9781412946872
- Online ISBN: 9781446280140
- Buy the book icon link
Subject index
Front matter.
- Geographical Index of Cases
- Chapter 1: The Global Tourism Marketing Environment
- Opening Vignette: Disney Expands Global Empire to Hong Kong
- Introduction
- Snapshot: War as a Tourism Attraction in Vietnam
- The Influence of Marketing on Tourism
- Snapshot: Repairing the Image of America
- Marketing Services
- Key Players in the Global Tourism Industry
- Snapshot: Opening the Home of Robert Graves
- Influences on the Tourism Marketing Environment
- Global Spotlight: The Holy Land Experience
- Chapter Summary
- Case Study: The Influence of Politics on Tourism: The Case of Myanmar
- Chapter 2: Consumer Behaviour
- Opening Vignette: Vacations from the Heart: Traveller Philanthropy
- Factors Influencing Consumer Behaviour
- Snapshot: Backpackers with Gold Cards
- Snapshot: Adventurer Annie
- The Buying Process
- Organizational Buyer Behaviour
- Global Trends in Consumer Behaviour
- Global Spotlight: Semester at Sea
- Snapshot: Longing for the Way We Were: Nostalgia Tourism
- Case Study: Rites of Passage: Schoolies Week in Queensland, Australia
- Chapter 3: Developing a Marketing Plan
- Opening Vignette: An Adventure with Bruce Poon Tip
- The Corporate Connection
- Analysis and Forecasting
- Global Spotlight: Targeting the Overweight: Size-friendly Vacations at Freedom Paradise
- Snapshot: Wine for Dudes
- Snapshot: Planning the Growing Chinese Travel Market
- Setting Marketing Goals and Objectives
- Marketing Strategy: Targeting and Positioning
- Snapshot: Positioning ‘Four’ Success: Four Seasons Hotels and Resorts
- Tactics and Action Plans
- Resource Requirements
- Marketing Control
- Communicating the Plan
- Case Study: The Failure of Roots Air
- Chapter 4: Marketing Research
- Opening Vignette: Mystery Shopping Uncovers Directional Selling in the UK
- Applied Research in Tourism and Hospitality
- Snapshot: Global Study Finds Travellers' Needs Not Being Met by the Travel Industry
- Stages in the Research Process
- Research Methodology
- Snapshot: Research in the Food Service Industry
- Snapshot: Measuring the Impact of Captain Corelli's Mandolin on Tourism in Cephalonia
- Global Spotlight: Lack of Research Contributes to EuroDisney Disaster
- Common Research Errors
- Effective Use of Marketing Research in Decision-making
- Case Study: How was the Skiing? Finding the Best Way to Measure Service Quality
- Chapter 5: The Tourism and Hospitality Product
- Opening Vignette: Concorde: A Journey Through the Product Life Cycle
- Product Levels
- Physical Evidence and Servicescape
- Snapshot: The Greatest Briton Ever: The New Churchill Museum in London
- Product Planning
- Global Spotlight: The Coolest Place in Town: Sweden's Icehotel
- Snapshot: Chefs as Brands: The Case of Jamie Oliver
- New Product Development
- Snapshot: Sydney BridgeClimb
- Approaches to New Product Development
- Case Study: Creating an Alpine Winter Experience
- Chapter 6: Pricing
- Opening Vignette: Space Tourism: Priced Out of This World
- Factors Determining Pricing Decisions
- Contributions of Economics to Pricing
- Snapshot: Pricing for the Luxury Market: Burj Al Arab Hotel, Dubai
- Pricing and Positioning
- Snapshot: Low-cost Airlines Take to the Air
- Basic Approaches to Pricing
- Pricing Strategies for New Products
- Other Pricing Techniques
- Global Spotlight: ‘Save Time, Save Money’: Ski by the Hour at Banff Mount Norquay
- Snapshot: Pricing at the Cherry Blossom Festival in Japan
- Strategic and Tactical Pricing
- Tourism and Hospitality Characteristics That Affect Pricing Policy
- Case Study: Safari and a Facelift: The Rise of Medical Tourism
- Chapter 7: Distribution
- Opening Vignette: Making Alliances in South Africa's Game Reserves
- The Nature and Types of Distribution Channels
- Functions of the Distribution System
- Distribution and Physical Location
- Snapshot: Travel Flows in the Ski Industry
- Marketing Intermediaries
- Snapshot: http://Weekendtrips.com
- Global Spotlight: Vocation Vacations
- Channel Conflict and Organization
- Snapshot: Expanding Overseas: Native Tribe Buys Hard Rock Café Chain
- Designing the Distribution System
- Distribution Channel Management
- Case Study: Profiting from Fun: Canadian Mountain Holidays
- Chapter 8: Marketing Communications: The Role of Advertising and Sales Promotions
- Opening Vignette: ‘What Happens in Vegas, Stays in Vegas’
- Marketing Promotion Tools
- The Communication Process
- Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) in Tourism
- Global Spotlight: VisitBritain Leverages Pottermania
- Push and Pull Promotional Strategies
- Snapshot: Carnival Cruise's Holiday Gift Marketing Campaign
- Tourism Advertising
- Snapshot: Advertising to Tourists You Don't Want: Sex Tourism in Brazil
- Snapshot: Promoting Cheddar Caves & Gorge
- Sales Promotions
- Joint Promotions
- Case Study: Club 18–30 Growing Up
- Chapter 9: Marketing Communications: Public Relations, Personal Selling, Direct Marketing, and Word of Mouth
- Opening Vignette: Marketing the Most Spectacular Train Trip in the World
- Roles and Functions of Public Relations
- Snapshot: Kenya's Efforts to Recover from a Crisis
- Public Relations Techniques
- Snapshot: Celebrity Power at Atlantis Resort
- Personal Selling
- Snapshot: Selling Beds at The Westin Edmonton
- Direct Marketing and Direct Response Advertising
- Global Spotlight: Dennis Campbell's Postcard Campaign
- Word of Mouth
- Case Study: Puerto Rico Targets Business Travellers
- Chapter 10: Internet Marketing
- Opening Vignette: Travel Blogs
- Snapshot: The End of the Brochure as We Know It?
- The Use of the Internet in Tourism and Hospitality
- Snapshot: How to Convert Website Hits into Sales
- Global Spotlight: Shatner Still Flying: the Priceline Model
- Snapshot: Why Do Travellers Purchase Online?
- Marketing Research
- Case Study: Where the bloody hell are you? Australia ad creates ‘global online traffic jam’
- Chapter 11: Providing Service Quality Through Internal Marketing
- Opening Vignette: Beyond the Call of Duty
- The Internal Marketing Process
- Snapshot: The Airline with a Sense of Humour: WestJet Airlines
- Snapshot: Internal Marketing at Fairmont Hotels & Resorts
- Delivering Service Quality
- Measuring Service Quality
- Global Spotlight: ‘It's Our Pleasure!’ – Service Excellence at the Sheraton Suites Calgary Eau Claire
- The Behavioural Consequences of Service Quality
- Loyalty and Relationship Marketing
- Snapshot: Travel Rewards Still a Hot Ticket
- Service Recovery
- Case Study: Richard Branson: Driving Service Quality From the Top
- Chapter 12: Destination Marketing
- Opening Vignette: From Prison Cell to Tourist Attraction: Robben Island, Cape Town, South Africa
- International Attractions
- Snapshot: Targeting Turtle-lovers: Praia do Forte in Brazil
- Objectives and Benefits of Destination Marketing
- Snapshot: Singapore Gambling on the Future
- The Role of Destination Marketing Organizations (DMOs)
- Tourism Development
- Destination Branding
- Snapshot: The Incredible India Campaign
- Destination Promotion
- Marketing Events, Festivals and Conferences
- Global Spotlight: The Greatest Outdoor Show on Earth – The Calgary Stampede
- Marketing All-inclusive resorts
- Case Study: Branding New Zealand as Middle Earth
- Chapter 13: Contemporary Issues in Tourism and Hospitality Marketing
- Opening Vignette: Second Life and the Virtual Hotel
- Demographic Trends
- Behavioural Trends
- Snapshot: Torture Tourism? Visit a Gulag in Russia
- Tourism Marketing in the Experiential Economy
- Snapshot: Promoting Destinations Through Film: The Case of the Bahamas
- Responsible Marketing of Tourism
- Global Spotlight: Machu Picchu in Peru Limits Access to Tourists
- Cause-related Marketing in Tourism
- Marketing Sport and Adventure Tourism
- Snapshot: Destination Marathoners
- Marketing Tourism in Times of Crisis
- Case Study: Marketing After a Crisis: Recovering from the Tsunami in Thailand
Back Matter
Sign in to access this content, get a 30 day free trial, more like this, sage recommends.
We found other relevant content for you on other Sage platforms.
Have you created a personal profile? Login or create a profile so that you can save clips, playlists and searches
- Sign in/register
Navigating away from this page will delete your results
Please save your results to "My Self-Assessments" in your profile before navigating away from this page.
Sign in to my profile
Please sign into your institution before accessing your profile
Sign up for a free trial and experience all Sage Learning Resources have to offer.
You must have a valid academic email address to sign up.
Get off-campus access
- View or download all content my institution has access to.
Sign up for a free trial and experience all Sage Learning Resources has to offer.
- view my profile
- view my lists
Promoting and Advertising Tourism and Hospitality Products
- First Online: 09 May 2021
Cite this chapter

- Richard George 2
3032 Accesses
1 Citations
This chapter discusses the communication methods that are used to promote tourism and hospitality offerings. Marketers must communicate these offerings to consumers (including the travel trade). Promotion is used to communicate information about offerings to target markets. The chapter begins by explaining the relationship between promotion and marketing communications. Next, each of the seven stages of the promotional campaign, from determining the marketing objectives through to assessing the impact of the promotional techniques are discussed. Further, this chapter presents the concepts of integrated marketing communications (which involves the use of the promotional tools in combination with each other), convergence, and below-, above-, and through-the-line marketing. In the second half of the chapter, the role of advertising, which is considered to be the most dominant tool of the promotions mix is discussed. Major advertising decisions such as assigning objectives and a budget, designing, and evaluating an advertisement, and selecting various types of media are considered. Finally, the role of media agencies in tourism and hospitality marketing is discussed. The chapter’s in-depth case study examines the principles of marketing communication and advertising in the context of Matchbox Hostel , a backpacker hostel located in Singapore.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Baines, P., Fill, C., Rosengren, S., & Antonetti, P. (2019). Marketing (5th ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Google Scholar
Fill, C. (2002). Marketing communications: Contexts, strategies, and applications (3rd ed.). Harlow, Essex: FT/Prentice-Hall.
Gronroos, C. (2004). The relationship marketing process: Communication, interaction, dialogue, value. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 19 (2), 99–103.
Article Google Scholar
Hilbert, M. (2015). Digital technology and social change. Retrieved from https://canvas.instructure.com/courses/949415 [18 July 2018].
Kitchen, P., & Burgmann, I. (2015). Integrated marketing communications: Making it work at a strategic level. Journal of Business Strategy, 36 , 34–39.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (2017). Principles of marketing (17th ed.). London: Pearson Education.
Kotler, P., Bowen, J., Makens, J., & Baloglu, S. (2017). Marketing for Hospitality and Tourism (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Lavidge, R., & Steiner, G. (1961). A model for predictive measurements of advertising effectiveness. Journal of Marketing , 2559–2562.
McCabe, S. (2012). Marketing communications in tourism and hospitality: Concept, strategies and cases . Abingdon: Routledge.
Middleton, V., Fyall, A., Morgan, M., & Ranchhod, A. (2009). Marketing in travel and tourism (4th ed). Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Pike, S. (2018). Tourism marketing for small businesses . Oxford: Goodfellow Publishers.
Richard, J., & Curran, C. (2002). Oracles on advertising: Searching for a definition. Journal of Advertising, 31 (2), 63–77.
Schramm, W. (1954). How communication works. In W. Schramm (Ed.), The process and effects of communication (pp. 3–426). Urbana, Illinois: University of Illinois Press.
Shannon, C. & Weaver, W. (1962). The mathematical theory of communication . Urbana, IL.: University of Illinois.
Stokes, R. (2018). eMarketing: The essential guide to online marketing (6th ed.). Cape Town: Quirk eMarketing.
Suggett, P. (2019). Steps to making a great billboard ad . https://www.thebalancecareers.com/six-steps-to-making-a-great-billboard-ad-38479
Sweney, M. (2018). Social media ad spend to overtake TV’s in spite of Facebook woes. The Guardian . Monday 2 April, p. 13.
Vizard, S. (2018). Marketing budget slows as marketers face challenging 12 months . https://www.marketingweek.com/2018/01/17/marketing-budget-growth-slows-ipa-bellwether/ [12 June 2018].
Further Reading
Luxton, S., Reid, M., & Mavondo, F. (2015). Integrated marketing communication capability and brand performance. Journal of Advertising, 44 (1), 37–46.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
ICON College of Technology and Management/Falmouth University, London, UK
Richard George
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
1 Electronic Supplementary Material
(pptx 4696 kb), rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
George, R. (2021). Promoting and Advertising Tourism and Hospitality Products. In: Marketing Tourism and Hospitality. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64111-5_10
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64111-5_10
Published : 09 May 2021
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-64110-8
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-64111-5
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- Market information
- Develop your tourism product
- Share this on:
How to get started developing your tourism product
Whether you are offering guided tours, boat rentals, accommodation or provide river cruises, you are offering services to your customers. For today’s tourists, just a service is not enough. They seek experiences, often even experiences that contribute to their quality of life. This document offers you guidelines to identify your customers’ needs and to develop innovative products, services or experiences that really matter to them.
Contents of this page
- Why develop your product with this method?
- This is what you need before you start
- Get inspired by your (potential) customer (Step 1)
- Make a persona for each type of customer (Step 2)
- Identify the core needs of the customers and the key opportunity areas for your business (Step 3)
- Develop a multitude of ideas for solutions, or new products, services or experiences (Step 4)
- Turn your best ideas into prototypes that can be tested and improved step by step (Step 5)
- Test your prototypes in practice (Step 6)
1. Why develop your product with this method?
The needs of tourists from Europe have evolved over the past few decades. Current tourists are looking for quality service and experiences that really matter to them. To offer quality and experiences that matter to your customers, you need to know them very well, personally. What quality means for some may be different from what it means to others. And an experience that is life-changing for some, may be dull to others. This report teaches you how to get in touch with your customers, how to learn what they really need to boost their quality of life, and how you can design products, services or experiences that really matter. The nice thing is that if you succeed, your customers will share their experiences with their friends and followers, also on social media. In other words: they will promote your product to others. For free!
The current coronavirus crisis has put international travel under pressure . In many countries, tourist arrivals have nearly dropped to zero. It is likely that international tourism will be affected by the COVID-19 crisis for the next couple of years. Several scenarios are possible. The frequent holidays made by Europeans to faraway destinations may decrease and this may turn into less frequent and longer holidays closer to home. The battle for tourist visits may become fiercer. The attention for sustainability may also increase. Europeans might be willing to travel longer distances, but only for a very good reason. To tempt potential tourists from Europe to come to your country, your region or your business, you need to stand out, to understand the traveller well and be super-innovative – more than ever. Amazing stories and experiences may become even more important. As will issues of safety, security and assisting tourists in returning to their home countries.
- Read more on this in our study on how to respond to COVID-19 . This study offers insight into actions you should take immediately, while also providing guidance on long-term decisions.
The method described in this report is based on the principles of design thinking. It has been employed internationally in all kinds of businesses. To mention a few examples in tourism:
- Destinations like the Bahamas (an example is the One-Stop Online Booking and Immigration Card ).
- Design for All , also referred to as ‘universal design’, to allow access for people with disabilities. You can read more about this in this thesis .
- Hotels. For example Hyatt Hotels has developed various prototype hotels around the world, which are free from regulation. Another example is The next-generation hotel experience , getting the details right to improve travellers’ stays, and designing a modern work experience for business travellers .
- Visitor attractions, like improving the tourist experience of the Polar Bear Society , a visitor attraction in Norway, or bringing Tourists to a hidden coastal gem .
- Travel and transport. Examples are pioneering a car-sharing service and developing a customer strategy for public transport in Oslo.
- Restaurants, like creating a fresh and modern take on the Indian culinary experience .
- Organisation and development. An example is turning a historic music college into a collaborative learning platform .
- Tourism-related services. An example is the mobile visitor centre in Saint Paul, Minnesota. Another example is to ‘design of waste out of the food system’, taking place in a collaboration between hotels, food banks, foundations, and entrepreneurs to fight food waste .
2. This is what you need before you start
The procedure described below is not difficult. To follow the steps, it helps to have a few basic tools – but only if you already have them) – since it is the idea of how you are doing this that is important .
- Lots of sticky notes (Post-its)
- Sheets of flipchart paper
In product development, we try to find a match between the needs of the European market and any of your local situation and business resources that might entail certain limitations. The following tips are related to this.
- Where possible, engage your customers to build a personal relationship and to get to know them well.
- If you find it difficult to engage with customers from a different culture or find it difficult to understand them, try to work with local partners who can serve as intermediaries (such as tour operators in source countries) with the guests or act as interpreter.
- Involve others working in your business or in other businesses in the community where you live, people working in education, or other people with an open and positive mind. This will make it more fun and rewarding. It will also contribute to the quality of the work.
- To work through the process described below, you may want to ask support from a local CBI coach and or an intern from a university abroad, for example via SAVE tourism .
Below, the steps are described to help you to develop innovative products and services for new and existing customers. Staying tuned with the market is an ongoing process. The outcomes of each step are illustrated in Figure 1.
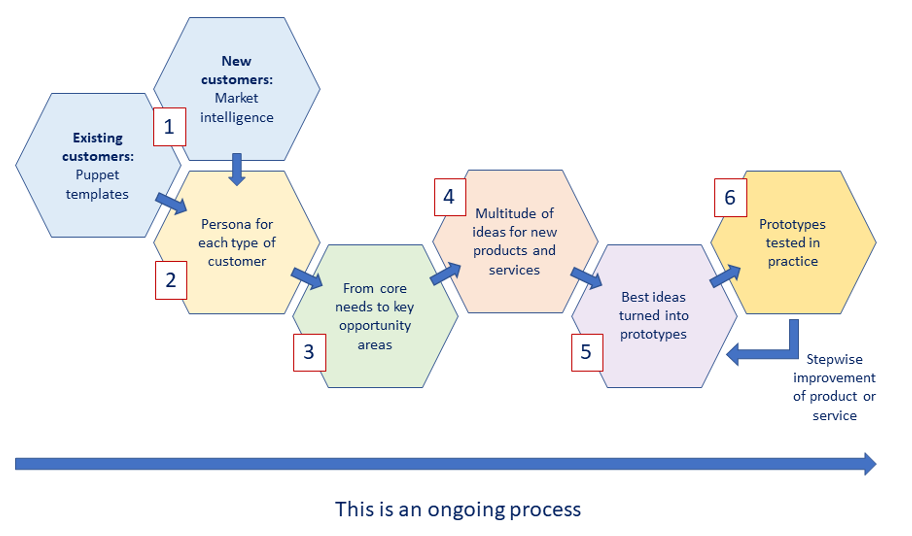
3. Get inspired by your (potential) customer (Step 1)
You can only create meaningful products, services and experiences for your customers if you truly understand them. So try to understand the situations and experiences that are or might be meaningful to them. If you do not have any customers yet, or are looking for new customers, you need to get your inspiration from existing market intelligence (step 1a). If you already have customers, you can use these customers as a source of inspiration (step 1b).

a. Get inspired by potential customers
The largest share of potential customers doesn’t know you or your product offering, or perhaps even the destination. So you have to draw their attention by offering products and services that matter. What do you need to do to make a start?
- Get access to market intelligence reports of the European market. Subscribe to free newsletters or blogs of market intelligence institutions, such as UNWTO , WTTC , Global Sustainable Tourism Council or IATA . Read the annual UNWTO publications , such as Tourism Highlights and World Tourism Barometer .
- Review and read the market intelligence information provided by CBI . This webpage gives access to a CBI trend report and promising market segments and target groups on the European market.
- These sources will help you to identify important (emerging) trends and markets in Europe on a regular basis.
- Try to identify a few target groups or niches that may feel attracted to your business.
b. Get inspired by existing customers
When customers make use of your service business they could also inspire you to make new products. This means that you would need to involve them in the development process. Do not ask them what they want (as they may not know) with a questionnaire, but try to get an idea of the needs they have in a different way.
There are three nice alternative methods you could use, although there are other methods available as well, such as the ones in Ideo’s free Human Centered Design Toolkit . The first time you do so, it might make you feel uneasy to approach a customer. However, always remember that communication with them is key in developing a better product or service.
- It is your duty as an entrepreneur to look after your customers. So you can see it as part of your job to observe your customers during different phases of their customer journey and to learn to understand this customer journey through their eyes. Such observation should be done discreetly and quietly, so as not to disturb or annoy them while enjoying their holiday or business trip. It gives you insights into what they think, what they do, how they interact with others, and what they dream and wish for. While you observe your customers, you can also make notes. Afterwards, you need to find a moment that suits your customer to share your observations in an informal setting, and ask questions about things you did not expect, did not understand, or what they found appropriate. Again, make notes!
- You may also ask your customers whether they would like to help you with improving your services. Ask your customers to take photographs . You could also ask your customers to document their customer journey with a camera and to take pictures of what they consider appropriate products or services. When they give you the pictures, ask them whether there is a suitable moment for them to share some thoughts about these. When you discuss them, do not forget to make notes. Do not insist if a person does not want to cooperate, but try others instead.
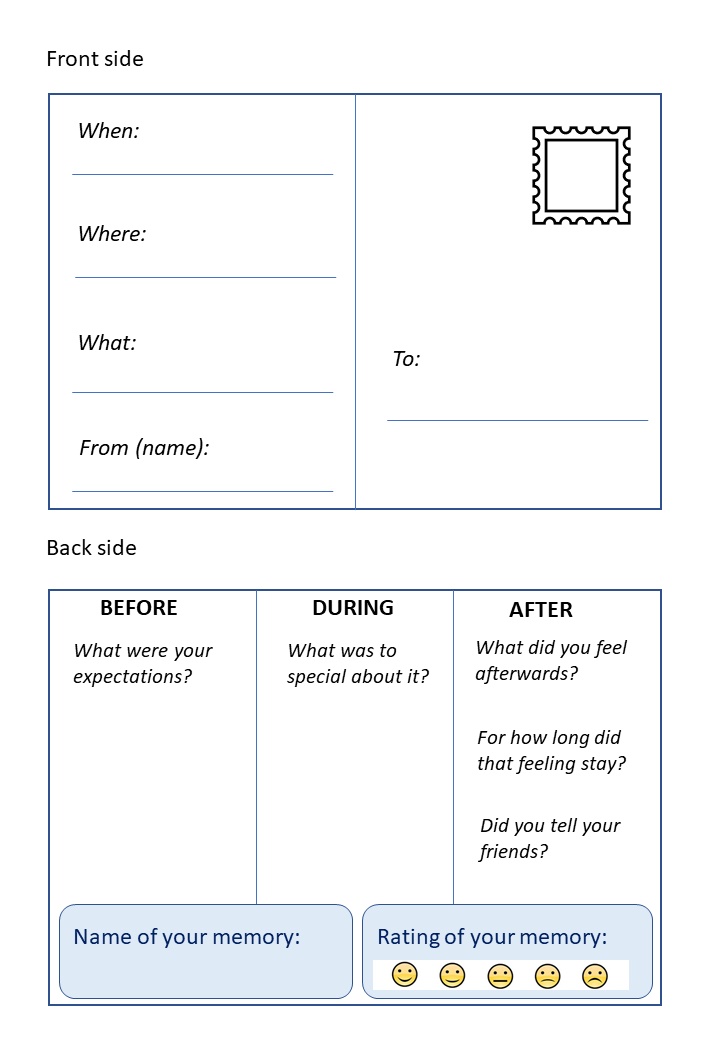
- The third approach also requires asking your customers for help in making your services more appealing to them. Ask your customers whether they are willing to take a number of ‘memory cards’ along with them while using your product or service. These cards have to be printed by you beforehand in a kind of postcard format (such as in Figure 2). Ask your customers to fill in a card each time they experience something they did not expect, or which they find very positive or negative. Ask them to return the cards to you by the end of each day or when they leave. If they are open to doing so, ask them whether they have time to share their thoughts with you. If so, be sure you make notes.
- Download and make use of the print version of the ‘memory card as shown in Figure 2.
A useful way to describe an individual customer is by using a puppet template. A puppet template is a simple picture of a single customer surrounded by clouds, words bubbles and icons, such as illustrated in Figure 3. Ideally you would make a puppet template together with a customer. This shows that you are open and willing to build a personal relationship with them. A good moment is when you have the chat about the observations, the photographs that they took, or the memory cards that they filled in. During this conversation you could also talk about the person’s age, where they come from, their work, what they do in their daily life, their main interests in life, their worries, their wishes and dreams, or their preferences in tourism. This generates a lot of relevant background information. Take notes! Each customer you talk with gets a separate puppet template.
You will end up with a number of puppet templates. Review the puppet templates and take a closer look at each one. What do you see? You will probably discover that some of the templates are similar to one another. This means that you have already started to understand your customers a little better! Now, group together the puppet templates that show similarities. Each group represents a type of tourist that makes use of your business .
- Involve people in your business or community to assist you with understanding the language or the culture of the customer.
- They may help you with making puppet templates and with grouping the templates into types of tourists.
- Download and use of the print version of the puppet template shown in Figure 3.

4. Make a persona for each type of customer (Step 2)
In the previous step, you grouped the puppet templates with similarities together. Each group represents a type of tourist who could be attracted to your business. Now the challenge is to turn each type of tourist into a market description. You will do this in the form of a so-called persona: one persona for each type of tourist. You might end up with 4-8 personas. You may need to go back to the market intelligence and the puppet templates in step 1 for detailed information. A persona describes each tourist profile, point for point. It would be nice to add a quote on each persona to bring them to life.
A persona includes:
- List of ages & countries or origin
- List of work and ambitions
- Details about personal lives
- List of main interests
- List of wishes, preferences and dreams
- You may want to add photographs (for example from magazines) and quotes that characterise the type of customer
- Key locations they went to
- Alone? Or with whom?
- What did they like and what not?
- Which emotions did they show?
- Key issues, needs, dilemma’s
Most organisations have their own template. The Interacting Design Foundation explains the use of personas in a video . In the figures below, you will find a few examples with different levels of detail and a different style. You can put each persona on a different flipchart sheet.

5. Identify the core needs of the customers and the key opportunity areas for your business (Step 3)
Now you need to identify the most prominent needs, hurdles, issues or disappointments of each type of customer (persona).
- What would be remarkable events and experiences for that persona? What were remarkable events and experiences for that persona?
- What would be stunning likes for that persona? What were stunning likes for that persona?
- What would be striking issues, hurdles, disappointments, wishes or needs for that persona? What were striking issues, hurdles, disappointments, wishes or needs for that persona?
- You may need to go back to the market intelligence and puppet templates in step 1 for possible answers.
- Write each possible answer on a separate sticky note no matter from which persona. Try to get at least 25 sticky notes in total. More would be even better.
- When you are finished, group the Post-its together into areas of which you think they could have a positive impact on your customers’ experiences. Label each grouping of Post-its with a short telegram-style sentence that identifies the impact area . You could write these labels on a Post-it. A label could be, for example: “customers need more personal attention during the excursion”, “customers like to enjoy local cuisine”, or “customers need to be able to connect online”.
- Finally, turn each label into a positive opportunity for your business, also known as an opportunity area , and write it on another Post-it that you put at the top of the label. The header could be for example: “much personal attention during excursion”, “provide local cuisine to the customer”, “adequate Wi-Fi network”.
- Try to do this step with your team or with people from the community.
Now you have created opportunity areas for your business! It would be great if you were able to end up with anywhere between two to five such opportunity areas.
6. Develop a multitude of ideas for solutions, or new products, services or experiences (Step 4)
During the previous steps you started with collecting a lot of information that, step by step, you worked into just a few opportunity areas for your business. Now we will try to generate ideas for new products, services or experiences that matter to your customers for each opportunity area. Ideally, you should take this step together with colleagues in your business (not just senior staff!). If you think it is outside the range of your core business, you may also want to involve other businesses in your community.
For a long-term benefit, you first need lots of ideas to get a single good one. This one idea should be innovative and really different from the others. It might be a completely new solution to a problem customers did not even know they had. Do not be satisfied with an obvious solution!
How does it work?
Brainstorm for each opportunity area
Write out each idea on separate Post-its
Sort and group/cluster the ideas that you wrote down
- Brainstorm for each opportunity area that you created in the previous step. Come up with as many ideas as possible. Try to think of weird solutions, products, services or experiences. Never worry whether ideas are right, wrong, absurd or obvious. That hampers your creative flow of thoughts. If you do it with your team you might end up with dozens of ideas.
- Write each idea on a separate Post-it . If it helps you to understand it better, you can make a drawing of what you have in mind.
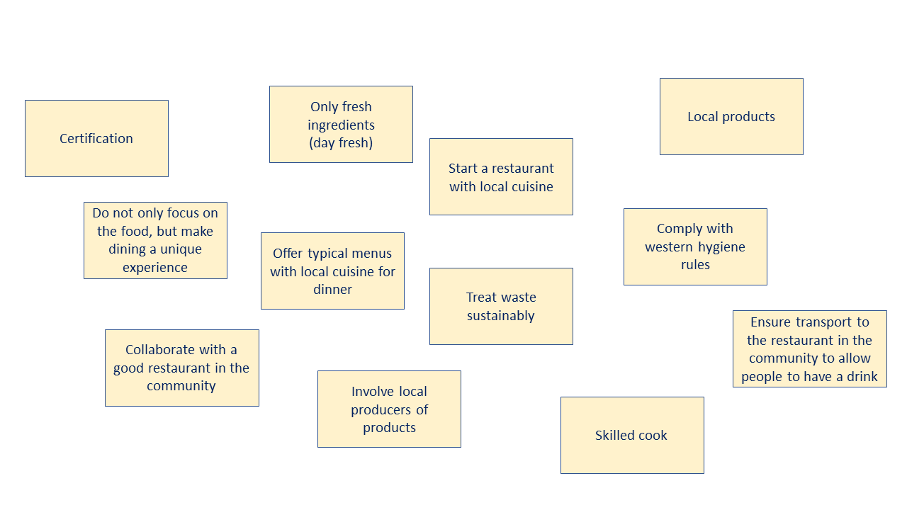
- Next, sort and group the ideas that you wrote down . Put the bad ideas to the side. Group the ideas that go well together into clusters. Give each cluster a label that tells you what the overarching idea is that the cluster is about. Brainstorming for the opportunity area “provide local cuisine to the customer” could lead to the following labels (Figure 5): start our own restaurant; authentic design of the restaurant; involve local farmers; kitchen staff recruitment and training programme; sustainable waste treatment.
- If you take a closer look at the clusters with the labels, you might get ideas about more details. You can write these down on additional Post-its. For example, once you have made a cluster with the label ‘waste treatment’, you may add other ideas: the name of a certification programme you would like to comply with; how you want to adhere to the certification programme; aspects of how you organise the waste flow in the restaurant and kitchen; communication of the certification with the customers, etc. So the labels give you inspiration to add to the clusters to make these more specific.
You will end up with a shortlist of your best ideas for solutions: new products, new services or new experiences. It is a good idea to show the ideas to some of your customers for feedback. In the case of Figure 6, you would end up with the following products and services: authentically designed restaurant (product); strengthened involvement with the community (service and products); collaboration with regional/national educational institutions to train qualified kitchen staff to be skilled at cooking, but to also always pay attention to hygiene rules; a certified waste treatment service.
7. Turn your best ideas into prototypes that can be tested and improved step by step (Step 5)
Now is the time to create a first design for the ideas for new products or services that you have created. We call this a prototype . If you make such a detailed design, this will help you to understand your idea better, but also to determine whether you have the resources to implement it, and whether there are any unforeseen challenges or consequences. These things are important for long-term success.
- Select the ideas that could upgrade one of your business’s current products or services or be integrated with such a product or service. These ideas will probably be the easiest to develop because they fit best with your everyday work.
- For each of the products or services that you selected, make a detailed description of how you want it to be designed. We call this a prototype of your product or service.
How do you make a prototype?
- Take a large piece of paper, such as a flipchart sheet, for each of your innovative ideas.
- Draw a cross on each sheet in order to divide it into four quarters. Each quarter is dedicated to one building block of your product or service idea, as illustrated in Figure 5.
- Describe and visualise what each building block would look like according to you. Put your description into a few sentences. Also use a few sketches, drawings and/or cartoons. You can use simple shapes, because the quality of the sketch is not so important at this stage.
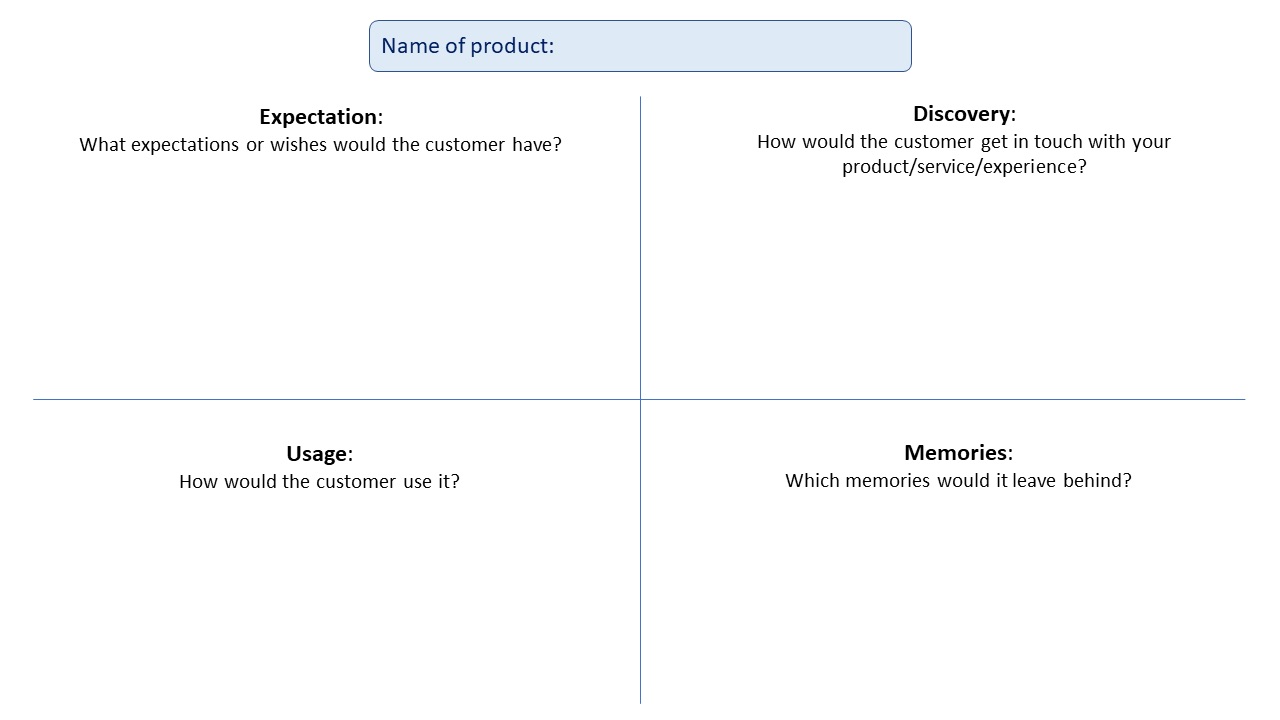
- Start with the name.
- Write down the persona(s) who would feel attracted to the product because it matches their needs. You need to go back to the steps you completed earlier.
- Write down an appealing story about your new product or service that can be communicated with the European market. If you have a website, you can put the name and story of your new product/service there.

Each sheet that you have finished is a prototype of the ideas that you have created for innovations for your business. These are ready to be tested, like the prototype of a new car or airplane that is tested in a wind tunnel.
Never worry that your prototype is incomplete or indistinguishable from the final product that you have in mind. This will be dealt with later in the process.
8. Test your prototypes in practice (Step 6)
The final step is to put your innovative idea into practice and offer it to your customers as you have described and visualised it in your prototype. It is a process of learning by doing. You get feedback from your customers on what worked and what did not. Based on this feedback, you then create a new and improved version of your product, service or experience. Then you once again get feedback and make more improvements. In this way, your product or service will improve step by step.
- Do not expect immediate success but accept that you can make mistakes now that otherwise would cost you a lot of money later on.
- See it as a learning process. Be open to the feedback and do not defend your prototype if the users are less positive than you expected. Try to get as much feedback and suggestions for improvement as possible.
- Try to put some speed and efficiency in this phase. This will help you with moving quickly from prototype to putting it to the test, to gathering feedback, and then to making a better version of your product or service.
- Never forget that new trends and new markets will arise. This means that your customer and the needs of your customers may change over the years. This is why you need to restart at step 1 every few years to stay tuned to the needs of the market.
This study was carried out on behalf of CBI by Molgo and ETFI .
Please review our market information disclaimer .
Enter search terms to find market research
Do you have questions about this research?
Ask your question
Webinar recording
29 September 2020
Related research
- What is the demand for outbound tourism on the European market?
- What trends offer opportunities or pose threats on the European outbound tourism market?
- What are the requirements for tourism services in the European market?
- (opens in a new tab) X
- (opens in a new tab) Facebook
- (opens in a new tab) LinkedIn
How do travel and tourism distribution channels work?

By Kevin Tjoe — 29 Nov 2021
tourism distribution channels
Updated January 2023 – A tourism distribution channel refers to the stakeholders and methods involved in taking a tourism product from the supplier to the consumer. Typically, the chain of distribution in tourism refers to the businesses and platforms involved in selling, distributing, and bundling tourism products. However, more components are involved across the entire distribution chain, including suppliers, wholesalers, resellers, and consumers.
By aligning your business with existing distribution channels, you connect with important stakeholders in the industry. This creates more efficiency in your marketing efforts and ultimately grows your tourism and activity business.
What is a distribution channel?

Tourism distribution channels are the avenues tourism products and services are made accessible to consumers. Typically, tourism products are sold directly by the primary provider or through a series of intermediaries. If brokers or travel wholesalers are involved, this is called indirect distribution. Consumers can access these products via various mediums, including traditional channels such as travel agents, government bodies such as information centers, and even other tour and activity operators .
How it works
While direct bookings may still account for a large part of business, branching out through additional distribution channels can help you to maximize your brand exposure, reduce risk and ultimately boost your bookings. Many distribution channels will have access to much larger marketing spend or broader customer bases. This can provide you with access to more exposure and quality bookings.
Typically speaking you’ll provide your availabilities to them, and they’ll, in turn, bring in bookings at a pre-agreed commission rate.
The chain of distribution
The chain of distribution in tourism refers to the businesses and platforms involved in selling, distributing, and bundling tourism products. This process begins with the primary tour and activity provider all the way to the end consumers experiencing it.
Generally, there are four steps to the distribution chain:
1. Suppliers/principals
2. Wholesales
3. Resellers
4. End consumers
The distribution chain for a particular product can go through all of the steps depending on its distribution channel. For example, direct distribution won’t require wholesalers or resellers, as suppliers sell their products directly to consumers, whereas indirect distribution requires intermediaries.
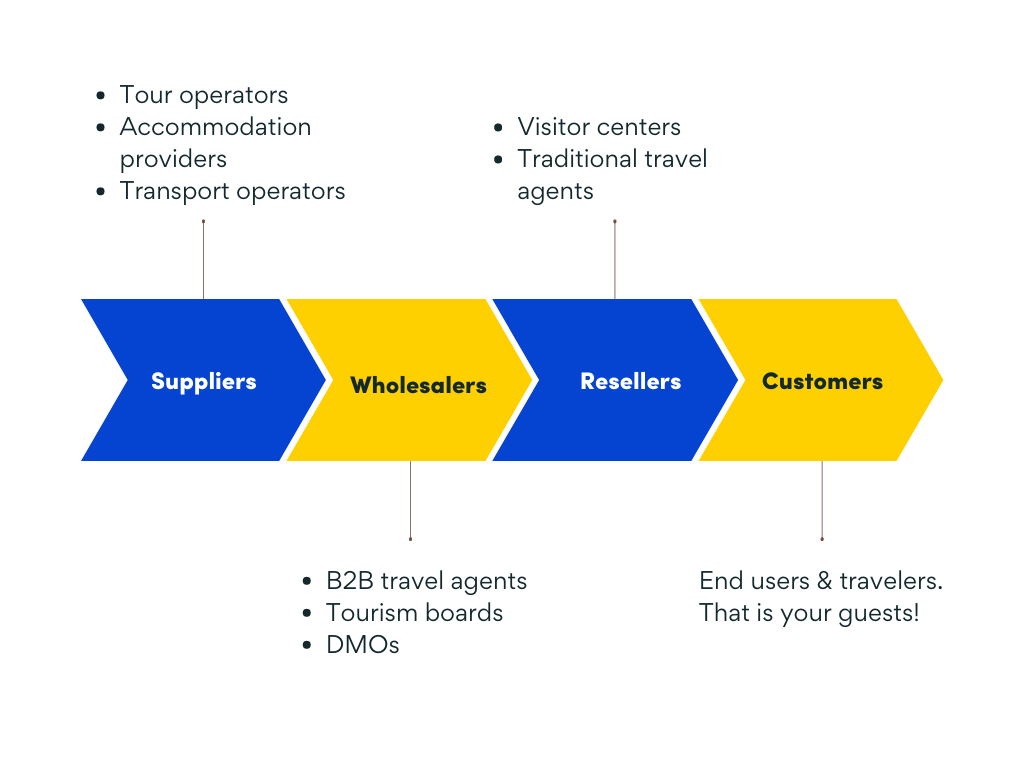
Suppliers or principals include the primary providers across accommodation, transportation and car hire companies, attractions, and experiences. Examples include hotels, Airbnb hosts, airlines, and the attractions such as the Empire State Building.
Wholesalers
Wholesalers develop packages of travel products for retailers to sell on, though in some cases they may actually sell directly to the consumer. These packages or itineraries might include tours, activities, accommodation, transport, and/or travel insurance.
Wholesalers can include:
- Destination Management Organisations (DMOs) or inbound tour operators, such as government tourism boards or tourism authorities
- Global Distribution Systems (GDSs), are used by retailers such as OTAs to easily see an inventory of availability from tourism operators.
Resellers purchase and bundle experiences to be sold directly to the consumer. A common example includes traditional travel agents, which create personalized travel packages. However, online travel agents (OTAs) such as Expedia and Tripadvisor are more commonly used these days. They provide accessibility to a range of tourism products such as airline tickets, hotel bookings, tours and activities, and more.
Consumers are the most critical component of the distribution chain. That is because they are the end user of the product. The choices and decisions consumers make have a huge impact on the rest of the distribution chain. Trends in consumer behavior, or individual decisions all influence how tourism products are marketed and sold.
Advantages of tourism distribution channels

Broadening your distribution channels involve heaps of advantages. Here are the top five:
Connectivity
By aligning your tour and activity business with the broader industry, you can connect with important stakeholders across every step of the tourism distribution chain. Forming strategic partnerships with resellers and tourism platforms enables you to access a broader customer base. This provides you with a greater opportunity to increase your sales.
Generating 100% of your revenue via direct marketing requires a great deal of investment in time and money. Existing distribution channels generally have larger marketing budgets that they can spend to attract more customers.
Typically, as the supplier, you’d only pay a fee when a booking has been made via their channel – making your marketing and sales costs predictable. This means you gain additional resources to expend on other areas of your business, such as improving your customer experience.
Flexibility
Given the wide array of potential partners, you have the freedom and flexibility to test and experiment with different methods of promoting your business. Plus, it’s more convenient for your customers to book your services through an array of trusted partners. This helps to increase customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Transparency
Utilizing existing distribution channels can make the entire booking process more transparent for both you and the end consumer. On the tour operator side, it provides you with a clearer understanding of your customer behavior and adjusts your marketing strategies for better outcomes. And on the customer side, information such as reviews displayed on your profile allows them to create informed decisions before choosing to book your services.
Accessibility
Promoting your tourism products via numerous distribution channels means that your customers can book your services where they like; when they like. Furthermore, your products and services will be found across multiple avenues – enabling a wider array of customers to book with you. In fact, operators are using an average of 14 distribution channels according to Arival’s Operator Insights 2021-2022 report.
What are the main types of tourism distribution channels?

There are many ways to get in front of customers, even more so since the rise of digital channels. From travel agents to mobile apps, tourism suppliers have never had more choices regarding promoting their products and services. There are four main distribution channel types. These include:
Traditional channels
Traditional distribution channels often refer to real-world marketing channels separate from online and mobile experiences. Indirect traditional distribution channels can include travel distribution services such as travel agents, tourism information centers, flyers and print/ digital brochures , promotional marketing services, and tour operators . Depending on your products and services, wholesalers can also make up part of your business’ traditional distribution channel.
Online channels
In recent years, online travel agencies (OTAs) have dominated the tourism industry. These online experiences allow users to plan, book, and pay for personalized travel plans through an easy-to-use centralized platform. Often flights, hotel bookings, car hire , and local experiences can be bundled and purchased through a single site, making the process convenient and intuitive. These platforms can also be cheaper due to the relatively low cost of maintaining a website over a brick-and-mortar travel agency.
Mobile channels
Like online channels, mobile distribution channels rely on digital platforms, such as apps, to promote and sell tourism products. Many popular mobile apps which centralize the tourism buying experience have cropped up in recent years. In addition, airlines, hotels, and other major suppliers have begun developing apps to improve customer loyalty and engagement. Other forms of mobile marketing can include SMS marketing, mobile advertising, and cold calling.
Direct channels
Direct marketing and sales channels include anything your business has direct control over and does not involve an intermediary. This type of marketing can occur through traditional, online, and mobile mediums. For example, direct online channels can include your website, direct bookings via a booking system, online chat assistance, and your social media accounts.
While direct marketing efforts via mobile can consist of sending promotional text messages to previous customers, cold calling potential customers, and sending personalized email marketing messages . More traditional measures may include brochures and flyers, a storefront, and salespeople.
Choosing the right tourism distribution channels
As a tour company, it’s essential to understand which distribution channels will achieve the most significant results for your business. While trial and error can bring results over the long run, understanding what makes a channel right for your business can accelerate your path to success.

Identify target market
To understand whether online or offline marketing, direct or indirect distribution, or mobile versus online platforms are best for your business, you need to understand your customers.
Demographics such as age, country of origin, the number of travelers in a party, and the number of children arriving can greatly impact how you communicate and effectively sell your services. For example, an older demographic may be more likely to use traditional channels such as a travel agent, while a young family might be found via online and social media . First, check over your previous customers and try to pull out any obvious trends amongst your clientele, then research which channels best suit your audience.
Research channels
It’s important to research which channels are available to promote your services. But also, it’s essential to understand the reputation of your potential strategic partners. When engaging in indirect marketing, you are aligning your brand with your distributors, so choosing platforms and businesses which align with your values is important. It’s also essential to understand the costs and benefits of each channel and make informed decisions based on what will work for your business.
Evaluate costs and benefits
Each platform and distribution channel will have different pricing models. Some may charge a flat fee for promotional services, others may purchase and resell your services, while others may charge a fee when you receive a booking. It’s essential to understand what level of return you can expect. If you are starting out, finding performance-based pricing options will allow you to pay as you go. Alternatively, flat fee services can sometimes provide a higher return as your budget can go directly to marketing spend.
Track performance
Once you choose one or more channels to distribute your services, ensure you track the performance versus how much it costs to attain them. By understanding the performance of your partnership, it enables you to eliminate ineffective channels and double down on your marketing efforts, thus, cutting you costs.
How can you manage all distribution channels easily?
It can take a lot of time to form and manage strategic partnerships with multiple resellers. Luckily, technology is here to help. A channel manager such as Rezdy Channel Manager can be accessed regardless of your booking system or size of business, and makes it simple to negotiate agreements, manage inventory, rates and manage commissions with a vast range of resellers, from local visitor centers to the big-name OTAs. Live availability of your tours, activities or attractions are visible from one dashboard, dropping the risk of pesky double bookings as well.
You can access the broadest reach of resellers in the industry, connect with desired resellers and easily distribute rates and availability in real-time. Rezdy is integrated with a number of alternative reservation systems and is continuously adding more, providing suppliers access to channel management tools, directly from their existing system. Suppliers with a custom built booking system can connect with Rezdy Channel Manager as well. For Rezdy booking software customers, channel management is included.
Find out more about how Rezdy’s channel management platform can support your business .
Ready to join the thousands of Rezdy customers that managed to grow their bookings by over 25% in 2022? Book a free channel manager demo with a product specialist to see how our products can fit the needs of your tour business. If you are interested in Rezdy’s booking software that includes channel management, you can start a free 21-day trail trial.
If you enjoyed this article, be sure to sign up to receive the Rezdy newsletter , a valuable resource for those who want to stay up-to-date on the latest industry happenings.
Want to know more about reseller commission rates? Read our guide to industry standard commission rates
Broaden your distribution channels with Rezdy
Enjoy 21 days to take a look around and see if we are a good fit for your business.
No obligations, no catches, no limits, nada
Distribution

eBook: Guide to growing your tourism business through distribution & channel management tools

How to navigate API connections with resellers

Case Study: Wendella Tours & Cruises

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 8. Services Marketing
8.5 Reaching the Consumer
Marketers have more choices than ever when it comes to broadcasting their message to consumers. Potential travellers and guests will respond, in varying degrees, to traditional channels and emerging online communications tools. There are many choices in marketing and communication channels, each with strengths and weaknesses. Determining the right mix, frequency, and message depends heavily on establishing objectives, completing research, performing a situational analysis, and creating a positioning approach (Morrison, 2010). Let’s take a closer look at communications channels that may form part of the marketing mix.
Traditional Channels
Mass media is best described as the use of channels that reach very large markets. Examples include national newspapers and radio or television advertising. The immediate advantage of using mass media is the ability to reach multiple target markets in significant numbers. Disadvantages include the high expense and difficulty in effective target marketing and measuring return.

Out-Of-Home (OOH)
Out-of-home (OOH ) channels refer to four major categories: billboards, transit, alternative outdoor, and street furniture. OOH advertising plays an important role in the tourism and hospitality industry as it provides an opportunity to inform travellers in unfamiliar territory. Transit advertising includes airports, rail, and taxi displays. Alternative outdoor refers to arenas, stadiums, and digital media. Street furniture includes bus shelters, kiosks, and shopping malls.
Print Media
Print media includes newspapers, magazines, journals, and directories. There is an increased trend away from traditional purchased print advertising toward editorial features, as these are more trusted by consumers. A print ad and an editorial feature created together is known as an advertorial .
Spotlight On: Beattie Tartan
In 2017, Britain’s Beattie Communications Group merged with Canada’s No. 1 travel public relations firm, the Tartan Group, to become one of the world’s most successful integrated communications consultancies, serving tourism and hospitality clients including Clayoquot Wilderness Resort, Harmony Hotel, Inn at Laurel Point, and Hotel Zed. The staff have extensive experience working in the industry, and the organization has relationships with multiple tourism associations and press groups. For more information, visit the Beattie Tartan Website .
Online Channels
As discussed in Chapter 7 , the internet is nearly twice as important as travel agents as an information source for travel (Deloitte, 2015). There are an estimated 4.5 billion people around the globe with internet access, and social media has become truly integrated into the travel and hospitality industry. TripAdvisor and similar sites have become the customer’s first point of connection with tourism and hospitality products and experiences. This can be both an opportunity and a threat: an opportunity to open the channels of communication, but a threat if negative information about the travel or hospitality organization is widely spread. As online distribution expands, empowered and savvy travellers are unbundling the booking component and self-booking directly (Deloitte, 2015).
Internet and mobile technology are referred to as interactive media . For tourism and hospitality businesses, an online presence is crucial: it’s cost effective, it provides global reach, it allows a business to be available 24/7, and it provides a reciprocal communication platform for customers. An online presence can also produce instant access to critical consumer data such as click through rates on websites, views of social media posts and pages, paths-to-purchase, and much more.
Social Media and Reputation Management
There are also challenges with online marketing, including being noticed within the volume of information customers are exposed to, and loss of control in delivering a message. Despite these challenges, as more consumers seek real-time information online, tourism marketers are responding with increasingly sophisticated online marketing strategies, such as search engine optimization, personalized content, and social media monitoring and analytics.
Social Media
Social media is a broad term that refers to web-based and mobile applications used for social interaction and the exchange of content (Zheng & Gerritsen, 2014). Social networking is the act of using social media to “communicate directly with people you’re already connected to or with whom you wish to be connected with” (Zheng & Gerritsen, 2014, p. 28). Unlike traditional media such as newspapers, magazines, and television, social media is largely powered by user-generated content. This refers to content created and shared by consumers rather than by marketers, journalists, experts, and other paid professionals, although they too contribute to social networks. Influencers also play a major role in generating content and hype about tourism products, services, and experiences, ultimately affecting consumer purchasing decisions. Tourism marketers are increasingly leveraging influencer authority, knowledge, and relationships to reach and capture new markets.
Word of Mouth in the Age of Social Media
Social networking has transformed how many people interact with businesses and share experiences with others, in a communication channel known as electronic word of mouth where customers share directly with each other in an online environment. Consumers now have a variety of channels (e.g., Twitter, Instagram, Facebook) and formats (e.g., videos, blogs, reviews) on which to leave ratings, express preferences, and share stories. Many of these platforms have large audiences, and much of this commentary is made in real time, on a smartphone, while the customer is still in the business.
Advertising and Trust
Social networks, and review sites in particular, are used more and more to seek information and advice on things to do and products and services to purchase. Travellers and locals alike check out these sites for ideas on where to stay, eat, relax, shop, and explore. These channels are highly trusted. A survey of over 28,000 consumers in 56 countries found that consumers trust the advice of people they know (92%) and consumer opinions posted online (70%) more than any other advertising source (Nielsen, 2012). A more recent survey of over 31,000 consumers in 36 countries confirmed that personal recommendations and internet sties are the most important planning sources for travellers (Skift, 2014).
Online Reviews = Business Success
Research shows a direct correlation between consumer reviews and purchase decisions. A 2019 survey by BrightLocal found that 92% of consumers made decisions based on online reviews and 76% trusted online reviews as much as personal recommendations (BrightLocal, 2019). A 2011 study conducted by Harvard Business School found that, for independent restaurants, a one-star increase in Yelp ratings led to a 5% to 9% increase in revenue (Luca, 2011). According to a study by the Cornell Center for Hospitality Research, if a hotel increases its review score on Travelocity by 1 point on a 5-point scale, it can raise its price by 11.2% without affecting demand (Anderson, 2012). Finally, a report published by TripAdvisor and Oxford Economics claims that TripAdvisor was responsible for $US 546 billion in traveller spending in 2017 alone (Tourism Economics, 2020).
Understanding Customer Needs
As we have discussed, service plays an important role in shaping customer impressions, where the ultimate goal of a tourism or hospitality business is to exceed expectations. Every customer has different wants and needs, but virtually all customers expect the following basic needs to be taken care of:
- Convenience
- Good service
To fully satisfy customers, businesses must deliver in all four areas. If they meet the basic needs listed above, they’ll create a passive customer — one who is satisfied, but not likely to write a review or mention a business to others.

On the other hand, failure to deliver on the promise can result in a disappointed customer undoing all the efforts of the marketing plan. For this reason, the entire process must be well coordinated and well executed.
The use of channels that reach very large markets.
Channels in four major categories: billboards, transit, alternative outdoor, and street furniture.
Newspapers, magazines, journals, and directories.
Print content (sometimes appearing online) that is a combination of an editorial feature and paid advertising.
Online and mobile platforms.
Refers to web-based and mobile applications used for social interaction and the exchange of content.
Individuals with a strong online presence and following who can use their knowledge, authority, and relationships with followers to share brand-aligned content and inspire travellers to visit destinations or purchase products.
Information about a service experience passed along orally or through other social information sources from past customers to potential customers.
A guest who is satisfied (won't complain, but won't celebrate the business either).
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC - 2nd Edition Copyright © 2015, 2020, 2021 by Morgan Westcott and Wendy Anderson, Eds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Travel, Tourism & Hospitality
Global tourism industry - statistics & facts
What are the leading global tourism destinations, digitalization of the global tourism industry, how important is sustainable tourism, key insights.
Detailed statistics
Total contribution of travel and tourism to GDP worldwide 2019-2034
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 1950-2023
Global leisure travel spend 2019-2022
Editor’s Picks Current statistics on this topic
Current statistics on this topic.
Leading global travel markets by travel and tourism contribution to GDP 2019-2022
Travel and tourism employment worldwide 2019-2034
Related topics
Recommended.
- Hotel industry worldwide
- Travel agency industry
- Sustainable tourism worldwide
- Travel and tourism in the U.S.
- Travel and tourism in Europe
Recommended statistics
- Basic Statistic Total contribution of travel and tourism to GDP worldwide 2019-2034
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism: share of global GDP 2019-2034
- Basic Statistic Leading global travel markets by travel and tourism contribution to GDP 2019-2022
- Basic Statistic Global leisure travel spend 2019-2022
- Premium Statistic Global business travel spending 2001-2022
- Premium Statistic Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 1950-2023
- Basic Statistic Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 2005-2023, by region
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism employment worldwide 2019-2034
Total contribution of travel and tourism to gross domestic product (GDP) worldwide in 2019 and 2023, with a forecast for 2024 and 2034 (in trillion U.S. dollars)
Travel and tourism: share of global GDP 2019-2034
Share of travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP worldwide in 2019 and 2023, with a forecast for 2024 and 2034
Total contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in leading travel markets worldwide in 2019 and 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Leisure tourism spending worldwide from 2019 to 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Global business travel spending 2001-2022
Expenditure of business tourists worldwide from 2001 to 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide from 1950 to 2023 (in millions)
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 2005-2023, by region
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide from 2005 to 2023, by region (in millions)
Number of travel and tourism jobs worldwide from 2019 to 2023, with a forecast for 2024 and 2034 (in millions)
- Premium Statistic Global hotel and resort industry market size worldwide 2022-2023
- Premium Statistic Most valuable hotel brands worldwide 2023, by brand value
- Basic Statistic Leading hotel companies worldwide 2023, by number of properties
- Premium Statistic Number of hotels in the construction pipeline worldwide 2024
- Premium Statistic Number of hotel rooms in the construction pipeline worldwide 2024
- Premium Statistic Countries with the most hotel construction projects in the pipeline worldwide 2024
Global hotel and resort industry market size worldwide 2022-2023
Market size of the hotel and resort industry worldwide in 2022 and 2023 (in trillion U.S. dollars)
Most valuable hotel brands worldwide 2023, by brand value
Leading hotel brands based on brand value worldwide in 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Leading hotel companies worldwide 2023, by number of properties
Leading hotel companies worldwide as of June 2023, by number of properties
Number of hotels in the construction pipeline worldwide 2024
Number of hotels in the construction pipeline worldwide as of the first quarter of 2024
Number of hotel rooms in the construction pipeline worldwide 2024
Number of hotel rooms in the construction pipeline worldwide as of the first quarter of 2024
Countries with the most hotel construction projects in the pipeline worldwide 2024
Countries with the highest number of hotel construction projects in the pipeline worldwide as of the first quarter of 2024
- Premium Statistic Airports with the most international air passenger traffic worldwide 2022
- Premium Statistic Market value of selected airlines worldwide 2023
- Premium Statistic Global passenger rail users forecast 2017-2028
- Premium Statistic Daily ridership of bus rapid transit systems worldwide by region 2023
- Premium Statistic Number of users of car rentals worldwide 2019-2028
- Premium Statistic Number of users in selected countries in the Car Rentals market in 2023
- Premium Statistic Carbon footprint of international tourism transport worldwide 2005-2030, by type
Airports with the most international air passenger traffic worldwide 2022
Leading airports for international air passenger traffic in 2022 (in million international passengers)
Market value of selected airlines worldwide 2023
Market value of selected airlines worldwide as of May 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Global passenger rail users forecast 2017-2028
Worldwide number of passenger rail users from 2017 to 2023, with a forecast through 2028 (in billion users)
Daily ridership of bus rapid transit systems worldwide by region 2023
Number of daily passengers using bus rapid transit (BRT) systems as of April 2023, by region
Number of users of car rentals worldwide 2019-2028
Number of users of car rentals worldwide from 2019 to 2028 (in millions)
Number of users in selected countries in the Car Rentals market in 2023
Number of users in selected countries in the Car Rentals market in 2023 (in million)
Carbon footprint of international tourism transport worldwide 2005-2030, by type
Transport-related emissions from international tourist arrivals worldwide in 2005 and 2016, with a forecast for 2030, by mode of transport (in million metric tons of carbon dioxide)
Attractions
- Premium Statistic Leading museums by highest attendance worldwide 2019-2022
- Basic Statistic Most visited amusement and theme parks worldwide 2019-2022
- Basic Statistic Monuments on the UNESCO world heritage list 2023, by type
- Basic Statistic Selected countries with the most Michelin-starred restaurants worldwide 2023
Leading museums by highest attendance worldwide 2019-2022
Most visited museums worldwide from 2019 to 2022 (in millions)
Most visited amusement and theme parks worldwide 2019-2022
Leading amusement and theme parks worldwide from 2019 to 2022, by attendance (in millions)
Monuments on the UNESCO world heritage list 2023, by type
Number of monuments on the UNESCO world heritage list as of September 2023, by type
Selected countries with the most Michelin-starred restaurants worldwide 2023
Number of Michelin-starred restaurants in selected countries and territories worldwide as of July 2023
Online travel market
- Premium Statistic Online travel market size worldwide 2017-2028
- Premium Statistic Estimated desktop vs. mobile revenue of leading OTAs worldwide 2023
- Premium Statistic Number of aggregated downloads of leading online travel agency apps worldwide 2023
- Basic Statistic Market cap of leading online travel companies worldwide 2023
- Premium Statistic Estimated EV/Revenue ratio in the online travel market 2024, by segment
- Premium Statistic Estimated EV/EBITDA ratio in the online travel market 2024, by segment
Online travel market size worldwide 2017-2028
Online travel market size worldwide from 2017 to 2023, with a forecast until 2028 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Estimated desktop vs. mobile revenue of leading OTAs worldwide 2023
Estimated desktop vs. mobile revenue of leading online travel agencies (OTAs) worldwide in 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Number of aggregated downloads of leading online travel agency apps worldwide 2023
Number of aggregated downloads of selected leading online travel agency apps worldwide in 2023 (in millions)
Market cap of leading online travel companies worldwide 2023
Market cap of leading online travel companies worldwide as of September 2023 (in million U.S. dollars)
Estimated EV/Revenue ratio in the online travel market 2024, by segment
Estimated enterprise value to revenue (EV/Revenue) ratio in the online travel market worldwide as of April 2024, by segment
Estimated EV/EBITDA ratio in the online travel market 2024, by segment
Estimated enterprise value to EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) ratio in the online travel market worldwide as of April 2024, by segment
Selected trends
- Premium Statistic Global travelers who believe in the importance of green travel 2023
- Premium Statistic Sustainable initiatives travelers would adopt worldwide 2022, by region
- Premium Statistic Airbnb revenue worldwide 2017-2023
- Premium Statistic Airbnb nights and experiences booked worldwide 2017-2023
- Premium Statistic Technologies global hotels plan to implement in the next three years 2022
- Premium Statistic Hotel technologies global consumers think would improve their future stay 2022
Global travelers who believe in the importance of green travel 2023
Share of travelers that believe sustainable travel is important worldwide in 2023
Sustainable initiatives travelers would adopt worldwide 2022, by region
Main sustainable initiatives travelers are willing to adopt worldwide in 2022, by region
Airbnb revenue worldwide 2017-2023
Revenue of Airbnb worldwide from 2017 to 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Airbnb nights and experiences booked worldwide 2017-2023
Nights and experiences booked with Airbnb from 2017 to 2023 (in millions)
Technologies global hotels plan to implement in the next three years 2022
Technologies hotels are most likely to implement in the next three years worldwide as of 2022
Hotel technologies global consumers think would improve their future stay 2022
Must-have hotel technologies to create a more amazing stay in the future among travelers worldwide as of 2022
- Premium Statistic Travel and tourism revenue worldwide 2019-2028, by segment
- Premium Statistic Distribution of sales channels in the travel and tourism market worldwide 2018-2028
- Premium Statistic Inbound tourism visitor growth worldwide 2020-2025, by region
- Premium Statistic Outbound tourism visitor growth worldwide 2020-2025, by region
Travel and tourism revenue worldwide 2019-2028, by segment
Revenue of the global travel and tourism market from 2019 to 2028, by segment (in billion U.S. dollars)
Distribution of sales channels in the travel and tourism market worldwide 2018-2028
Revenue share of sales channels of the travel and tourism market worldwide from 2018 to 2028
Inbound tourism visitor growth worldwide 2020-2025, by region
Inbound tourism visitor growth worldwide from 2020 to 2022, with a forecast until 2025, by region
Outbound tourism visitor growth worldwide 2020-2025, by region
Outbound tourism visitor growth worldwide from 2020 to 2022, with a forecast until 2025, by region
Further reports Get the best reports to understand your industry
Get the best reports to understand your industry.
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Abstract. This chapter explores how marketers design and manage tourism and hospitality products. It begins with definitions for the terms "product", "offering", and "product mix". It the chapter explains that the product is a complex concept that should be considered on three levels. These are the core, expected, and augmented product.
Now boarding: Faces, places, and trends shaping tourism in 2024. Global travel is back and buzzing. The amount of travel fell by 75 percent in 2020; however, travel is on its way to a full recovery by the end of 2024. More regional trips, an emerging population of new travelers, and a fresh set of destinations are powering steady spending in ...
Product Development. As defined by UN Tourism, a Tourism Product is "a combination of tangible and intangible elements, such as natural, cultural and man-made resources, attractions, facilities, services and activities around a specific center of interest which represents the core of the destination marketing mix and creates an overall visitor experience including emotional aspects for the ...
The tourism product features and processes identified in the central part of Fig. 1 can be further understood using ideas developed by Schumpeter ... Anatolia: An International Journal of Tourism and Hospitality Research, 21 (1) (2010), pp. 89-106. CrossRef View in Scopus Google Scholar. Dwyer and Kim, 2003.
The products of tourism cannot be easily standardized as they are created for the customers of varied interests and demands. As the tourism products are mainly the tourists' experience, they can be stored only in the tourists' memories. Let us understand more about tourism products and services −. Types of Tourism Products. The tourism ...
Tourism Products are a combination of goods and services demanded by a tourist during travel to and stay at a destination. These include natural, cultural and manmade attractions and facilities such as hotels, transport and ancillary services. In this process, tourists derive an experience which varies from individual to individual.
Branding tourism and hospitality products is a strategic marketing management tool as competition in the marketplace has become fierce in the con-temporary business environment. Price is the only component of the market-ing mix that produces revenue (Kotler & Armstrong, 2019).
Chapter 5: The Tourism and Hospitality Product; Opening Vignette: Concorde: A Journey Through the Product Life Cycle; Introduction; Product Levels; Physical Evidence and Servicescape; Snapshot: The Greatest Briton Ever: The New Churchill Museum in London; Product Planning;
(DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-64111-5_8) This chapter explores how marketers design and manage tourism and hospitality products. It begins with definitions for the terms "product", "offering", and "product mix". It the chapter explains that the product is a complex concept that should be considered on three levels. These are the core, expected, and augmented product. Next, the product ...
This chapter discusses the communication methods that are used to promote tourism and hospitality offerings. Marketers must communicate these offerings to consumers (including the travel trade). Promotion is used to communicate information about offerings to target markets. The chapter begins by explaining the relationship between promotion and ...
For academics, this special issue serves as starting point to push the boundaries and to encourage looking at the current global environment through difference lenses. For example, medical tourism and medical hotels are not the same products. The latter suggests a very different type of service and a convergence of health care and hospitality.
In other words: they will promote your product to others. For free! The current coronavirus crisis has put international travel under pressure. In many countries, tourist arrivals have nearly dropped to zero. It is likely that international tourism will be affected by the COVID-19 crisis for the next couple of years. Several scenarios are ...
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities ...
The chain of distribution in tourism refers to the businesses and platforms involved in selling, distributing, and bundling tourism products. This process begins with the primary tour and activity provider all the way to the end consumers experiencing it. Generally, there are four steps to the distribution chain: 1. Suppliers/principals.
Tourism and hospitality product. Aug 2, 2013 •. 14 likes • 37,753 views. AI-enhanced description. Kosala Wimukthi. The document discusses different levels of products including the core product, which is central to the company's performance. It also discusses tangible products, which have specific features, and augmented products, which ...
There are an estimated 4.5 billion people around the globe with internet access, and social media has become truly integrated into the travel and hospitality industry. TripAdvisor and similar sites have become the customer's first point of connection with tourism and hospitality products and experiences.
Travel, Tourism & Hospitality. ... Total contribution of travel and tourism to gross domestic product (GDP) worldwide in 2019 and 2023, with a forecast for 2024 and 2034 (in trillion U.S. dollars) ...
This chapter discusses tourism products and their importance to the tourism and hospitality industries. It defines a tourism product as anything tied to travel and tourism, and identifies key players in developing and delivering tourism products, including private companies, public sector organizations, suppliers of transportation, accommodations, food and beverage, attractions and events. The ...
The document discusses the tourism and hospitality product. It describes the three levels of any product - the core, tangible, and augmented levels. It outlines the components that make up the physical environment where services are delivered. Product planning considers a product mix and five options for matching markets and products. New product development follows a model and there are ...
The World Travel & Tourism Council reports that the travel sector's contribution to the global economy is set to reach an all-time high of USD 11.1 Trillion in 2024. Customer Demands Continue to Surge. Nearly half of Americans Intend to embark on trips involving flights or hotel stays this summer, spending an average of USD 3,594.
TTI Technologies: A B2B hospitality technology company that leads with the true value of good old-fashioned service and advanced technologies. They speak directly to their prospect's pain points.
Zhangjiajie launched eight themed tourism products: World Natural Heritage Tours, Folk Culture Experiences, Sports and Fitness Adventures, Wellness and Residential Retreats, Science Education ...
Total number of rooms reached 81. The hotel has got a number of significant advantages: comfortable location, luxury and standard hotel rooms, free parking, moderate prices and highly qualified staff. According the experts in the tourism and hospitality business the hotel is reckoned the leading middle class hotel in Moscow region.
Total number of rooms reached 81. The hotel has got a number of significant advantages: comfortable location, luxury and standard hotel rooms, free parking, moderate prices and highly qualified staff. According the experts in the tourism and hospitality business the hotel is reckoned the leading middle class hotel in Moscow region.
A mix of the charming, modern, and tried and true. See all. Apelsin Hotel. 43. from $48/night. Apart Hotel Yantar. 2. from $28/night. Elektrostal Hotel.
A mix of the charming, modern, and tried and true. See all. Vyazemgrad Hotel. 13. from $23/night. Park-Hotel Golitsyn Club. 94. from $39/night. Mini-Hotel GRC-Gorki 10.