

Family Life

AAP Schedule of Well-Child Care Visits

Parents know who they should go to when their child is sick. But pediatrician visits are just as important for healthy children.
The Bright Futures /American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) developed a set of comprehensive health guidelines for well-child care, known as the " periodicity schedule ." It is a schedule of screenings and assessments recommended at each well-child visit from infancy through adolescence.
Schedule of well-child visits
- The first week visit (3 to 5 days old)
- 1 month old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
- 9 months old
- 12 months old
- 15 months old
- 18 months old
- 2 years old (24 months)
- 2 ½ years old (30 months)
- 3 years old
- 4 years old
- 5 years old
- 6 years old
- 7 years old
- 8 years old
- 9 years old
- 10 years old
- 11 years old
- 12 years old
- 13 years old
- 14 years old
- 15 years old
- 16 years old
- 17 years old
- 18 years old
- 19 years old
- 20 years old
- 21 years old
The benefits of well-child visits
Prevention . Your child gets scheduled immunizations to prevent illness. You also can ask your pediatrician about nutrition and safety in the home and at school.
Tracking growth & development . See how much your child has grown in the time since your last visit, and talk with your doctor about your child's development. You can discuss your child's milestones, social behaviors and learning.
Raising any concerns . Make a list of topics you want to talk about with your child's pediatrician such as development, behavior, sleep, eating or getting along with other family members. Bring your top three to five questions or concerns with you to talk with your pediatrician at the start of the visit.
Team approach . Regular visits create strong, trustworthy relationships among pediatrician, parent and child. The AAP recommends well-child visits as a way for pediatricians and parents to serve the needs of children. This team approach helps develop optimal physical, mental and social health of a child.
More information
Back to School, Back to Doctor
Recommended Immunization Schedules
Milestones Matter: 10 to Watch for by Age 5
Your Child's Checkups
- Bright Futures/AAP Recommendations for Preventive Pediatric Health Care (periodicity schedule)
- Getting Pregnant
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
- Birth Clubs
- See all in Community
- Ovulation Calculator
- How To Get Pregnant
- How To Get Pregnant Fast
- Ovulation Discharge
- Implantation Bleeding
- Ovulation Symptoms
- Pregnancy Symptoms
- Am I Pregnant?
- Pregnancy Tests
- See all in Getting Pregnant
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Pregnant Sex
- Weight Gain Tracker
- Signs of Labor
- Morning Sickness
- COVID Vaccine and Pregnancy
- Fetal Weight Chart
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy Discharge
- Find Out Baby Gender
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- See all in Pregnancy
- Baby Name Generator
- Top Baby Names 2023
- Top Baby Names 2024
- How to Pick a Baby Name
- Most Popular Baby Names
- Baby Names by Letter
- Gender Neutral Names
- Unique Boy Names
- Unique Girl Names
- Top baby names by year
- See all in Baby Names
- Baby Development
- Baby Feeding Guide
- Newborn Sleep
- When Babies Roll Over
- First-Year Baby Costs Calculator
- Postpartum Health
- Baby Poop Chart
- See all in Baby
- Average Weight & Height
- Autism Signs
- Child Growth Chart
- Night Terrors
- Moving from Crib to Bed
- Toddler Feeding Guide
- Potty Training
- Bathing and Grooming
- See all in Toddler
- Height Predictor
- Potty Training: Boys
- Potty training: Girls
- How Much Sleep? (Ages 3+)
- Ready for Preschool?
- Thumb-Sucking
- Gross Motor Skills
- Napping (Ages 2 to 3)
- See all in Child
- Photos: Rashes & Skin Conditions
- Symptom Checker
- Vaccine Scheduler
- Reducing a Fever
- Acetaminophen Dosage Chart
- Constipation in Babies
- Ear Infection Symptoms
- Head Lice 101
- See all in Health
- Second Pregnancy
- Daycare Costs
- Family Finance
- Stay-At-Home Parents
- Breastfeeding Positions
- See all in Family
- Baby Sleep Training
- Preparing For Baby
- My Custom Checklist
- My Registries
- Take the Quiz
- Best Baby Products
- Best Breast Pump
- Best Convertible Car Seat
- Best Infant Car Seat
- Best Baby Bottle
- Best Baby Monitor
- Best Stroller
- Best Diapers
- Best Baby Carrier
- Best Diaper Bag
- Best Highchair
- See all in Baby Products
- Why Pregnant Belly Feels Tight
- Early Signs of Twins
- Teas During Pregnancy
- Baby Head Circumference Chart
- How Many Months Pregnant Am I
- What is a Rainbow Baby
- Braxton Hicks Contractions
- HCG Levels By Week
- When to Take a Pregnancy Test
- Am I Pregnant
- Why is Poop Green
- Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp
- Insemination
- UTI During Pregnancy
- Vitamin D Drops
- Best Baby Forumla
- Postpartum Depression
- Low Progesterone During Pregnancy
- Baby Shower
- Baby Shower Games
Your baby's checkup schedule: What to expect at doctor visits
There are a lot of doctor visits in your baby's first few years, and they're all important! Your baby's pediatrician will monitor their growth and development, stay on top of their vaccinations, and answer your questions and concerns.

It can seem like you're always headed to the doctor, even when all is well with your baby. But there's good reason for all those appointments.
"There's so much that happens in the first year of life that it's important that nothing gets missed!" explains Chandani DeZure, M.D., a neonatal and pediatric hospitalist at Lucile Packard Children's Hospital/Stanford University Opens a new window in Palo Alto, California and member of the BabyCenter Medical Advisory Board .
"Babies need to be developing and growing appropriately, eating well, and getting vaccinated to protect against diseases so they can thrive as they get older and be as healthy as possible. All this and more happens at regular well-baby checkups," says Dr. DeZure.
Checkups are also the perfect time to ask questions and raise concerns about your baby's sleep habits , crying , poop , breastfeeding , formula feeding , development milestones , and more.
Learn how to find a pediatrician for your baby .
What newborn doctor visits will my baby have?
In the first week, the doctor will want to check your newborn to make sure they're doing well. Then you'll have scheduled visits at 1 and 2 months.
A lot happens right after birth and while you're still at the hospital with your newborn . At birth, the medical team will assess your baby's health and assign an Apgar score – which evaluates your baby's heart rate, breathing, muscle tone, reflex response, and color.
They'll weigh your baby and measure your baby's length and head circumference . These numbers will be recorded on a growth chart , which will be used to keep track of your baby's growth at all future doctor's visits.
Your baby's progress along the growth chart is just one way to evaluate their health. "Growth charts are not intended to be used as a sole diagnostic instrument," explains the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Opens a new window (CDC). "Instead, growth charts are tools that contribute to forming an overall health picture for the child being measured."
At the hospital, your baby will get antibiotic eye ointment (to prevent dangerous eye infections) and a vitamin K shot (to help their blood clot normally and protect them from a rare but dangerous bleeding disorder). They'll also receive their first hepatitis B shot .
Your pediatrician or a pediatric hospitalist will give your newborn a complete physical at the hospital within 24 hours of birth. They'll examine your baby head to toe, checking their skin tone, reflexes, alertness, heart, lungs, and skin (for rashes and jaundice ).
If you're having your baby circumcised , that will be done a day or two after birth.
Your baby will also receive screening tests while at the hospital. These include tests for hearing loss , congenital heart defects , and metabolic disorders (such as PKU and sickle cell disease ). Screening tests are usually done between 24 hours and 48 hours after birth.
Read more about what happens to your baby right after birth .
Your baby's checkup schedule
Some pediatricians' schedules vary slightly, but the American Academy of Pediatrics Opens a new window (AAP) recommends babies get checkups at birth, 3 to 5 days after birth, and then at 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. (Once your baby is a toddler and child, they'll have routine checkups at 30 months, 3 years, and annually after that.)
If you've gotten behind, talk with your child's doctor about a catch-up schedule. "It's particularly important for parents to work with their child's doctor or nurse to make sure they get caught up on missed well-child visits and recommended vaccines," says the CDC Opens a new window . "Making sure that your child sees their doctor for well-child visits and recommended vaccines is one of the best things you can do to protect your child and community from serious diseases that are easily spread."
At each visit, your baby's doctor will:
- Do a complete physical examination, checking your baby's eyes and ears, heart and lungs, head, body, belly, genitals, and hips and legs
- Weigh your baby and take their measurements (length and head circumference). The doctor will chart these numbers on your baby's growth chart and let you know how they're progressing.
- Ask about your baby's eating habits and number of wet and poopy diapers
- Ask about your baby's sleeping habits
- Watch how your baby responds to movement. They'll ask you if you've noticed anything unusual about your baby's eyes or the way they look at things.
- Watch how your baby responds to sounds. The doctor will ask if your baby responds to your voice and other sounds by turning in the direction of the sound.
- Run any appropriate tests (screening and diagnostic), depending on your baby's needs
- Give needed vaccinations
- Chat about your baby's developmental skills, including gross motor skills and fine motor skills , social skills , and language skills
- Answer your questions and concerns
Follow the links below for more detailed information about what to expect at each visit, but here are some highlights:
1-month doctor appointment
At the 1-month checkup , the doctor will check your baby's soft spots (fontanels) and the shape of your baby's head. They'll also review the results of your baby's newborn screening tests.
Your baby may also get their second hepatitis B shot. The first was probably given at birth, and the second shot can be given at the 1- or 2-month visit.
The doctor may also ask about your baby's head control and cooing. They'll also ask how you're doing and ask you some screening questions for postpartum depression . (They'll continue to monitor you for postpartum depression through your baby's 6-month checkup.)
2-month doctor appointment
At the 2-month visit , your baby will receive their first shots of DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis), Hib (haemophilus influenzae type B), IPV ( polio ), and PCV (pneumococcal disease), along with an oral vaccine for RV ( rotavirus ).
The doctor will check your baby's posture and may ask about their head control, ability to push up , and whether they're smiling voluntarily yet.
4-month doctor appointment
Your baby's 4-month checkup will include another oral dose of the rotavirus vaccine and a second DTaP vaccine. They'll also receive the second dose of the IPV, Hib, and PCV vaccines. (Some offices have combination vaccines, so your baby may receive less pokes than they would if each vaccine were given individually.)
The doctor will screen your baby for iron-deficiency anemia and lead poisoning (by asking you questions about breast milk or formula intake and environmental exposures) and test for these if necessary. They may ask what sounds your baby's making and whether they're reaching for and grabbing things . And they'll check your baby's gums and refer you to a dentist to establish dental care whenever the first tooth erupts .
6-month doctor appointment
At the 6-month checkup , the doctor may talk with you about your baby's readiness to start solids and other developmental strides, such as rolling over and babbling.
The third hepatitis B, DTaP, Hib, PCV, and IPV vaccines are typically given at 6 months, along with an oral rotavirus vaccine. Your baby can also get their first COVID vaccine now and, if it's flu season, they'll also get a flu shot . Your baby will need a second dose of the flu shot 4 weeks later.
9-month doctor appointment
At their 9-month checkup , your baby will catch up on any missed vaccinations (including a flu shot if it's flu season).
The doctor will check for any new teeth and ask you if your baby is crawling or scooting around, if they know any words , and if they can pick up objects with their thumb and forefinger.
They may remind you of the importance of babyproofing your home now that your baby is mobile.
12-month doctor appointment
At your baby's 12-month checkup , your baby's doctor will order tests to rule out iron-deficiency anemia. Depending on risk factors, they may also offer tests for tuberculosis and lead exposure , if your baby is at risk. And they may ask you if your baby points at things , says words, and stands on their own .
Your baby will also get a handful of vaccines:
- COVID, if the timing is right based on when your baby got their first shot
- Flu, if it's flu season and your baby hasn't been immunized yet.
- MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella), which can be given between 12 and 15 months and again between 4 and 6 years
- Varicella (chickenpox), given between 12 and 15 months and again between 4 and 6 years
- Hepatitis A (HepA), which they can receive between 12 months and 23 months, with a second dose at least 6 months later)
- Hib vaccine. The fourth dose can be given now or anytime between 12 and 15 months.
- PCV. The fourth dose can be given between 12 and 15 months.
Some of these shots will be combined. And your baby's doctor may spread them out between this visit and your baby's 15-month visit.
15-month doctor appointment
Your child's doctor will give your baby a fourth dose of the DTaP vaccine (given between now and 18 months), and – if they haven't already had them – your baby may now get their Hib, PCV, MMR, hepA, and varicella immunizations.
Your child may also get a flu vaccine, if it's flu season, and/or a COVID vaccine, if appropriate.
The doctor may check your baby for new teeth and apply fluoride unless you have a dentist taking care of this. And they may check your child's blood pressure, hearing, and vision.
18-month doctor appointment
At the 18-month check-up , your child's doctor will make sure your toddler is caught up on any missed immunizations and give them another round of DTaP and hepatitis A vaccines. If your child has risk factors for anemia or lead poisoning, the doctor will screen for those.
And they'll ask about your toddler's sleeping, eating, potty-training readiness , walking , and ability to follow simple commands .
24 month doctor appointment
Your toddler's 2-year checkup is a good time to make up any missed immunizations and screen for anemia and/or lead poisoning if your child has risk factors. The doctor will probably ask your child to walk so they can check their gait and coordination.
Your child's doctor may ask about potty training and temper tantrums , and they may encourage you to take your child for a dental checkup if you haven't done so yet.
How can I prepare for my baby's doctor appointments?
Here are some tips:
Consider timing
If possible, schedule your visit at a time when your baby is usually happy (fed, and not on the verge of needing a nap ). If this time coincides with a time when the office isn't usually very busy, even better! This isn't always practical – doctor's offices don't always have appointment times that coincide with your preferences, and your baby may not be on enough of a schedule to make even an educated guess at the best time for them. But it's worth a try.
Dress (both of you) comfortably
Your baby will need to be undressed for their exam, so dress them in something that's easy off/easy on. (Practicality over cuteness today!) Make sure you're dressed for the appointment, too – in something comfortable and that you can easily nurse in, if you're breastfeeding . Bring a sweater for you and your child (or a blanket for your baby), in case the office is chilly (doctor's offices often are).
Pack thoughtfully
Before your appointment, make sure your diaper bag is stocked with everything you might need. This includes diapering supplies ( diapers , wipes , a change of clothes) and feeding supplies (a bottle if you're bottle feeding and snacks if your baby is eating solids), a blankie or other lovey , burp cloths , and a pacifier if your baby uses one. Bring your current insurance information and any other paperwork, too.
Jot things down
The doctor will ask you about your baby: the number of wet and soiled diapers they have each day, how many hours they sleep, and how much and often they eat. They'll ask about motor and language skills, too. When did your baby start rolling over, sitting up, and crawling? Are they babbling yet? It's a good idea to keep ongoing notes about these things, or jot them down before your visit.
Importantly, bring a list of questions you have. These visits are the perfect time to get them answered!
Make sure you tell the doctor about any concerns, too, no matter how small they seem. Do you wonder if your baby sometimes doesn't hear you or if they favor one side of their body when they crawl across the floor? Are you worried that your baby should be walking or talking by now or that they often wake up screaming ?
Remember that you and the doctor are partners in managing your baby's health. Don't hesitate to give your perspective, and make sure your questions are addressed.
Learn more:
- Everything you need to know about baby poop
- How your baby's skull, skeleton, and bones develop after birth
- The importance of tummy time for your baby
- How to make shots less painful for your baby
Was this article helpful?
Vaccine schedule for babies and kids

Postpartum depression screening for new moms

Hearing loss in babies

How to raise a smart baby

BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies .
AAP. 2023. AAP schedule of well-child care visits. The American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/family-life/health-management/Pages/Well-Child-Care-A-Check-Up-for-Success.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
AAP. 2023. All about the recommended immunization schedules. The American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/safety-prevention/immunizations/Pages/Recommended-Immunization-Schedules.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
AAP. 2023. Recommended childhood and adolescent immunization schedule for 2023. The American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/news/Pages/recommended-childhood-and-adolescent-immunization-schedule-for-2023.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
AAP. 2023.Vaccines Opens a new window your child needs by age 6. The American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/safety-prevention/immunizations/Pages/Your-Babys-First-Vaccines.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
AAP. 2022. Why your newborn needs a vitamin K shot. The American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/prenatal/delivery-beyond/Pages/Where-We-Stand-Administration-of-Vitamin-K.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
AAP. 2022. Your child's checkups. The American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/Your-Childs-Checkups/Pages/default.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
CDC. 2022. Growth charts. National Center for Health Statistics. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/index.htm Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
CDC. 2023. Stay up to date with COVID-19 vaccines. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/stay-up-to-date.html Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
Nemours KidsHealth. 2022. Your child's checkup: 1 month. https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/checkup-1mo.html Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]

Where to go next

Your Guide to Well-Baby Visits
Medical review policy, latest update:, what are well-baby visits and why are they so important, when will my child's well-baby visits happen, read this next, what you can expect at well-baby visits, tips on making the most of well-baby visits, time it right, make a checklist, write down your questions, have some answers, too, dress baby for success.
What to Expect the First Year , 3rd edition, Heidi Murkoff. WhatToExpect.com, Your Baby's Vaccine Schedule: What Shots Should Your Child Get When? , January 2021. American Academy of Pediatrics, AAP Schedule of Well-Child Care Visits , September 2021. American Academy of Pediatrics, Checkup Checklist: 1 Month Old , September 2021. KidsHealth From Nemours, Your Child's Checkup: 1 Month , April 2021.
Go to Your Baby's Age
Trending on what to expect, the covid-19 vaccine for infants, toddlers and young children, how to create a night shift system when you have a newborn, ⚠️ you can't see this cool content because you have ad block enabled., when do babies start laughing, baby-led weaning, what happens in the ‘4th trimester’ (and is it a real thing).

Personalize Your Experience
Log in or create an account for a personalized experience based on your selected interests.
Already have an account? Log In
Free standard shipping is valid on orders of $45 or more (after promotions and discounts are applied, regular shipping rates do not qualify as part of the $45 or more) shipped to US addresses only. Not valid on previous purchases or when combined with any other promotional offers.
Register for an enhanced, personalized experience.
Receive free access to exclusive content, a personalized homepage based on your interests, and a weekly newsletter with topics of your choice.
Home / Parenting, Kids & Teens / Quick guide to your infant’s first pediatrician visits
Quick guide to your infant’s first pediatrician visits
Please login to bookmark.

Frequent checkups with a health care provider are an important part of your baby’s first few years. These checkups — often called well-child visits — are a way for you and your child’s health care provider to keep tabs on your child’s health and development, as well as spot any potential problems. Well-child visits also give you a chance to discuss any questions or concerns you might have and get advice from a trusted source on how to provide the best possible care for your child.
The benefit of seeing your child’s provider regularly is that each visit adds critical information to your child’s health history. Over time, you and the provider will get a good idea of your child’s overall health and development.
In general, the provider will be more attentive to your child’s pattern of growth over time, rather than to specific one-time measurements. Typically what you’ll see is a smooth curve that arcs upward as the years go by. Regularly reviewing your child’s growth chart can also alert you and the provider to unexpected delays in growth or changes in weight that may suggest the need for additional monitoring.
Each health care provider does things a bit differently, but here’s what will generally be on the agenda during your first well-child exams.
Body measurements
Checkups usually begin with measurements. During first-year visits, a nurse or your baby’s health care provider will measure and record your baby’s length, head circumference and weight.
Your child’s measurements will be plotted on his or her growth chart. This will help you and the provider see how your child’s size compares with that of other children the same age. Try not to fixate on the percentages too much, though. All kids grow and develop at different rates. In addition, babies who take breast milk gain weight at a different rate than do babies who are formula-fed.
Keep in mind that a child who’s in the 95th percentile for height and weight isn’t necessarily healthier than a child who’s in the fifth percentile. What’s most important is steady growth from one visit to the next. If you have questions or concerns about your child’s growth rate, discuss them with your child’s provider.
Physical exam
Your child’s health care provider will give your child a thorough physical exam and check his or her reflexes and muscle tone. Be sure to mention any concerns you have or specific areas you want the doctor to check out.
Here are the basics of what providers commonly check for during an exam:
- Head — In the beginning, your child’s health care provider will likely check the soft spots (fontanels) on your baby’s head. These gaps between the skull bones give your baby’s brain plenty of room to grow in the coming months. They’re safe to touch and typically disappear within two years, when the skull bones fuse together. The health care provider may also check baby’s head for flat spots. A baby’s skull is soft and made up of several movable plates. If his or her head is left in the same position for long periods of time, the skull plates might move in a way that creates a flat spot.
- Ears — Using an instrument called an otoscope, the health care provider can see in your child’s ears to check for fluid or infection in the ears. The provider may observe your child’s response to various sounds, including your voice. Be sure to tell the provider if you have any concerns about your son’s or daughter’s ability to hear or if there’s a history of childhood deafness in your family. Unless there’s cause for concern, a formal hearing evaluation isn’t usually needed at a well-child exam.
- Eyes — Your child’s health care provider may use a flashlight to catch your child’s attention and then track his or her eye movements. The provider may also check for blocked tear ducts and eye discharge and look inside your child’s eyes with a lighted instrument called an ophthalmoscope. Be sure to tell the provider if you’ve noticed that your child is having any unusual eye movements, especially if they continue beyond the first few months of life.
- Mouth — A look inside your baby’s mouth may reveal signs of oral thrush, a common, and easily treated, yeast infection. The health care provider might also check your baby’s mouth for signs of tongue-tie (ankyloglossia), a condition that affects the tongue’s range of motion and can interfere with a baby’s oral development as well as his or her ability to breast-feed.
- Skin — Various skin conditions may be identified during the exam, including birthmarks, rashes, and jaundice, a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes. Mild jaundice that develops soon after birth often disappears on its own within a week or two. Cases that are more severe may need treatment.
- Heart and lungs — Using a stethoscope, your child’s health care provider can listen to your child’s heart and lungs to check for abnormal heart sounds or rhythms or breathing difficulties.
- Abdomen, hips and legs — By gently pressing a child’s abdomen, a health care provider can detect tenderness, enlarged organs, or an umbilical hernia, which occurs when a bit of intestine or fatty tissue near the navel breaks through the muscular wall of the abdomen. Most umbilical hernias heal by the toddler years without intervention. The provider may also move your child’s legs to check for dislocation or other problems with the hip joints, such as dysplasia of the hip joint.
- Genitalia — Your child’s care provider will likely inspect your son’s or daughter’s genitalia for tenderness, lumps or other signs of infection. The provider may also check for an inguinal hernia, which results from a weakness in the abdominal wall.
For girls, the doctor may ask about vaginal discharge. For boys, the provider will make sure a circumcised penis is healing well during early visits. The provider may also check to see that both testes have descended into the scrotum and that there’s no fluid-filled sac around the testes, a condition called hydrocele.
Your child’s provider will likely ask you about your child’s eating habits. If you’re breastfeeding, the provider may want to know how often you’re feeding your baby during the day and night and whether you’re having any problems. If you’re pumping, the provider may offer suggestions for managing pumping frequency and storing breast milk. If you’re formula-feeding, the provider will likely want to know how often you feed and how many ounces of formula your baby takes at each feeding. In addition, the provider may discuss with you your baby’s need for vitamin D and iron supplements.
Bowel and bladder function
In the first few visits, your child’s health care provider will likely also ask how many wet diapers and bowel movements your baby produces a day. This information offers clues as to whether your baby is getting enough to eat.
Sleeping status
Your child’s health care provider may ask you questions about your child’s sleep habits, such as your regular bedtime routine and how many hours your child is sleeping during the day and night. Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns you may have about your child’s sleep, such as getting your baby to sleep through the night. Your child’s provider may also help you figure out how to find rest for yourself, especially in the early baby months.
Development
Your child’s development is important, too. The health care provider will monitor your child’s development in the following five main areas.
- Gross motor skills — These skills, such as sitting, walking and climbing, involve the movement of large muscles. Your child’s health care provider may ask you how well your baby can control his or her head. Is your baby attempting to roll over? Is your baby trying to sit on his or her own? Is your child starting to walk or throw a ball? Can your toddler walk up and down steps?
- Fine motor skills — These skills involve the use of small muscles in the hand. Does your baby reach for objects and bring them to his or her mouth? Is your baby using individual fingers to pick up small objects?
- Personal and social skills — These skills enable a child to interact and respond to his or her surroundings. Your child’s health care provider may ask if your baby is smiling. Does your baby relate to you with joy and enthusiasm? Does he or she play peekaboo?
- Language skills — These skills include hearing, understanding and use of language. The health care provider may ask if your baby turns his or her head toward voices or other sounds. Does your baby laugh? Is he or she responding to his or her name?
- Cognitive skills — These skills allow a child to think, reason, solve problems and understand his or her surroundings. Your child’s provider might ask if your baby can bang together two cubes or search for a toy after seeing you hide it.
Vaccinations
Your baby will need a number of scheduled vaccinations during his or her first years. The health care provider or a nurse will explain to you how to hold your baby as he or she is given each shot. Be prepared for possible tears. Keep in mind, however, that the pain caused by a shot is typically short-lived but the benefits are long lasting.
Your child’s provider may talk to you about safety issues, such as the importance of placing your baby to sleep on his or her back and using a rear-facing infant car seat as long as possible.
Questions and concerns
During your son’s or daughter’s checkups, it’s likely that you’ll have questions, too. Ask away! Nothing is too trivial when it comes to caring for your baby. Write down questions as they arise between appointments so that you’ll be less likely to forget them when you’re at your child’s checkup.
Also, don’t forget your own health. If you’re feeling depressed, stressed-out, run-down or overwhelmed, describe what’s happening. Your child’s provider is there to help you, too.
Before you leave the health care provider’s office, make sure you know when to schedule your child’s next appointment. If possible, set the next appointment before you leave the provider’s office. If you don’t already know, ask how to reach your child’s provider in between appointments. You might also ask if the provider has a 24-hour nurse information service. Knowing that help is available when you need it can offer peace of mind.

Relevant reading
I'm a Paramedic
A lively, illustrated introduction to the essential work of paramedics as community helpers and health heroes.

Discover more Parenting, Kids & Teens content from articles, podcasts, to videos.
Want more children’s health and parenting information? Sign up for free to our email list.
Children’s health information and parenting tips to your inbox.
Sign-up to get Mayo Clinic’s trusted health content sent to your email. Receive a bonus guide on ways to manage your child’s health just for subscribing.
You May Also Enjoy

by Pat McCaw, M.D.

by Guillaume Federighi AKA Hey Gee

Privacy Policy
We've made some updates to our Privacy Policy. Please take a moment to review.
Internet Explorer Alert
It appears you are using Internet Explorer as your web browser. Please note, Internet Explorer is no longer up-to-date and can cause problems in how this website functions This site functions best using the latest versions of any of the following browsers: Edge, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, or Safari . You can find the latest versions of these browsers at https://browsehappy.com
- Publications
- HealthyChildren.org
Shopping cart
Order Subtotal
Your cart is empty.
Looks like you haven't added anything to your cart.
- Career Resources
- Philanthropy
- About the AAP
- Safe Administration of Medication in School: Policy Statement
- Policy Outlines Steps to Take When Students Need Medicine at School
- When Your Child Needs to Take Medication at School
- American Academy of Pediatrics Updates Guidance on Medication Administration In School
- News Releases
- Policy Collections
- The State of Children in 2020
- Healthy Children
- Secure Families
- Strong Communities
- A Leading Nation for Youth
- Transition Plan: Advancing Child Health in the Biden-Harris Administration
- Health Care Access & Coverage
- Immigrant Child Health
- Gun Violence Prevention
- Tobacco & E-Cigarettes
- Child Nutrition
- Assault Weapons Bans
- Childhood Immunizations
- E-Cigarette and Tobacco Products
- Children’s Health Care Coverage Fact Sheets
- Opioid Fact Sheets
- Advocacy Training Modules
- Subspecialty Advocacy Report
- AAP Washington Office Internship
- Online Courses
- Live and Virtual Activities
- National Conference and Exhibition
- Prep®- Pediatric Review and Education Programs
- Journals and Publications
- NRP LMS Login
- Patient Care
- Practice Management
- AAP Committees
- AAP Councils
- AAP Sections
- Volunteer Network
- Join a Chapter
- Chapter Websites
- Chapter Executive Directors
- District Map
- Create Account
- Tools and Templates
- Common Patient Concerns
- Personnel Management
- Patient Scheduling
- Information Technology
- OSHA Regulations
- In Office Labs
- Preventing Fraud and Abuse
- Protecting the Practice
- Medical Malpractice
- Family-Professional Partnerships
- Low Health Literacy
- Shared Decision Making
- Soliciting Feedback from Families
- Bright Futures
- Medical Home
Preventive Care/Periodicity Schedule
The Bright Futures/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Recommendations for Preventive Pediatric Health Care , also known as the "Periodicity Schedule," is a schedule of screenings and assessments recommended at each well-child visit from infancy through adolescence.
Each child and family is unique; therefore, these recommendations are designed for the care of children who are receiving nurturing parenting, have no manifestations of any important health problems, and are growing and developing in a satisfactory fashion. Additional visits also may become necessary if circumstances suggest concerns. Developmental, psychosocial and chronic disease issues for children and adolescents may require frequent counseling and treatment visits separate from preventive care visits.
These recommendations represent a consensus by the AAP and Bright Futures. The AAP continues to emphasize the great importance of continuity of care in comprehensive health supervision and the need to avoid fragmentation of care. Refer to the specific guidance by age as listed in the Bright Futures Guidelines (Hagan JF, Shaw JS, Duncan PM, eds. Bright Futures: Guidelines for Health Supervision of Infants, Children and Adolescents. 4th ed. American Academy of Pediatrics; 2017).
Recommendations for Preventive Pediatric Health Care— Periodicity Schedule (PDF)
For more background information, click here to review the related Bright Futures Guidelines , 4th Edition Evidence and Rationale chapter.
At selected visits, Bright Futures recommends universal screening for issues such as child development, maternal or adolescent depression, behavior/social/emotional concerns, or oral health. A number of screening tools have been developed and are commonly used. Click here for a list of links to tools for use at specific Bright Futures visits at the discretion of the health care professional. The links go to the author and/or the owner to ensure accessibility to the most up-to-date version of the specific tool.
For implementation and coding information for each visit on the Periodicity Schedule, please see the Bright Futures and Preventive Medicine Coding Fact Sheet .
Review and comply with any copyright and permissions requirements before use.
- The HIV screening recommendation has been updated to extend the upper age limit from 18 to 21 years (to account for the range in which the screening can take place) to align with recommendations of the US Preventive Services Task Force and AAP policy (“Adolescents and Young Adults: The Pediatrician’s Role in HIV Testing and Pre- and Postexposure HIV Prophylaxis”).
- Footnote 30 has been updated to read as follows: “Screen adolescents for HIV at least once between the ages of 15 and 21, making every effort to preserve confidentiality of the adolescent, as per ‘Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection: Screening’ ( https://www. uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/human-immunodeficiency-virus-hiv-infection-screening ); after initial screening, youth at increased risk of HIV infection should be retested annually or more frequently, as per ‘Adolescents and Young Adults: The Pediatrician’s Role in HIV Testing and Pre- and Postexposure HIV Prophylaxis’ ( https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2021-055207 ).”
Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- Assessing risk for hepatitis b virus (HBV) infection has been added to occur from newborn to 21 years (to account for the range in which the risk assessment can take place) to be consistent with recommendations of the USPSTF and the 2021–2024 edition of the AAP Red Book: Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases .
- Footnote 31 has been added to read as follows: “Perform a risk assessment for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection according to recommendations per the USPSTF and in the 2021– 2024 edition of the AAP Red Book: Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases , making every effort to preserve confidentiality of the patient.”
Sudden Cardiac Arrest and Sudden Cardiac Death
- Assessing risk for sudden cardiac arrest and sudden cardiac death has been added to occur from 11 to 21 years (to account for the range in which the risk assessment can take place) to be consistent with AAP policy (“Sudden Death in the Young: Information for the Primary Care Provider”).
- Footnote 33 has been added to read as follows: “Perform a risk assessment, as appropriate, per ‘ Sudden Death in the Young: Information for the Primary Care Provider ’.”
Depression and Suicide Risk
- Screening for suicide risk has been added to the existing depression screening recommendation to be consistent with the GLAD-PC and AAP policy.
- Footnote 16 has been updated to read as follows: “Screen adolescents for depression and suicide risk, making every effort to preserve confidentiality of the adolescent. See ‘ Guidelines for Adolescent Depression in Primary Care (GLAD-PC): Part I. Practice Preparation, Identification, Assessment, and Initial Management ’, ‘ Mental Health Competencies for Pediatric Practice ’, ‘ Suicide and Suicide Attempts in Adolescents ’, and ‘ The 21st Century Cures Act & Adolescent Confidentiality ’.”
Behavioral/Social/Emotional
- The Psychosocial/Behavioral Assessment recommendation has been updated to Behavioral/Social/Emotional Screening (annually from newborn to 21 years) to align with AAP policy, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (Women’s Preventive Services Initiative) recommendations, and the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry guidelines.
- Footnote 14 has been updated to read as follows: “Screen for behavioral and social-emotional problems per ‘ Promoting Optimal Development: Screening for Behavioral and Emotional Problems ’, ‘ Mental Health Competencies for Pediatric Practice ’, ‘ Clinical Practice Guideline for the Assessment and Treatment of Children and Adolescents With Anxiety Disorders ’, and ‘ Screening for Anxiety in Adolescent and Adult Women: A Recommendation From the Women’s Preventive Services Initiative ’. The screening should be family centered and may include asking about caregiver emotional and mental health concerns and social determinants of health, racism, poverty, and relational health. See ‘ Poverty and Child Health in the United States ’, ‘ The Impact of Racism on Child and Adolescent Health ’, and ‘ Preventing Childhood Toxic Stress: Partnering With Families and Communities to Promote Relational Health ’.”
Fluoride Varnish
- Footnote 37 has been updated to read as follows: “The USPSTF recommends that primary care clinicians apply fluoride varnish to the primary teeth of all infants and children starting at the age of primary tooth eruption. Once teeth are present, apply fluoride varnish to all children every 3 to 6 months in the primary care or dental office based on caries risk. Indications for fluoride use are noted in ‘ Fluoride Use in Caries Prevention in the Primary Care Setting ’.”
Fluoride Supplementation
- Footnote 38 has been updated to read as follows: “If primary water source is deficient in fluoride, consider oral fluoride supplementation. See ‘ Fluoride Use in Caries Prevention in the Primary Care Setting ’.”
Developmental
- Footnote 12 has been updated to read as follows: “Screening should occur per ‘ Promoting Optimal Development: Identifying Infants and Young Children With Developmental Disorders Through Developmental Surveillance and Screening ’.”
Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Footnote 13 has been updated to read as follows: “Screening should occur per ‘ Identification, Evaluation, and Management of Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder ’.”
Hepatitis C Virus Infection
- Screening for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection has been added to occur at least once between the ages of 18 and 79 years (to be consistent with recommendations of the US Preventive Services Task Force and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention).
- Footnote 32 has been added to read as follows: “All individuals should be screened for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection according to the USPSTF and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations at least once between the ages of 18 and 79. Those at increased risk of HCV infection, including those who are persons with past or current injection drug use, should be tested for HCV infection and reassessed annually.”
Maternal Depression
- Footnote 16 has been updated to read as follows: “Screening should occur per ‘ Incorporating Recognition and Management of Perinatal Depression Into Pediatric Practice ’.”
Blood Pressure
- Footnote 6 has been updated to read as follows: "Screening should occur per 'Clinical Practice Guideline for Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents.' Blood pressure measurement in infants and children with specific risk conditions should be performed at visits before age 3 years."
- Footnote 24 has been updated to read as follows: "Perform risk assessment or screening, as appropriate, per recommendations in the current edition of the AAP Pediatric Nutrition: Policy of the American Academy of Pediatrics (Iron chapter)."
- Footnote 25 has been updated to read as follows: "For children at risk of lead exposure, see 'Prevention of Childhood Lead Toxicity' and 'Low Level Lead Exposure Harms Children: A Renewed Call for Primary Prevention'."
- Timing and follow-up of the screening recommendations for hearing during the infancy visits have been delineated.
- The accompanying footnotes (#8 & #9) has been updated and added.
- Adolescent hearing risk assessment has changed to screening once during each time period
- An accompanying footnote (#10) has been added.
Psychosocial/Behavorial Assessments
- An accompanying footnote (#13) has been added.
Tobacco, Alcohol or Drug Use Assessment
- The header was updated to be consistent with recommendations.
Depression Screening
- Adolescent depression screening begins routinely at 12 years of age.
Maternal Depression Screening
- Screening for maternal depression at 1-, 2-, 4-, and 6-month visits has been added.
- An accompanying footnote (#16) has been added.
Newborn Blood
- Timing and follow-up of the newborn blood screening recommendations have been delineated.
- The accompanying footnotes (#19 & #20) has been updated and added.
Newborn Bilirubin
- Screening for bilirubin concentration at the newborn visit has been added.
- An accompanying footnote (#21) has been added.
DyslipIdemia
- Screening for dyslipidemia has been updated to occur once between 9 and 11 years of age, and once between 17 and 21 years of age.
Sexually Transmitted Infection (STIs)
- An accompanying footnote (#29) has been added.
- Screening for HIV has been updated to occur once between 15 and 18 years of age.
- A subheading has been added for the HIV universal recommendation to avoid confusion with STIs selective screening recommendation.
- An accompanying footnote (#30) has been added.
Oral Health
- Assessing for a dental home has been updated to occur at the 12-month and 18-month through 6-year visits.
- The accompanying footnotes (#32 & #33) have been updated.
- A subheading has been added for fluoride supplementation, with a recommendation from the 6-month through 12-month and 18-month through 16-year visits.
- An accompanying footnote (#35) has been added.
Last Updated
American Academy of Pediatrics
Official websites use .gov
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Catch Up on Well-Child Visits and Recommended Vaccinations

Many children missed check-ups and recommended childhood vaccinations over the past few years. CDC and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommend children catch up on routine childhood vaccinations and get back on track for school, childcare, and beyond.

Making sure that your child sees their doctor for well-child visits and recommended vaccines is one of the best things you can do to protect your child and community from serious diseases that are easily spread.
Well-Child Visits and Recommended Vaccinations Are Essential

Well-child visits and recommended vaccinations are essential and help make sure children stay healthy. Children who are not protected by vaccines are more likely to get diseases like measles and whooping cough . These diseases are extremely contagious and can be very serious, especially for babies and young children. In recent years, there have been outbreaks of these diseases, especially in communities with low vaccination rates.
Well-child visits are essential for many reasons , including:
- Tracking growth and developmental milestones
- Discussing any concerns about your child’s health
- Getting scheduled vaccinations to prevent illnesses like measles and whooping cough (pertussis) and other serious diseases

It’s particularly important for parents to work with their child’s doctor or nurse to make sure they get caught up on missed well-child visits and recommended vaccines.
Routinely Recommended Vaccines for Children and Adolescents
Getting children and adolescents caught up with recommended vaccinations is the best way to protect them from a variety of vaccine-preventable diseases . The schedules below outline the vaccines recommended for each age group.
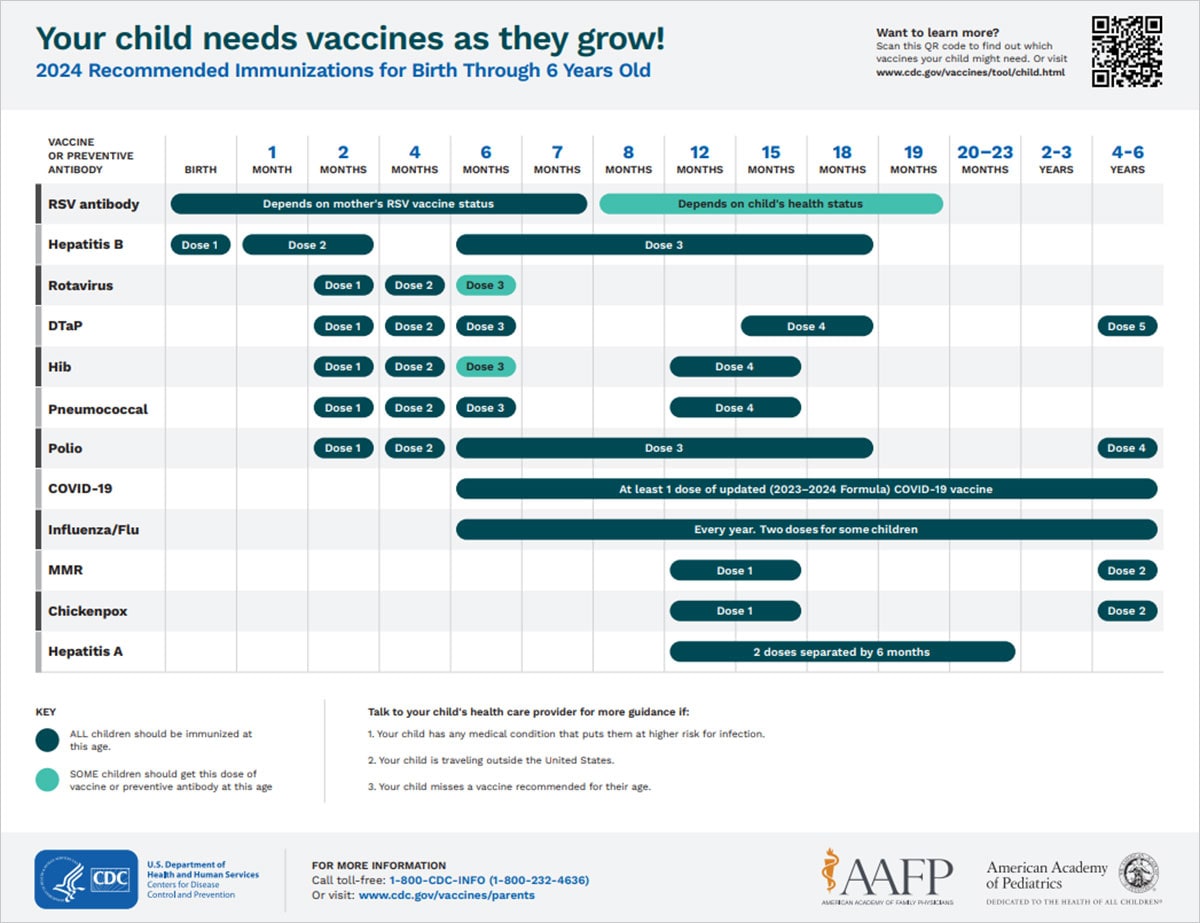
See which vaccines your child needs from birth through age 6 in this easy-to-read immunization schedule.
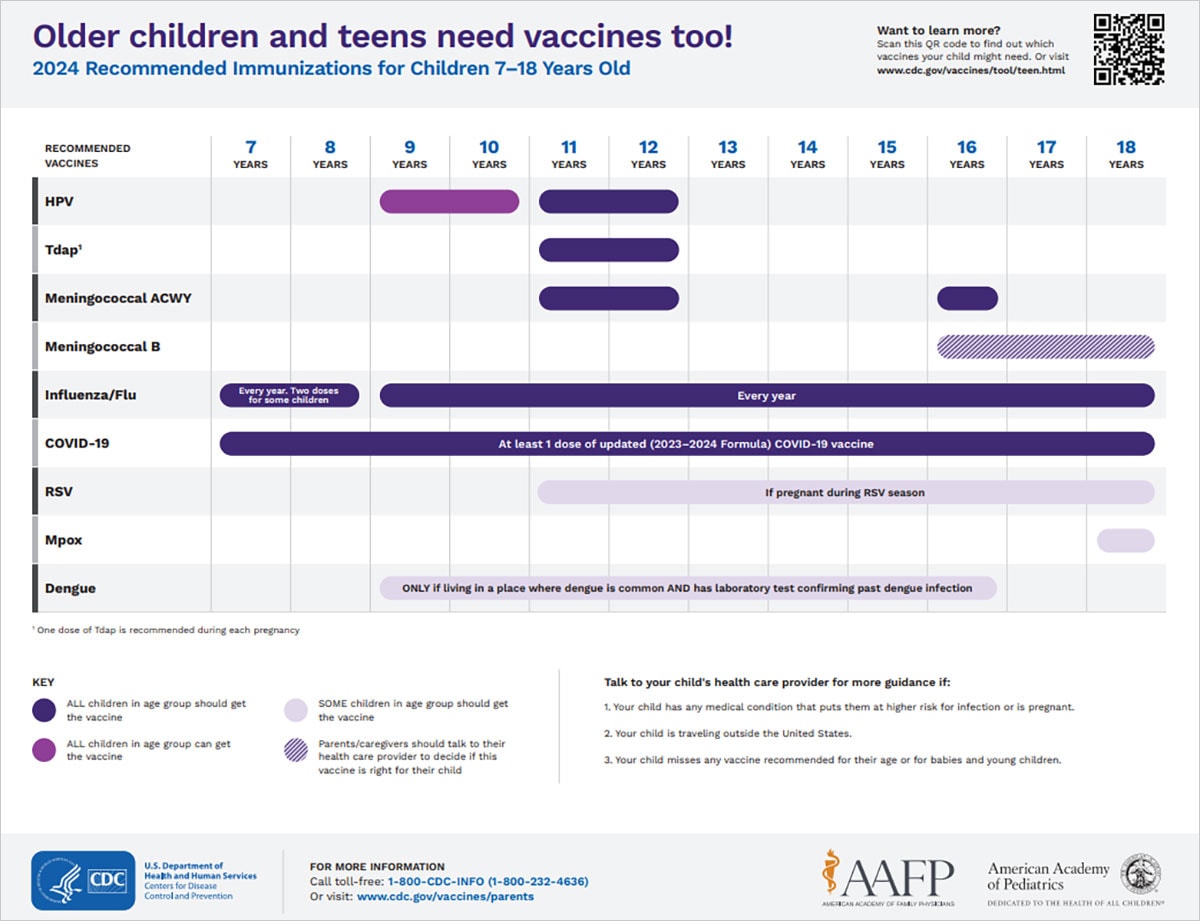
See which vaccines your child needs from ages 7 through 18 in this easy-to-read immunization schedule.
The Vaccines for Children (VFC) program provides vaccines to eligible children at no cost. This program provides free vaccines to children who are Medicaid-eligible, uninsured, underinsured, or American Indian/Alaska Native. Check out the program’s requirements and talk to your child’s doctor or nurse to see if they are a VFC provider. You can also find a VFC provider by calling your state or local health department or seeing if your state has a VFC website.
COVID-19 Vaccines for Children and Teens
Everyone aged 6 months and older can get an updated COVID-19 vaccine to help protect against severe illness, hospitalization and death. Learn more about making sure your child stays up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines .
- Vaccines & Immunizations
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Metro accepts BlueCross BlueShield healthcare plans as an in-network provider. Learn More
Well-Child Visit and Vaccine Schedule
Vaccines are essential for pediatric wellness.
Vaccines prevent serious illness by exposing the body to a weakened or inactive form of a virus or bacteria. This immunization process supercharges the body’s immune system to recognize and defend against natural, but harmful microorganisms that cause disease. Those who are immunized are less likely to spread the disease to others who may be more vulnerable, saving millions of lives each year. Talk to your child’s doctor if you have any questions or concerns about your child’s vaccine schedule.
Book a Well Visit
Metro Pediatrics strongly urges children to receive the vaccines recommended for their age at regularly scheduled visits. Our pediatricians follow the routine schedule and guidelines approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). Learn more about the importance of a well-child visit.
New patients are always welcome.

Visit Age = By 1 Week
What to expect.
- Weight check
- Feeding check
- Hepatitis B (if not given in hospital)
Visit Age = 2 Weeks
- State newborn screen
- Hepatitis B (if not given in hospital or at first visit)
- Well-child health screen | Spanish
Visit Age = 1 Month
- Discuss Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
- Postnatal depression screen | Spanish | Russian | Vietnamese
Visit Age = 2 Months
- Hepatitis B
- Pneumococcal
- Rotavirus (by mouth)
Visit Age = 4 Months
Visit Age = 6 Months
- Starting at 6 months of age, all patients should get an annual influenza vaccine in fall/winter. They should also start the COVID series per CDC, ACIP, and OHA recommendations.
- Home safety checklist
Visit Age = 9 Months
- Fluoride varnish (if patient has teeth)
- Standardized development screen | Spanish
Visit Age = 12 Months
- Vision screen
- Hemoglobin level
- Hepatitis A
Visit Age = 15 Months
- Hemoglobin level (if low at 12 months)
- Fluoride varnish
- Standardized social-emotional screen | Spanish | Vietnamese

Visit Age = 18 Months
- Standardized autism screen | Spanish | Russian | Vietnamese
Visit Age = 2 Years
Visit age = 2½ years, visit age = 3 years.
- Blood pressure check
Visit Age = 4 Years
- Hearing screen
Visit Age = 5 Years
Visit age = 6-10 years, annually.
- Hearing screen (6, 8, and 10 years)
- Lipid panel screen (once between 9-11 years)
- Well-child health screen | Spanish
- Additional adolescent screening | Spanish | Russian | Vietnamese
- Sports pre-participation questionnaire | Spanish | Russian | Vietnamese
Visit Age = 11-13 Years, Annually
- Hearing screen (12 years)
- Meningococcal
- HPV (2- or 3-shot series based on age)
Visit Age = 14+ Years, Annually
Patients 14+ must provide approval for disclosure of their health information according to Oregon law.
- Hearing screen (16 years)
- Lipid panel screen (once between 16-18 years)
- STD/HIV screen (16-18 years)
- Meningococcal booster (at or after age 16)
- Option of meningococcal B vaccine (at or after age 16)
- Teen health screen | Spanish
Our Comfort Promise
We want children to feel as comfortable as possible during their vaccinations and learn healthy ways to cope with discomfort and stress. Our Comfort Promise offers a menu of choices to help your child get through the needle pokes. From distraction techniques to numbing sprays, and comfort positions, our team will help your little one feel better about this important wellness routine.
Great Vaccine App
Apple devices: Download on the App Store Android devices: Get it on Google Play
Definitions
- Hemoglobin = checks for anemia
- Lipid panel screen = checks cholesterol and triglyceride levels
- DTaP = combination vaccine containing diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (whooping cough)
- Hib = Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine
- HPV = Human papillomavirus vaccine
- MMR = combination vaccine containing measles, mumps, and rubella
- Pentacel = combination vaccine containing DTaP, polio, and Hib
- Tdap = booster of tetanus and pertussis
- Varicella = chickenpox vaccine
Vaccine Resources
- HealthyChildren .org (American Academy of Pediatrics)
- Boost Ore g on
- Vaccine Education Center (Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia)
- National Network for Immunization Information
- Vaccinate Your Baby
- Voices for Vaccines
- Vaccine Information Statements (CDC)
Vaccine FAQs
What is in a vaccine.
A vaccine contains:
- Suspending fluid like saline or water and a piece of the virus or bacteria that we are protecting against. These two components make up the majority of the fluid injected during a vaccination.
- Preservatives or stabilizers to make sure that the vaccine is safe and will not cause transmission of unwanted bacteria or viruses. As much as possible, we use vaccines that are preservative-free, but that is not an option for all vaccines. The amount of preservatives or stabilizers in vaccines is very small—you consume more mercury by eating ONE can of tuna than by receiving all of your lifetime vaccines!
- Adjuvants like aluminum to increase the body’s immune response to the vaccine, ensuring stronger, longer protection. Essentially they irritate the body a little to draw the attention of our immune system to the virus or bacteria we are protecting against. Adjuvants are at very small concentrations in vaccines and are very safe in our bodies. Aluminum is naturally occurring in the environment, so we are exposed to it just by eating and drinking. The vaccines given in the first 6 months of life contain only 4.4 milligrams (mg) of aluminum. In comparison, a breast fed baby consumes 7 mg of aluminum just by nursing in the first 6 months of life. A baby who eats formula for 6 months ingests 38 mg, and a baby who eats soy formula ingests 117 mg of aluminum.
Do vaccines cause autism?
NO, absolutely not! Vaccines do NOT cause autism. The concern about a connection between vaccines and autism originated from a study published in The Lancet in 1998 by a scientist named Andrew Wakefield. He suggested that the MMR vaccine caused autism. Other researchers attempted to replicate his findings and no one could. It was later revealed that he was paid to report this information and that his study was fabricated. The article was retracted from the journal, and he lost his medical license. Although the study was a complete fraud, concern about the connection between vaccines and autism was taken seriously. Many well-designed scientific studies have been done since that clearly disprove that vaccines cause autism. In fact, we are learning more and more about autism. Some fascinating studies are revealing symptoms of autism that exist before babies are old enough for vaccines, maybe even in utero. The true cause of autism is being investigated, but we feel very confident that it is NOT from vaccines.
Do vaccines overwhelm the immune system? How is it safe to give so many at one time?
Our world is teeming with bacteria and microorganisms! Just by being on earth and breathing, eating, and touching our environment, we are exposed to bacteria and viruses every minute. Our immune system’s function is to identify these bacteria and viruses and to remember them to protect us from future illnesses. The number of bacteria and viruses in vaccines is a small drop in the bucket compared to what our immune systems recognize on a daily basis. Based on the number of antibodies in the blood, babies’ immune systems could likely respond to 10,000 vaccines at one time — so much for a weak immune system, right?!
Why are there so many vaccines nowadays?
Many parents express concern about the number of vaccines. Although the number of vaccines has increased over time, the number of components in those vaccines has decreased. Advances in protein chemistry have resulted in better, simpler vaccines. Whereas previously one vaccine like smallpox contained about 200 proteins, the 11 routinely recommended vaccines today contain fewer than 130 proteins in total.
Won’t my baby get the needed protection from breastmilk?
We strongly encourage breastfeeding when possible for the many benefits it offers to moms and to babies, but breastmilk does not ensure long-lasting immunity. Immunity is defined as the presence of an antibody to a virus or bacteria. Antibodies are the part of our immune system that fights off disease, and antibodies are specific to that certain disease.
Immunity can be passive or active. Passive immunity means that the antibody was given to the body (for example, through mom’s placenta or breastmilk), but not created by the body. Passive immunity lasts for only weeks to months. Active immunity means that the immune system was exposed to the virus or bacteria and created antibodies. Antibodies created by active immunity ensure long-lasting immunity.
Do vaccines contain dangerous components like formaldehyde, thimerosal (mercury), or aluminum?
See the information above about what components are in vaccines and the small quantity of those additions.
Formaldehyde, mercury, and aluminum can cause health problems depending on the amount that we are exposed to. If they are in vaccines, they are in microscopic amounts that do not affect our health. As discussed above, you get more mercury from ONE can of tuna than all of your vaccines. Babies get more aluminum in their body by nursing or drinking formula than from vaccines. Our own metabolic system naturally creates more formaldehyde in our body than the amount in vaccines. The amount of these chemicals in vaccines does not decrease the safety of the vaccines. In fact, it increases the safety of vaccines by ensuring that they are free of unwanted bacteria and viruses and that they are as effective as possible.
Are the risks of vaccines greater than the benefits?
Vaccines have been so effective at eradicating disease that the side effects of vaccines now sometimes feel more intimidating than the actual disease they are preventing. However, don’t be fooled. The reasons that vaccines are given for these specific illnesses is because they are illnesses that can cause very significant morbidity (illness) and mortality (death). The majority of children have no side effects from vaccines beyond a few tears from a needle poke. The children who do experience side effects from vaccines generally get relief simply with Tylenol. Occasionally children can have more intense allergies or reactions to vaccines, but the risk of that is less than one in a million — a lot less than the chance of contracting vaccine-preventable illnesses! So NO, the risks of vaccines do not outweigh the benefits.
Vaccines can infect you with the illness they are meant to prevent, right?
This is a common concern that we hear regarding the flu shot. The bacteria or virus in the vaccine is not a functioning living organism. The majority of vaccines contain just a little microscopic piece of the outside shell of the virus or bacteria. That tiny piece cannot cause an infection. Other immunizations are called live attenuated vaccines. In this case, the virus or bacteria is alive, but it has been modified (or attenuated) so that it cannot actually cause illness. You may get some achiness or a low-grade fever as your immune system reacts to vaccines, but you CANNOT get the illness that is being prevented by the vaccine.
How can vaccinating my child help other people?
There are people in our communities who cannot safely receive vaccines or do not have strong enough immune systems to become protected by vaccines (for example, infants, elderly, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems like cancer patients). These people depend on what we call “herd immunity.” When enough people in a community are immunized, the ability of a bacteria or virus to spread through the community decreases. In essence, this “herd immunity” is able to protect the people among us who cannot receive vaccines. If enough healthy people choose not to vaccinate, everyone else in the community is put at risk for outbreaks. We strongly believe that vaccines benefit the individual and the health of the community. Please do you part to keep yourself and those around you healthy!
Aren’t infection rates low enough in the US that my child would be safe?
Unfortunately, no. The illnesses that vaccines prevent are not fully eradicated in the US or anywhere else in the world. As our ability to travel increases, exposures and spread of disease increases. Even if you are not planning to travel, your neighbor or the stranger next to you may have just returned from abroad. If vaccine refusal rates increase, herd immunity will decrease and the risk of outbreaks will rise. Outbreaks can happen anywhere at any time.
Can I wait until my baby is older?
We strongly recommend vaccinating on the recommended schedule. No vaccine can be put on the schedule until there is data that it does not affect the safety or efficacy of other vaccines on the schedule. When families opt to modify the vaccine schedule, it introduces more potential for vaccine error and vaccine interactions. It creates more pokes and traumatic experiences for kids. We don’t like scaring kids or creating needle phobia! But most importantly, it leaves kids unprotected from preventable illnesses during a time when they are most vulnerable.
Doctor Visits
Make the Most of Your Child’s Visit to the Doctor (Ages 5 to 10 Years)

Take Action
Children ages 5 to 10 years need to go to the doctor or nurse for a “well-child visit” once a year.
A well-child visit is when you take your child to the doctor to make sure they’re healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury.
At a well-child visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch any problems early, when they may be easier to treat. You’ll also have a chance to ask any questions you may have about your child’s behavior or development.
Learn what to expect so you can make the most of each visit.
Child Development
How do i know if my child is growing and developing on schedule.
Your child’s doctor or nurse can help you understand how your child is developing and learning to do new things — like read or brush their teeth. These are sometimes called “developmental milestones.”
Developmental milestones for children ages 5 to 10 years include physical, learning, and social skills — things like:
- Developing skills for success in school (like listening, paying attention, reading, and math)
- Taking care of their bodies without help (like bathing, brushing teeth, and getting dressed)
- Learning from mistakes or failures and trying again
- Helping with simple chores
- Following family rules
- Developing friendships and getting along with other children
- Participating in activities like school clubs, sports teams, or music lessons
See a complete list of developmental milestones for kids who are:
- Age 5 years
- Ages 6 to 8 years
- Ages 9 to 11 years
Take these steps to help you and your child get the most out of well-child visits.
Gather important information.
Take any medical records you have to the appointment, including a record of vaccines (shots) your child has received. If your child gets special services at school because of a health condition or disability, bring that paperwork, too.
Make a list of any important changes in your child’s life since the last doctor’s visit, like a:
- New brother or sister
- Separation or divorce — or a parent spending time in jail or prison
- New school or a move to a new neighborhood
- Serious illness or death of a friend or family member
Use this tool to keep track of your child’s family health history .
Help your child get more involved in doctor visits.
You can help your child get involved by letting them know what to expect. Learn how to prepare your child for a doctor visit .
What about cost?
Under the Affordable Care Act, insurance plans must cover well-child visits. Depending on your insurance plan, you may be able to get well-child visits at no cost to you. Check with your insurance company to find out more.
Your child may also qualify for free or low-cost health insurance through Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP). Learn about coverage options for your family.
If you don’t have insurance, you may still be able to get free or low-cost well-child visits. Find a health center near you and ask about well-child visits.
To learn more, check out these resources:
- Free preventive care for children covered by the Affordable Care Act
- How the Affordable Care Act protects you and your family
- Understanding your health insurance and how to use it [PDF - 698 KB]
Ask Questions
Make a list of questions you want to ask the doctor..
Before the well-child visit, write down 3 to 5 questions you have. This visit is a great time to ask the doctor or nurse any questions about:
- A health condition your child has (like asthma, allergies, or a speech problem)
- Changes in behavior or mood
- Problems in school — with learning or with other children
Here are some important questions to ask:
- Is my child up to date on vaccines?
- How can I make sure my child is getting enough physical activity?
- How can I help my child eat healthy?
- Is my child at a healthy weight?
- How can I teach my child to use the internet safely?
- How can I talk with my child about bullying?
- How can I help my child know what to expect during puberty?
Take a notepad, smartphone, or tablet and write down the answers so you can remember them later.
Ask what to do if your child gets sick.
Make sure you know how to get in touch with a doctor or nurse when the office is closed. Ask how to get hold of the doctor on call, or if there's a nurse information service you can call at night or on the weekend.
What to Expect
Know what to expect..
During each well-child visit, the doctor or nurse will ask you questions about your child, do a physical exam, and update your child’s medical history. You'll also be able to ask your questions and discuss any problems.
The doctor or nurse will ask you and your child questions.
The doctor or nurse may ask about:
- Behavior — Does your child have trouble following directions at home or at school?
- Health — Does your child often complain of headaches or other pain?
- Emotions — Is your child often very worried about bad things happening?
- School — Does your child look forward to going to school?
- Activities — What does your child like to do after school and on weekends?
- Eating habits — What does your child eat on a normal day?
- Family — Have there been any changes in your family since your last visit?
They may also ask questions about safety, like:
- Does your child always ride in the back seat of the car?
- Does anyone in your home have a gun? If so, is it unloaded and locked in a place where your child can’t get it?
- Is there a swimming pool or other water around your home?
Your answers to questions like these will help the doctor or nurse make sure your child is healthy, safe, and developing normally.
Physical Exam
The doctor or nurse will also check your child’s body..
To check your child’s body, the doctor or nurse will:
- Measure your child’s height and weight
- Check your child’s blood pressure
- Check your child’s vision and hearing
- Check your child’s body parts (this is called a physical exam)
- Give your child shots they need
Learn more about your child’s health care.
- Find out how to get your child’s vaccines on schedule
- Learn about getting your child’s vision checked
Content last updated May 10, 2023
Reviewer Information
This information on well-child visits was adapted from materials from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institutes of Health.
Reviewed by: Sara Kinsman, M.D., Ph.D. Director, Division of Child, Adolescent, and Family Health Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
Bethany Miller, M.S.W. Chief, Adolescent Health Branch Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
Diane Pilkey, R.N., M.P.H. Nursing Consultant, Division of Child, Adolescent, and Family Health Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
September 2021
You may also be interested in:

Talk to Your Kids About Sex and Healthy Relationships

Talk to Your Kids About Tobacco, Alcohol, and Drugs

Healthy Snacks: Quick Tips for Parents
The office of disease prevention and health promotion (odphp) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website..
Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by ODPHP or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Get a Passport
Renew or Replace a Passport
Get My Passport Fast
Prepare to Apply
Passport Help
Legal Matters
Get a Passport Homepage
Share this page:
Apply for your First Adult Passport
Apply for a Child Under 16
Apply as a 16 or 17 Year Old
Get My Application Status
Get a Passport Card
Respond to a Letter or Email
- Both parents or guardians must approve that we can issue a passport to a child, and go with the child to apply in person.
- If one or both parents or guardians cannot apply with their child, you will need to show us more documents.
- You cannot renew your child's passport using Form DS-82.
- Passports for children under age 16 are only valid for 5 years.
Steps to Apply
1. fill out form ds-11 and print it.
Use our Form Filler tool to fill out your child's form on a desktop or laptop computer and then print it. If you are experiencing technical issues with the Form Filler, download a PDF .

Tips to complete your child's form :
- Do not sign your child's form until asked to do so by a passport acceptance agent or employee.
- You can apply for a passport book , a passport card , or both documents.
- You may ask for a larger passport book with more visa pages, at no extra cost, by checking the 'large book' box at the top of the DS-11.
2. Get Evidence of U.S. Citizenship (and a photocopy)
Your evidence must be an original or replacement copy. The document must have the official seal or stamp of the office which issued it. You must submit one of the following documents for your child:
- Issued by the city, county, or state of birth
- Lists applicant's full name, date of birth, and place of birth
- Lists the parent(s)' full names
- Has the date filed with registrar's office (must be within one year of birth)
- Has the registrar's signature
- Has the seal or stamp of the city, county, or state which issued it
- Consular Report of Birth Abroad or Certification of Birth
- Certificate of Citizenship
- Please note you must also provide a document, such as a birth certificate, that lists the parent(s) or legal guardian(s) of the child. Full validity means the document is or was valid for 10 years for adults and 5 years for children under 16.
If you cannot submit one of these documents, go to our Citizenship Evidence page for more information.
Paper only : You cannot submit digital evidence of U.S. citizenship such as a mobile or electronic birth certificate. You must submit physical evidence of U.S. citizenship and a photocopy of the document.
Returning your child's document : We will return your child's document in a separate mailing up to 8 weeks after you receive the new passport.
Tips for making a photocopy :
- Black and white (no color)
- Use 8.5 inch by 11 inch paper
- Use a single side of the paper
If you do not submit a photocopy, you must submit a second copy of your citizenship evidence. We will keep this copy for our records.

3. Show Your Relationship to Your Child
You must submit a document that lists the parent(s) or legal guardian(s) of the child. Examples include:
- U.S. birth certificate (also evidence of U.S. citizenship)
- Foreign birth certificate
- Adoption decree
- Divorce or custody decree
- A court order
Some documents, like a U.S. birth certificate, show both U.S. citizenship and parental relationship. These documents must be originals or certified copies (not photocopies).
You and your child may have different last names, as long as the document showing your relationship to your child lists your full name.
If your name is different than the one on the document showing your relationship to your child, submit proof of your legal name change.
4. Get a Photo ID (and a photocopy)
Both parents or guardians must bring a physical, photo ID and a photocopy of it. If your photo ID is from a different state than the state in which you are applying, bring a second photo ID.
You must show at least one of these photo IDs:
- Valid or expired, undamaged U.S. passport book or passport card
- In-state, fully valid driver's license or enhanced driver's license with photo
- Certificate of Naturalization
- Certificate of Citizenship
- Government employee ID (city, county, state, or federal)
- U.S. military or military dependent ID
- Current (valid) foreign passport
- Matricula Consular (Mexican Consular ID) used by a parent of a U.S. citizen child applicant
- U.S. Permanent Resident Card (Green Card) used by a parent of a U.S. citizen child applicant
- Trusted Traveler IDs (including valid Global Entry, FAST, SENTRI, and NEXUS cards)
- Enhanced Tribal Cards and Native American tribal photo IDs
- In-state, fully-valid learner's permit with photo
- In-state, fully-valid non-driver ID with photo
- Temporary driver's license with photo
If you do not have one of these photo IDs, go to our Identification page for more information.
5. Show More Documents (if both parents or guardians cannot apply)
- Both parents or guardians must approve that we can issue a passport to a child, and go with the child to apply in person.
- If one or both parents or guardians cannot apply in person with their child, you will need to show more documents.
Important : Submit Form DS-3053 and other notarized statements within three months of signing them.
6. Provide a Photo
You must provide one photo with your child's application. Go to our Passport Photo page for photo requirements and to see examples of photos.
- Do not attach or staple your child's photo to the form. The acceptance agent or passport employee will review the photo and staple it to your form.
- Some passport acceptance facilities
- A company which offers photo services
- Home. Ask your friend or family member to take your child's photo. Print it on glossy or matte photo quality paper.
7. Calculate Fees
When applying using Form DS-11, you will pay two separate fees - an application fee and an execution (acceptance) fee. You will pay the application fee to the U.S. Department of State, and the execution (acceptance) fee to the facility which takes your application.
- Add $60 to your application fee if you want expedited service .
- Add $19.53 to your application fee if you want us to ship your completed passport in 1-2 days after we issue it.
Child Applicants :
For more information on how to pay and a full list of fees, go to our Passport Fees page.
*How to fill out your check and pay the application fee to the U.S. Department of State. Please note you must pay a separate execution (acceptance) fee.
Families may write one check or money order to the U.S. Department of State if they are applying at the same time. The check or money order must include the name and date of birth of each applicant.
8. Find Location to Apply
In the United States:
- Traveling in more than 3 weeks? Go to a passport acceptance facility such as a post office, library, or local government office. Check with the facility to see if you need to make an appointment.
- Traveling in less than 3 weeks? Make an appointment to apply at a passport agency or center.
In another country:
- Contact your U.S. embassy or consulate .
9. Track Your Application Status
You can subscribe to email updates about your application status, and learn more about each status update .
It may take 2 weeks from the day you apply until your child's application status is “In Process.”
Frequently Asked Questions
How will you send my child's passport and supporting documents.
You will get multiple mailings. The number of mailings depends on what document(s) you asked for.
Passport Book : You may get your new passport and citizenship documents in two mailings. You may wait 8 weeks after getting your passport before you get a second mailing with your citizenship documents. We will return the passport book using a trackable delivery service.
Passport Card : You may get your new passport card and your citizenship documents in two mailings. You may wait 8 weeks after getting your passport before you get a second mailing with your citizenship documents. We only send the passport card via First Class Mail. We do not send cards using 1-2 day delivery services.
Both a Passport Book and Card : You may get three separate mailings:
- New passport book
- New passport card
- Citizenship documents
Contacting Us : If you have been waiting more than 8 weeks for your documents, call us at 1-877-487-2778 to report that you have not received your documents.
If you want us to reimburse you for a lost supporting document, you must contact us within 90 days of the date which we mailed your passport. You will also need to provide a receipt to show the cost of replacing the document.
Can I pay for faster delivery and return shipping?
Yes. You may choose one or both of the following shipment options:
- Delivering application to us : Pay for Priority Mail Express for faster shipping. The price for this service varies depending on the area of the country.
- Returning the passport to you : Pay $19.53 for 1-2 day delivery. This means you will receive your passport 1-2 days after we send it. Include this fee with your check or money order payable to the U.S. Department of State. Do not submit a return envelope to us with postage pre-paid.
You may receive your passport and supporting documents in separate mailings. If you are renewing a passport card, we will send it to you via First Class Mail. We do not use 1-2 day delivery services if you only applied for a passport card.
What countries require Form DS-3053 "Statement of Consent" to be notarized at an embassy or consulate?
In certain countries, a DS-3053 must be notarized at a U.S. embassy or consulate and cannot be notarized by a local notary public. Currently, these countries include:
Special Passport Fairs
Find a Special Passport Fair near you!
We're holding special passport fairs all across the United States to help you get your passport more easily. New events are added to our site every week.
Most events are for first-time applicants and children, (who use Form DS-11). If you can use Form DS-82, you can renew by mail at your convenience!
Processing Times
Routine: 6-8 weeks*
Expedited: 2-3 weeks and an extra $60*
*Consider the total time it will take to get a passport when you are booking travel. Processing times only include the time your application is at a passport agency or center.
- It may take up to 2 weeks for applications to arrive at a passport agency or center. It may take up to 2 weeks for you to receive a completed passport after we print it.
- Processing times + mailing times = total time to get a passport
Urgent Travel: See our Get my Passport Fast page.
How to Apply for your Child's Passport
Watch this video to learn how to apply in person for your child's U.S. passport!
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Jewish Calendar 2015 Elektrostal’, Moscow Oblast, Russia
- Monthly calendar
- Candle-lighting times only
Advertisement
Calendar settings.
Select your calendar app:
- Outlook Web
Apple iOS & macOS
This subscription is a 4-year perpetual calendar feed with events for the current year (2024) plus 3 future years.
Step-by-step: iPhone / iPad or macOS
Use this download alternative if you prefer to manually import the calendar events and merge with your own calendar.
Outlook Windows PC Desktop
Internet Calendar Subscriptions are used by Windows PCs with Microsoft 365, Outlook 2021, Outlook 2019, and 2016.
Step-by-step: Outlook for Windows
Use this download alternative if you prefer to manually import the calendar events into Outlook and merge with your own calendar.
Google Calendar
Icalendar feed url.
The iCalendar (.ics) format is used by many calendar apps.
Outlook Web (Outlook.com)
Outlook.com calendars are used by Windows 10 & 11, Outlook Mac, and Microsoft email accounts such as Hotmail.com, MSN.com and Live.com
Comma Separated Values (CSV)
CSV is a legacy calendar file format for Outlook 97-2003. Select the file that matches your computer’s date format:
- Download CSV - USA mm/dd/yyyy
- Download CSV - Europe dd/mm/yyyy
Step-by-step: CSV for Outlook for Windows
Print PDF (formatted for 8.5"x11" paper)
Download PDF Calendar
Weekly Shabbat times email
Get candle-lighting times for Elektrostal’, Parashat ha-Shavua & Havdalah delivered to your inbox every Thursday.
Email Privacy Policy : We will never sell or give your email address to anyone. We will never use your email address to send you unsolicited offers.
Generating preview
This may take a few moments...

- Bahasa Indonesia
- Eastern Europe
- Moscow Oblast
Elektrostal
Elektrostal Localisation : Country Russia , Oblast Moscow Oblast . Available Information : Geographical coordinates , Population, Altitude, Area, Weather and Hotel . Nearby cities and villages : Noginsk , Pavlovsky Posad and Staraya Kupavna .
Information
Find all the information of Elektrostal or click on the section of your choice in the left menu.
- Update data
Elektrostal Demography
Information on the people and the population of Elektrostal.
Elektrostal Geography
Geographic Information regarding City of Elektrostal .
Elektrostal Distance
Distance (in kilometers) between Elektrostal and the biggest cities of Russia.
Elektrostal Map
Locate simply the city of Elektrostal through the card, map and satellite image of the city.
Elektrostal Nearby cities and villages
Elektrostal weather.
Weather forecast for the next coming days and current time of Elektrostal.
Elektrostal Sunrise and sunset
Find below the times of sunrise and sunset calculated 7 days to Elektrostal.
Elektrostal Hotel
Our team has selected for you a list of hotel in Elektrostal classified by value for money. Book your hotel room at the best price.
Elektrostal Nearby
Below is a list of activities and point of interest in Elektrostal and its surroundings.
Elektrostal Page

- Information /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#info
- Demography /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#demo
- Geography /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#geo
- Distance /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#dist1
- Map /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#map
- Nearby cities and villages /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#dist2
- Weather /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#weather
- Sunrise and sunset /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#sun
- Hotel /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#hotel
- Nearby /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#around
- Page /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#page
- Terms of Use
- Copyright © 2024 DB-City - All rights reserved
- Change Ad Consent Do not sell my data
Current time by city
For example, New York
Current time by country
For example, Japan
Time difference
For example, London
For example, Dubai
Coordinates
For example, Hong Kong
For example, Delhi
For example, Sydney
Geographic coordinates of Elektrostal, Moscow Oblast, Russia
City coordinates
Coordinates of Elektrostal in decimal degrees
Coordinates of elektrostal in degrees and decimal minutes, utm coordinates of elektrostal, geographic coordinate systems.
WGS 84 coordinate reference system is the latest revision of the World Geodetic System, which is used in mapping and navigation, including GPS satellite navigation system (the Global Positioning System).
Geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) define a position on the Earth’s surface. Coordinates are angular units. The canonical form of latitude and longitude representation uses degrees (°), minutes (′), and seconds (″). GPS systems widely use coordinates in degrees and decimal minutes, or in decimal degrees.
Latitude varies from −90° to 90°. The latitude of the Equator is 0°; the latitude of the South Pole is −90°; the latitude of the North Pole is 90°. Positive latitude values correspond to the geographic locations north of the Equator (abbrev. N). Negative latitude values correspond to the geographic locations south of the Equator (abbrev. S).
Longitude is counted from the prime meridian ( IERS Reference Meridian for WGS 84) and varies from −180° to 180°. Positive longitude values correspond to the geographic locations east of the prime meridian (abbrev. E). Negative longitude values correspond to the geographic locations west of the prime meridian (abbrev. W).
UTM or Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system divides the Earth’s surface into 60 longitudinal zones. The coordinates of a location within each zone are defined as a planar coordinate pair related to the intersection of the equator and the zone’s central meridian, and measured in meters.
Elevation above sea level is a measure of a geographic location’s height. We are using the global digital elevation model GTOPO30 .
Elektrostal , Moscow Oblast, Russia

COMMENTS
The Bright Futures/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) developed a set of comprehensive health guidelines for well-child care, known as the "periodicity schedule." It is a schedule of screenings and assessments recommended at each well-child visit from infancy through adolescence. Schedule of well-child visits. The first week visit (3 to 5 ...
Your baby's checkup schedule. Some pediatricians' schedules vary slightly, but the American Academy of Pediatrics Opens a new window (AAP) recommends babies get checkups at birth, 3 to 5 days after birth, and then at 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. (Once your baby is a toddler and child, they'll have routine checkups at 30 months, 3 years, and annually after that.)
Our well-child visit schedule for checkups lets you know how often kids should see a doctor, even when they're not sick. Read the articles below to find out what to expect at your child's next wellness checkup! Well-Child Visit: Newborn; Well-Child Visit: 3-5 Days; Well-Child Visit: 1 Month;
Your baby's first official checkup (and first immunization) will take place at the hospital. After that, well-baby visits are scheduled throughout the first two years at: The first week (usually a couple of days after you're discharged from the hospital) 1 month. 2 months.
15-month well-baby checkup (and a sneak peek at 18 months) At your baby's 15-month checkup, your child will receive final doses of PCV, Hib, DTaP vaccines. And at 18 months, they'll get their final Hep A shot. So, other than annual flu shots, your child's next round of immunizations won't begin until between the ages of 4 and 6.
Take blood pressure. Measure oxygen levels. Listen to your child's lungs. Look at your child's eyes, ears, and throat. Press on your child's tummy to feel organs. Move your child's hips ...
Young children grow quickly, so they need to visit the doctor or nurse regularly to make sure they're healthy and developing normally. Children ages 1 to 4 need to see the doctor or nurse when they're: 12 months old. 15 months old (1 year and 3 months) 18 months old (1 year and 6 months) 24 months old (2 years) 30 months old (2 years and 6 ...
Checkups usually begin with measurements. During first-year visits, a nurse or your baby's health care provider will measure and record your baby's length, head circumference and weight. Your child's measurements will be plotted on his or her growth chart. This will help you and the provider see how your child's size compares with that ...
By age 4 months, most babies: Bring their hands to their mouth. Make cooing sounds. Hold toys that you put in their hand. Turn their head to the sound of your voice. Make sounds when you talk to them. See a complete list of milestones for kids age 4 months.
Your child's doctor will recommend a schedule for well-child visits. One example is for visits at ages: footnote 1. 3 to 5 days old. By 1 month. 2 months. 4 months. 6 months. 9 months. 1 year. 15 months. 18 months. 2 years. 30 months. 3 years. After age 3, well-child visits are usually scheduled yearly through the teen years.
The Bright Futures/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Recommendations for Preventive Pediatric Health Care, also known as the "Periodicity Schedule," is a schedule of screenings and assessments recommended at each well-child visit from infancy through adolescence. Each child and family is unique; therefore, these recommendations are designed ...
Overview. Kids ages 11 to 14 years need to go to the doctor or nurse for a "well-child visit" once a year. A well-child visit is when you take your child to the doctor to make sure they're healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury. At a well-child visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch ...
What a well-child visit schedule looks like . Well-child visits are recommended at specific times during your child's life. Typically, you can expect: 7-9 visits between birth and 18 months old; A visit every six months between 18 months and 3 years old; Yearly visits from 4-17 years old ; Do I need to vaccinate my child before they start ...
Lurie Children's follows the recommended schedule for visits and screenings from the American Academy of Pediatrics. After leaving the hospital (where babies get checked by a hospital pediatrician), you'll bring your baby to the pediatrician at around: 3 - 5 days, often with a follow-up weight check around two weeks of life.
The Vaccines for Children (VFC) program provides vaccines to eligible children at no cost. This program provides free vaccines to children who are Medicaid-eligible, uninsured, underinsured, or American Indian/Alaska Native. Check out the program's requirements and talk to your child's doctor or nurse to see if they are a VFC provider.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends the following: Newborn: Checkup within five days of returning home from the hospital. HBV, if not given in the hospital. 2-4 weeks: Well-child check ...
Visit Age = 14+ Years, Annually. What to Expect. Vaccines. Screeners. Patients 14+ must provide approval for disclosure of their health information according to Oregon law. Hearing screen (16 years) Vision screen. Lipid panel screen (once between 16-18 years) Blood pressure check.
Regular well-child visits can keep your kid and family healthy and prevent serious illness. It's normal to have questions as they quickly grow from birth to adulthood. Make sure you have plenty of time before and after their checkup to avoid any stress. Write down questions or concerns as soon as they come to mind before your kid's well ...
A well-child visit is when you take your child to the doctor to make sure they're healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury. At a well-child visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch any problems early, when they may be easier to treat. You'll also have a chance to ask any questions you may ...
Both parents or guardians must approve that we can issue a passport to a child, and go with the child to apply in person. If one or both parents or guardians cannot apply with their child, you will need to show us more documents. You cannot renew your child's passport using Form DS-82. Passports for children under age 16 are only valid for 5 years.
Elektrostal , lit: Electric and Сталь , lit: Steel) is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located 58 kilometers east of Moscow. Population: 155,196 ; 146,294 ...
Internet Calendar Subscriptions are used by Windows PCs with Microsoft 365, Outlook 2021, Outlook 2019, and 2016.
Elektrostal Geography. Geographic Information regarding City of Elektrostal. Elektrostal Geographical coordinates. Latitude: 55.8, Longitude: 38.45. 55° 48′ 0″ North, 38° 27′ 0″ East. Elektrostal Area. 4,951 hectares. 49.51 km² (19.12 sq mi) Elektrostal Altitude.
Geographic coordinates of Elektrostal, Moscow Oblast, Russia in WGS 84 coordinate system which is a standard in cartography, geodesy, and navigation, including Global Positioning System (GPS). Latitude of Elektrostal, longitude of Elektrostal, elevation above sea level of Elektrostal.