

What Is Regional Tourism?
By Anna Duncan
Regional tourism is a type of travel that focuses on exploring and experiencing the local culture, history, and attractions of a particular region. It involves visiting destinations outside of major cities or tourist hotspots and immersing oneself in the local way of life. This type of tourism can be incredibly rewarding, as it allows travelers to gain a deeper understanding and appreciation for the region they are visiting.
Why Is Regional Tourism Important? Regional tourism plays a significant role in supporting local economies by generating revenue for small businesses, promoting cultural exchange, and preserving local heritage. It also helps to reduce the impact of overtourism in popular tourist destinations by diverting visitors to lesser-known regions.
Types Of Regional Tourism There are several types of regional tourism, including:
- Cultural tourism: This involves experiencing the art, music, food, and traditions of a particular region.
- Nature-based tourism: This involves exploring natural landscapes such as forests, mountains, lakes, and rivers.
- Adventure tourism: This involves participating in activities such as hiking, camping, kayaking, or rock climbing.
- Historical tourism: This involves learning about the history and heritage of a particular region through visits to museums, monuments, or other historical sites.
The Benefits Of Regional Tourism Regional tourism has numerous benefits for both travelers and locals. Some of these include:
1. Authentic Experiences: One of the biggest advantages of regional travel is that it provides an opportunity to experience authentic local culture. Visitors can interact with locals and learn about their traditions firsthand.
2. Economic Development: Regional tourism can support small businesses by providing them with a steady stream of customers. This helps to create jobs and boost economic growth in rural areas.
3. Environmental Preservation: By diverting visitors away from overcrowded cities and popular tourist destinations, regional tourism can help to reduce the environmental impact of tourism. It can also promote sustainable practices such as ecotourism and responsible travel.
4. Cultural Preservation: Regional tourism can help to preserve local culture and traditions by supporting community events, festivals, and art shows. It can also help to raise awareness about the importance of preserving cultural heritage.
Examples Of Regional Tourism
There are countless examples of regional tourism destinations around the world. Here are a few:
The Scottish Highlands:
The Scottish Highlands offer breathtaking natural landscapes, rich history, and unique cultural experiences. Visitors can explore ancient castles, taste local whisky, and hike through rugged mountains.
The Amalfi Coast, Italy:
The Amalfi Coast is a stunning region on the southern coast of Italy known for its colorful villages, rugged coastline, and delicious cuisine. Visitors can take boat tours along the coast or hike through lemon groves.
Chiang Mai, Thailand:
Chiang Mai is a vibrant city in northern Thailand known for its beautiful temples, night markets, and outdoor adventures. Visitors can take cooking classes or trek through nearby mountains to experience local hill tribe culture.
8 Related Question Answers Found
What is cultural heritage tourism, what is cultural tourism, what is local tourism, what is a festival tourism, what is gastronomic tourism, what is meant by cultural tourism, what is heritage tourism, what is visitor tourism, backpacking - budget travel - business travel - cruise ship - vacation - tourism - resort - cruise - road trip - destination wedding - tourist destination - best places, london - madrid - paris - prague - dubai - barcelona - rome.
© 2024 LuxuryTraveldiva
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Product development.
- Rural tourism
- Gastronomy and Wine Tourism
- Mountain Tourism
- Urban Tourism
- Sports Tourism
- Shopping Tourism
share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Rural tourism has a high potential to stimulate local economic growth and social change because of its complementarity with other economic activities, its contribution to GDP and job creation, and its capacity to promote the dispersal of demand in time (fight seasonality) and along a wider territory.
UN Tourism understands Rural Tourism as "a type of tourism activity in which the visitor’s experience is related to a wide range of products generally linked to nature-based activities, agriculture, rural lifestyle / culture, angling and sightseeing.
Rural Tourism activities take place in non-urban (rural) areas with the following characteristics: i) low population density, ii) landscape and land-use dominated by agriculture and forestry and iii) traditional social structure and lifestyle".

Best Tourism Villages by UN Tourism
With the vision of making tourism a positive force for transformation, rural development and community wellbeing, UN Tourism launched the ' Best Tourism Villages by UN Tourism ' initiative.
It seeks to advance the role of tourism in valuing and safeguarding rural villages along with their associated landscapes, knowledge systems, biological and cultural diversity, local values and activities (agriculture, forestry, livestock and/or fisheries), including their gastronomy.
- STAR, digital self-assessment tool for rural destinations
UN Tourism has unveiled its pioneering digital self-assessment tool designed to progress tourism development in rural areas. The UN Tourism Self-assessment Tool to Assist Rural Destinations, STAR, allows local public authorities in rural destinations to self-evaluate and measure their level of tourism development. It also provides tailored recommendations, benchmarking different destinations and generating valuable data and insights for Member States to enhance sustainable and inclusive tourism policies.
Tourism and Rural Development: Understanding Challenges on the Ground – Lessons learned from the Best Tourism Villages by UNWTO Initiative

Tourism and Rural Development: A Policy Perspective
Tourism and Rural Development: A Policy Perspective - Results of the UN Tourism Survey on Tourism for Rural Development to Member States

Compilación de buenas prácticas del turismo indígena – Enfoque regional sobre las Américas

UN Tourism Recommendations on Tourism and Rural Development

UN Tourism Recommendations on Tourism and Rural Development – A Guide to Making Tourism an Effective Tool for Rural Development
AlUla Framework for inclusive Community Development through Tourism

The Framework provides guidance and inspiration to all governments, as well as all other key stakeholders in the tourism sector – including regional and local governments, the private sector, industry associations, civil society, communities and tourists – with the aim of fostering a truly holistic and integrated approach to inclusive community development through tourism.
AlUla Framework for inclusive Community Development through Tourism
AlUla Framework for inclusive Community Development through Tourism – Executive Summary
International Rural Tourism Development – An Asia-Pacific Perspective

International Rural Tourism Development – An Asia-Pacific Perspective


Caribbean Tourism Organisation (CTO)
The Caribbean Tourism Organization (CTO) with headquarters in Barbados, is the Caribbean’s tourism development agency comprising membership of 24 countries and territories including Dutch, English, French and Spanish, as well as a myriad of private sector allied members.
The primary objective of the Caribbean Tourism Organization is to provide to and through its members the services and information necessary for the development of sustainable tourism for the economic and social benefit of the Caribbean people by:
providing an instrument for close collaboration in tourism among the various territories, countries and other interests concerned;
developing and promoting regional travel and tourism programs to and within the Caribbean;
providing members with opportunities to market their products more effectively to both the Caribbean and the international tourism marketplaces;
assisting member countries, particularly the smaller member countries with minimal promotional budgets, to maximize their marketing impact through the collective CTO forum;
carrying out advertising, promotions, publicity and information services calculated to focus the attention of the public upon the Caribbean as one of the world’s outstanding tourist destinations;
providing a liaison for tourism matters between member countries;
providing a sound body of knowledge on tourism through data collection, collation and research;
creating processes and systems for disseminating and sharing tourism information;
providing advice, technical assistance and consultancy services with respect to tourism;
providing training and education for Caribbean nationals and for international travel agents;
seeking to maximize the contribution of tourism to the economic development of member countries and the Caribbean through programs likely to increase foreign exchange earnings, increase employment, strengthen linkages between tourism and other economic sector like manufacturing and agriculture, and to reduce leakages from Caribbean economies;
encouraging coordination with respect to research and planning and the efficient allocation of local, regional and international resources at both government and non-governmental levels in tourism development;
researching and identifying the ecological effects of tourism with a view to recommending and /or initiating action aimed at minimizing the negative and enhancing the positive effects;
promoting the consciousness of the need to preserve both the natural and man-made beauty of the Caribbean environment and demonstrating its direct relationship to the development of an attractive tourism product;
developing a tourism product which is essentially Caribbean and which, through maximizing economic benefits, has minimal adverse social and psychological effects on the integrity of Caribbean peoples
Vision and Purpose
The CTO’s vision is to position the Caribbean as the most desirable, year-round, warm weather destination and our purpose is Leading Sustainable Tourism – One Sea, One Voice, One Caribbean.

Visit Website

- Business Guide
- Destination Guide
- Hotel Guide
- Places to visit
- Things to do
Tourism Planning: Importance, Benefits, Types & Levels
Planning is to prepare a Road Map to achieve goals.
In 1987 D.Getz defined tourism planning as “a process, based on research and evaluation, which seeks to optimize the potential contribution of tourism to human welfare and environmental quality”.
Faludi, in 1973, defined tourism planning as “Planning is a very important part of the process by which governments manage tourism at the national, local and organizational levels”.
What is Tourism Planning?

The upkeep and expansion of the tourism sector in a particular area is referred to as tourism planning. Planning for tourism is, of course, a crucial component.
Creating strategies and plans to increase, develop, and stimulate tourism for/in a destination may be summed up as tourism planning. The primary motivation behind establishing and implementing strategies for the tourist industry is to generate money, which will eventually raise the GDP of a nation or region.
What is the need for Tourism Planning?

For the expansion of the sector important to plan tourism activities for the following reasons:
- It is necessary to plan tourism activities on different levels and in various manners to promote tourism and boost the economy.
- To provide quality to both tourists and residents.
- It involves making major decisions which cannot be taken spontaneously.
What are the components of Tourism Planning

- Exploration phase/ Preparatory
- Planning phase/Feasibility/
- Zoning phase/Formal planning
- Design and implementation phase
- Operational phase
Most nations that have successfully planned their tourism can be found online and are regarded as incredible holiday destinations. People go to these nations hoping their travel vlogs will increase their subscriber count on YouTube. That is an indication of success in the modern day.
Benefits of Tourism Planning

Tourism destination planning should be a vital component of every destination’s tourism development plan to get the best outcomes and please all stakeholders. While some places do a great job of maintaining sustainable tourism, others (typically developing countries) need to recognize the significance of comprehensive tourism development planning.
Tourism planning can benefit various parties involved from the industry in the following ways:
- It boosts revenue and employment thanks to tourist spending.
- It safeguards cultural and natural assets so that visitors can enjoy them.
- It broadens the comprehension of cultural diversity
- It constructs new infrastructure, such as sewage systems, roads, etc., for the community.
Impacts of Tourism Planning

The impacts of tourism destination planning can be sorted into seven general categories:
- Environmental
- Social and cultural
- Crowding and congestion
- Community attitude
Formulating an approach to tourism policy and planning:
According to Inskeep, six “golden standards” should be followed when creating a strategy for tourist planning and policy (1991).

1. Goal Oriented:
Tourism Planning should be oriented to achieve broad national and community goals.
2. Integrative:
Integrating tourist policy and planning into the economy, land use and infrastructure, conservation, and environmental planning.
3. Market Driven:
Planning for successful tourism growth in a cutthroat international market.
4. Resource Driven:
Developing tourism that capitalizes on the location’s inherent advantages while preserving and improving the features and experiences of existing tourism resources.
5. Consultative:
Considering broader community attitudes, needs, and desires to determine what the population will accept.
6. Systematic:
utilizing primary or secondary information to support planners conceptually or predictably, incorporating knowledge from other tourist locations
Levels of Tourism Planning

Planning and policy for the tourism industry occur at several levels. This can be done in a top-down approach, with international or national bodies, or a bottom-up approach from a local level.
1. International Tourism Planning:
Tourism planning at the international level typically involves international transportation services, the movement and scheduling of tourist tours between different countries, the development of significant tourist attractions and facilities in neighboring countries, as well as the working strategies and promotional programs of many nations.
2. National Tourism Planning:
Tourism policy, infrastructural facilities, and a physical structure plan, which includes significant tourist attractions, chosen tourism development regions, international entrance points, facilities, and services, are all addressed at the national level of tourism planning. Additionally, it is concerned with the quantity, types, and quality of lodging and other essential tourist facilities and services; the country’s major travel routes and their regional connections; tourism organization
rights, laws, and investment policies; marketing and promotion strategies for the industry; education and training initiatives; and environmental, economic, and sociocultural analysis.
3. Regional Tourism Planning:
Regional planning considers factors such as regional policy, regional entrance points, transportation facilities, and services; the types and locations of tourism attractions; the quantity, varieties, and places of lodging and other tourist facilities and services; and the sites of tourist development regions, such as resort areas.
They will also oversee sociocultural, environmental, economic, and impact analyses, regional education and training programmes, marketing strategies, investment policies, organizational structures, legal frameworks, and implementation strategies, including project plans and zoning ordinances.
4. Local Tourism Planning:
Participants at the local level will think about the analyses, outputs, outcomes, and assessment of tourism planning at the ground level.
Types of Tourism Planning

Before creating a comprehensive plan to market the destination, the following types of tourism planning are taken into account:
Spatial Tourism Planning:
Spatial tourism planning attempts to thoroughly process social, environmental, and economic change to bring about certain ends. Drawing plans, maps or diagrams are put together to decide where socio-spatial activities can occur.
Sectoral Tourism Planning:
In this kind of planning, the regions are divided into sections, and each section is called a sector. It concentrates on a manageable area and takes into account the specific infrastructure, land use, transportation, and environmental requirements of that region. Depending on the nature of the products or services provided, economic, social, and administrative activities are grouped into sectors.
Complex Tourism Planning:
When various regions are considered for the purpose of tourism planning, it is known as complex tourism planning. These regions are to be developed comprehensively because of the significant interest shown by international tourists. There is a possibility that these regions are located far away from one another.
Integrated Tourism Planning:
Integrated tourism refers to making tourism the primary industry in a given area by systematically and comprehensively promoting all available economic, social, and tourism resources.
Sustainable Tourism Planning:
Sustainable tourism planning involves striking the correct balance between the requirements of people and the environment. It entails stating the community’s mission, vision, and unique selling point or identity in clear terms. With the help of this type of destination planning in our local communities, we are better equipped to plan for the long term, and respond to changing target markets, trends, and emergencies like the Covid-19 outbreak. Additionally, it guarantees that resources are allocated properly while ethically and sustainably establishing local communities. This method of tourism planning benefits people and places in positive ways on all fronts—socially, economically, culturally, and environmentally—puts sustainability at its core.
Centralized Tourism Planning:
Centralized tourism planning is done by a single authority, usually the state or central government.
Decentralized Tourism Planning:
Organizations are interested in developing tourist spots and planning the various activities visitors can enjoy. (Joint Venture).
They take assistance from government. Suggested Read: Sustainable Tourism
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is tourism planning important.
Destination development plans should include tourism planning since it promotes a destination’s long-term viability and encourages cooperation among important stakeholders..
What are the features of tourism planning?
Three general principles of planning for tourism can be specified as anticipation, regulation and monitoring.
What are the barriers to tourism planning?
According to earlier research conducted in several nations, a common pattern of issues has emerged. For instance, financial constraints, a lack of knowledge, an insufficient amount of time, and other issues have prevented local governments from incorporating tourism into their development plans.

My passion as a guitar maker comes from a life-long obsession with making things. From a young age I have always tried to manipulate objects and materials in order to create something entirely different. I find that working with wood is a way for me to connect with nature. The simple act of shaping wood to make something functional or beautiful brings me endless satisfaction.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Talk To Us!
Latest posts.
- Top 4 Washington, DC Itineraries for Every Vacation
- Washington DC Packages for Various Hotels
- Best Places to visit in India in December – An unforgettable family holiday
- Dive into Wonder: Exploring SeaWorld Abu Dhabi’s Marine Magic
- Explore India in July: Plan Your Travel
1.1.2. Regional Tourism
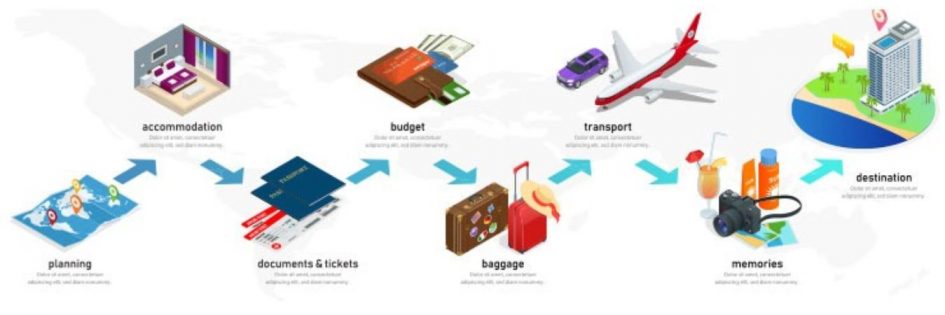
The topic in this unit is related to regional and rural tourism. Regional tourism is tourism concentrated in a region. A region is an area that can be distinguished of other area’s by its own culture and structure. A regional tourist is a tourist visiting a region or province other than in which she/he has a normal residence but with a defined geographic region as a modification of the Wiki.com definition. So if you are living in the Dutch province Utrecht, you are a regional inland tourist in Limburg.
In a region Tourist is in movement from L. to S. in a certain area just for fun. It can be with all kind of transportation, but also on foot.
Regional tourism is not only movement, it is also imagination and expectation: what shall I see on the route, which challenges are there, what can I do, whom shall I meet. What is nature like and what about the villages I am walking or riding through, the castles on the top, the regional meals to eat, etc.
Access to that attractive region must be more or less comfortable and fast, be it by plane, train or car to reach. Inside the region the infrastructure of all kind of routes has to be good and safe as far as necessary, taking into account the target group you are aiming for.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Regional tourism is a type of travel that focuses on exploring and experiencing the local culture, history, and attractions of a particular region. It can be rewarding, sustainable, and culturally enriching for both travelers and locals. Learn more about the types, benefits, and examples of regional tourism.
A tourism region is a geographical region that has been designated by a governmental organization or tourism bureau as having common cultural or environmental characteristics. These regions are often named after historical or current administrative and geographical regions. Others have names created specifically for tourism purposes.
It identifies three regional tourism functions that are characterized by the exclusive practice of a recreational function: the observation place, the practiced place, and the service place. Tourists, through their mobilities, assign regional tourist functions to places in order to organize their stay and define the tourist region adapted to ...
The UN Tourism Data Dashboard - provides statistics and insights on key indicators for inbound and outbound tourism at the global, regional and national levels. Data covers tourist arrivals, tourism receipts, tourism share of exports and contribution to GDP, source markets, seasonality, domestic tourism and data on accommodation and employment.
Tourism and regional development research is focused primarily on the role of tourism in regional development and whether tourism leads to balanced or unbalanced growth. Most research in tourism and regional development informs policies for reducing regional disparity and creating more employment (Vu and Turner, 2006; Zhou-Grundy and Turner, 2014).
Rural tourism has a high potential to stimulate local economic growth and social change because of its complementarity with other economic activities, its contribution to GDP and job creation, and its capacity to promote the dispersal of demand in time (fight seasonality) and along a wider territory. UN Tourism understands Rural Tourism as "a ...
Yet regional tourism officials seem to be interested in understanding the long-term sustainability of tourism impacts, particularly when the industry is considered crucial. ... such as the will to take social and ecological responsibility and the ambition to re-think and radically transform the meaning of hospitality and tourism work (Higgins ...
Although regional tourism is an important phenomenon in the developing world, it has largely been overlooked by international tourism scholars. The promotion of regional tourism can make a positive contribution to tourism development. This article stresses the importance of regional tourists to the expanding tourism economy of South Africa.
As such, international tourism can generate a tourism trade surplus when receipts exceed expenditure, or a deficit (vice versa) in the travel balance of countries. In 2019, the United States of America had the world's largest travel surplus with USD 62 billion, resulting from tourism receipts of USD 214 billion and expenditure of USD 152 billion.
This publication lays the foundation for tourism development of a country and its regions. It establishes the principal guidelines for preparing tourism development plans at the national and regional levels with emphasis on the integrated approach, balancing economic, environmental, and socio-cultural factors achieving sustainable tourism.
This paper reviews the literature on the topic of "regional tourism performance," which helps to reflect the historical accumulation, current situation, and latest progress of the current research topic of "regional tourism performance," and can reflect the new trends, new trends, new levels, new principles, and new technologies of relevant research ().
Regional tourism is becoming an important source of revenue for many developing countries. Through regional tourism, countries can enhance employment opportunities and increase government revenue. The objective of this study was to profile South African tourists visiting Lesotho and their motivations in visiting the country. This
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
Regional tourism is becoming an important source of revenue for many developing countries. Through such tourism, countries can enhance their employment opportunities and increase their government revenue. The objective of this study was to profile South African tourists visiting Lesotho, and their motivations in visiting the
National and regional tourism is a $900B industry in the United States alone. Learn how tourism differs worldwide, how different departments have a hand in certain areas, and what unique travel ...
The Caribbean Tourism Organization (CTO) with headquarters in Barbados, is the Caribbean's tourism development agency comprising membership of 24 countries and territories including Dutch, English, French and Spanish, as well as a myriad of private sector allied members. ... regional and international resources at both government and non ...
Matt Knowles, CTC/DS, owner of Sea Escape Travel in Folsom, California, agrees with Schumacher that one of regional travel's top appeals is the ability "to slow things down, immersing ...
Regional Tourism Planning: Regional planning considers factors such as regional policy, regional entrance points, transportation facilities, and services; the types and locations of tourism attractions; the quantity, varieties, and places of lodging and other tourist facilities and services; and the sites of tourist development regions, such as ...
Regional tourism is tourism concentrated in a region. A region is an area that can be distinguished of other area's by its own culture and structure. A regional tourist is a tourist visiting a region or province other than in which she/he has a normal residence but with a defined geographic region as a modification of the Wiki.com definition.
Tourism integration is a trend in regional tourism economic development and cultural integration. Tourism economic linkages greatly influence regional tourism integration, becoming progressively obvious with the strength of linkages. However, their influence on regions with rich tourism resources and underdeveloped economies are understudied.
The Tourism sector is considered as one of the cornerstones of the SADC regional economy. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO), the sector directly contributed around 2.8% (US$19.4 billion) of the total SADC GDP in 2017 and, when considering its indirect and induced impacts, the sector contributed as much as 8% (US$56 billion) of SADC GDP.
Topic 1 Domestic, regional and international tourism Overview Thitopic introducey ou to tourism d the impact of glob eventon the touri indury well the potive d neg ive effectfor country of hoing event of glob g nific ce. In thitopic you will le n about: • ˙ ob evento f internation g nific ce • The potive